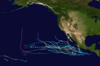
The 1992 Atlantic hurricane season was a significantly below average season in which only ten tropical or subtropical cyclones formed. Six became named tropical storms, of which four became hurricanes. Among the four was Hurricane Andrew, a major hurricane, and the costliest Atlantic hurricane on record at the time, surpassing Hugo of 1989. The season officially started on June 1 and officially ended on November 30. However, tropical cyclogenesis is possible at any time of the year, as demonstrated by formation in April of an unnamed subtropical storm in the central Atlantic. A June tropical depression caused flooding in Cuba and in Florida, where two people were killed. In August, Andrew struck the Bahamas, Florida, and Louisiana. In all, it caused $27.3 billion in damage, mostly in Florida, as well as 65 fatalities. The greatest impact was in South Florida, where the storm made landfall with 1-minute sustained winds of 175 mph (280 km/h).
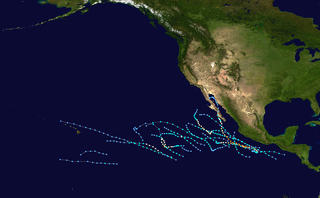
The 2001 Pacific hurricane season was a relatively near-average Pacific hurricane season which produced sixteen named storms, though most were rather weak and short-lived including one unnamed tropical storm which was operationally recognized as a tropical depression, the first such occurrence since 1996. Only eight hurricanes formed and two major hurricanes. The season officially began on May 15 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific basin. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year.

The 2000 Pacific hurricane season was an above-average Pacific hurricane season, although most of the storms were weak and short-lived. There were few notable storms this year. Tropical storms Miriam, Norman, and Rosa all made landfall in Mexico with minimal impact. Hurricane Daniel briefly threatened the U.S. state of Hawaii while weakening. Hurricane Carlotta was the strongest storm of the year and the second-strongest June hurricane in recorded history. Carlotta killed 18 people when it sank a freighter. Overall, the season was significantly more active than the previous season, with 19 tropical storms. In addition, six hurricanes developed. Furthermore, there were total of two major hurricanes.

The 1998 Pacific hurricane season was a fairly average Pacific hurricane season. Despite this, it had nine hurricanes and six major hurricanes, which was well above average. The season officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific and on June 1 in the central Pacific, and ended on November 30; these dates conventionally delimit the period during which most tropical cyclones form in that region. The first tropical cyclone developed on June 11, about ten days later than the normal start of the season. The final storm of the year, Hurricane Madeline, dissipated on October 20. Storm activity in the Central Pacific Hurricane Center's warning zone was low, with just one tropical depression observed in the region. Two tropical cyclones from the eastern Pacific also entered the central Pacific; the former did so as a hurricane.

The 1995 Pacific hurricane season was the least active Pacific hurricane season since 1979, and marked the beginning of a multi-decade period of low activity in the basin. Of the eleven tropical cyclones that formed during the season, four affected land, with the most notable storm of the season being Hurricane Ismael, which killed at least 116 people in Mexico. The strongest hurricane in the season was Hurricane Juliette, which reached peak winds of 150 mph (240 km/h), but did not significantly affect land. Hurricane Adolph was an early-season Category 4 hurricane. Hurricane Henriette brushed the Baja California Peninsula in early September.

The 1992 Pacific hurricane season is the most active Pacific hurricane season on record, featuring 27 named storms, and the third-costliest Pacific hurricane season in history, behind the 2013 season, and the 2023 seaszon. The season also produced the second-highest ACE value on record in the basin, only surpassed by the 2018 season. The season officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific, and on June 1 in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. However, these bounds were easily exceeded when Hurricane Ekeka formed on January 28 and again a couple months later with Tropical Storm Hali.

The 1991 Pacific hurricane season was a near-average Pacific hurricane season. The worst storm this year was Tropical Storm Ignacio, which killed 23 people in Mexico and injured 40 others. Elsewhere, Hurricane Fefa caused flooding in Hawaii. Hurricane Kevin was the strongest system of the season and became the then longest-lasting hurricane in the eastern north Pacific basin at the time, and Hurricane Nora was the strongest November storm to that point. The season officially started on May 15, 1991, in the eastern Pacific, and on June 1, 1991, in the central Pacific. It lasted until November 30, 1991, in both basins. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean.

The 1989 Pacific hurricane season was a near normal season. It officially started on May 15, 1989, in the eastern Pacific, and on June 1, 1989, in the central Pacific, and lasted until November 30, 1989. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. A total of 18 storms and 9 hurricanes formed, which was near long-term averages. Four hurricanes reached major hurricane status on the Saffir–Simpson scale.

Hurricane Sergio was the third strongest Pacific hurricane in the month of November on record. The twenty-fifth and final tropical cyclone, nineteenth named storm and eleventh hurricane of the 2006 Pacific hurricane season, Sergio developed from a tropical wave on November 13 about 460 miles (740 km) south of Manzanillo, Mexico, and steadily intensified as it tracked southeastward. It reached peak winds of 110 mph (180 km/h) on November 15, and subsequently began to weaken due to increased wind shear as it turned to the north. Sergio later turned to the west, remaining well off the coast of Mexico, and dissipated on November 20 about 320 miles (510 km) west-northwest of it originally formed.

Hurricane Olga was the largest tropical cyclone by diameter of gale-force winds on record in the Atlantic at the time. The fifteenth named storm, ninth and final hurricane of the 2001 Atlantic hurricane season, Olga formed as a subtropical cyclone on November 24. After acquiring tropical characteristics later that day, Olga meandered westward, and eventually reached hurricane status on November 26. Olga peaked as a 90 mph (140 km/h) Category 1 hurricane before the storm turned southwestward and weakening back into a tropical storm. On November 30 it deteriorated further to a tropical depression, although it re-intensified two days later to tropical storm intensity. Olga then dissipated as a tropical cyclone on December 4 east of the Bahamas. Its damaging effects were limited to ships at sea. The cyclone's remnants produced heavy rainfall across the Bahamas and Florida. It was a relatively rare storm to exist in December, which is outside of the normal Atlantic hurricane season.
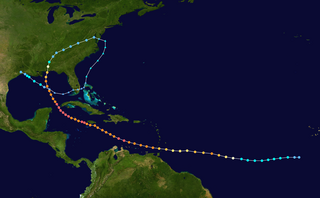
The meteorological history of Hurricane Ivan, the longest tracked tropical cyclone of the 2004 Atlantic hurricane season, lasted from late August through late September. The hurricane developed from a tropical wave that moved off the coast of Africa on August 31. Tracking westward due to a ridge, favorable conditions allowed it to develop into Tropical Depression Nine on September 2 in the deep tropical Atlantic Ocean. The cyclone gradually intensified until September 5, when it underwent rapid deepening and reached Category 4 status on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale; at the time Ivan was the southernmost major North Atlantic hurricane on record.

The 2006 Pacific hurricane season was the first above-average season since 1997 which produced twenty-five tropical cyclones, with nineteen named storms, though most were rather weak and short-lived. Only eleven hurricanes formed and six major hurricanes. Following the inactivity of the previous seasons, forecasters predicted that season would be only slightly above active. It was also the first time since 2003 in which at least one cyclone of tropical storm intensity made landfall. The season officially began on May 15 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific basin. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year.

Hurricane Virgil was a late season hurricane of the 1992 Pacific hurricane season that struck southwestern Mexico in October 1992. Forming from a tropical wave that left Africa on September 13, it slowly developed into a tropical depression. It soon strengthened into Tropical Storm Virgil, and rapidly intensified into a hurricane on October 2. Continuing to intensify, the hurricane attained major hurricane strength, and peaked as a Category 4 hurricane off the coast of Mexico. Shortly before landfall, it weakened to a Category 2 hurricane, and it dissipated on October 5. Damage was generally minimal, though one person was reported missing.

The 2009 Pacific hurricane season was the most active Pacific hurricane season since 1997. The season officially started on May 15 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Eastern Pacific tropical cyclone basin; however, tropical cyclone formation is possible at any time of the year. The first system of the season, Tropical Depression One-E, developed on June 18, and the last, Hurricane Neki, dissipated on October 27, keeping activity well within the bounds of the season.

Hurricane Juliette was the strongest hurricane and final tropical cyclone of the inactive 1995 Pacific hurricane season. The tenth named storm of the season, Juliette formed on September 16 from a tropical wave off the southwest coast of Mexico. For the majority of its track, the storm moved toward the west-northwest, and Juliette quickly intensified to major hurricane status. On September 20, the hurricane reached peak winds of 150 mph (240 km/h). Later it turned toward the northeast, briefly threatening the Baja California Peninsula, although the hurricane never affected land.
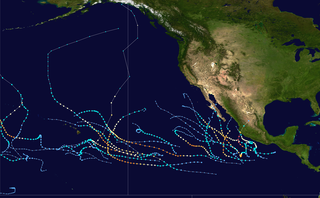
The 2015 Pacific hurricane season is the second-most active Pacific hurricane season on record, with 26 named storms, only behind the 1992 season. A record-tying 16 of those storms became hurricanes, and a record 11 storms further intensified into major hurricanes throughout the season. The Central Pacific, the portion of the Northeast Pacific Ocean between the International Date Line and the 140th meridian west, had its most active year on record, with 16 tropical cyclones forming in or entering the basin. Moreover, the season was the third-most active season in terms of accumulated cyclone energy, amassing a total of 290 units. The season officially started on May 15 in the Eastern Pacific and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Northeast Pacific basin. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year. This was shown when a tropical depression formed on December 31. The above-average activity during the season was attributed in part to the very strong 2014–16 El Niño event.

The 2016 Pacific hurricane season was tied as the fifth-most active Pacific hurricane season on record, alongside the 2014 season. Throughout the course of the year, a total of 22 named storms, 13 hurricanes and six major hurricanes were observed within the basin. Although the season was very active, it was considerably less active than the previous season, with large gaps of inactivity at the beginning and towards the end of the season. It officially started on May 15 in the Eastern Pacific, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific ; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in these regions of the Pacific Ocean. However, tropical development is possible at any time of the year, as demonstrated by the formation of Hurricane Pali on January 7, the earliest Central Pacific tropical cyclone on record. After Pali, however, no tropical cyclones developed in either region until a short-lived depression on June 6. Also, there were no additional named storms until July 2, when Tropical Storm Agatha formed, becoming the latest first-named Eastern Pacific tropical storm since Tropical Storm Ava in 1969.

Tropical Storm Zeke was the final named storm of the record-breaking 1992 Pacific hurricane season. Forming out of a tropical wave on October 25, Zeke began as a disorganized depression. Tracking west-northwestward, the system gradually developed organized convection and intensified into a tropical storm. However, it soon entered a high wind shear environment, causing Zeke to weaken to a tropical depression. The following day, the storm re-intensified despite unfavorable conditions and later attained peak winds of 50 mph (80 km/h) on October 29. Rapid weakening followed shortly thereafter as convection dissipated and the center became exposed. During the afternoon of October 30, Zeke degenerated into a remnant low pressure system and dissipated several days later several hundred miles south of Baja California Sur.
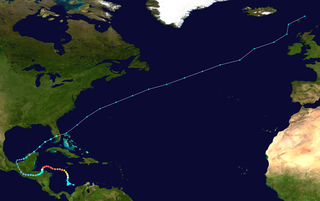
Hurricane Mitch's meteorological history began with its origins over Africa as a tropical wave and lasted until its dissipation as an extratropical cyclone north of the United Kingdom. Tropical Depression Thirteen formed on October 22, 1998, over the southwestern Caribbean Sea from a tropical wave that exited Africa on October 10. It executed a small loop, and while doing so intensified into Tropical Storm Mitch. A weakness in a ridge allowed the storm to track slowly to the north. After becoming disorganized due to wind shear from a nearby upper-level low, Mitch quickly intensified in response to improving conditions which included warm waters and good outflow. It became a hurricane on October 24 and developed an eye. After turning to the west, Mitch rapidly intensified, first into a major hurricane on October 25 and then into a Category 5 on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale the next day.

The 2019 Pacific hurricane season was a near average season which produced nineteen named storms, most of which were rather weak and short-lived. Only seven hurricanes formed, the fewest since 2010. The season officially began on May 15 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific basin. This season was one of the latest-starting Pacific hurricane seasons on record, with the first tropical cyclone, Hurricane Alvin, forming on June 25. The final system, Tropical Depression Twenty-One-E, dissipated on November 18.