
Hurricane Erick brought moderate impacts to the western coastline of Mexico in July 2013, and was the last of a succession of four Category 1 hurricanes to affect the Pacific coast of Mexico early in the 2013 Pacific hurricane season. The fifth named storm and fourth hurricane of the annual season, Erick originated from a tropical wave that moved off the western coast of Africa on June 18. The wave tracked swiftly westward with little development, emerging into the eastern Pacific on July 1. As a result of favorable environmental conditions, the wave developed into a tropical depression on July 4, and further into Tropical Storm Erick at 0000 UTC on July 5. Steered generally west-northwest, Erick intensified into a Category 1 hurricane and reached its peak intensity with winds of 80 mph (130 km/h) on July 6. Its proximity to land and track over increasingly cooler waters caused the storm to deteriorate into a tropical storm the following day, though it remained at such intensity until degenerating into a remnant low early on July 9. The remnant circulation dissipated a few hours later, southwest of Baja California Sur.

Hurricane Amanda was the strongest Eastern Pacific tropical cyclone ever recorded in the month of May. The first named storm, hurricane and major hurricane of the 2014 Pacific hurricane season, Amanda originated from a tropical wave that had entered the Eastern Pacific on May 16. Slow development occurred as it tracked westward, and development into a tropical depression occurred on May 22. The depression later strengthened into a tropical storm on May 23. Amid very favorable conditions, Amanda then rapidly intensified late on May 23, eventually reaching its peak intensity on May 25 as a high-end Category 4 hurricane. Afterwards, steady weakening occurred due to upwelling beneath the storm, and Amanda fell below major hurricane intensity on May 26. Rapid weakening occurred and the cyclone eventually dissipated on May 29.

Hurricane Norbert produced a 1-in-1,000 year rainfall event in Arizona in early September 2014. The fifteenth named storm, tenth hurricane, and seventh major hurricane of the 2014 Pacific hurricane season, Norbert originated from an area of disturbed weather in association with an area of low pressure on September 2. Tracking generally northwestward, the newly designated tropical storm steadily organized in a moderate shear environment. Norbert attained hurricane intensity early on September 4 and Category 2 hurricane strength the next afternoon. Thereafter, the cyclone began a period of rapid deepening, and it subsequently attained its peak intensity with winds of 125 mph (201 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 950 mbar early on September 6. A track over progressively cooler waters and into a more stable environment prompted a weakening trend after peak intensity, and by early on September 8, the system no longer maintained enough convection to be considered a tropical cyclone.

Hurricane Patricia was the most powerful tropical cyclone on record worldwide in terms of maximum sustained winds and the second-most intense on record worldwide in terms of pressure, with a minimum atmospheric pressure of 872 mbar, behind Typhoon Tip's 870 mbar. Originating from a sprawling disturbance near the Gulf of Tehuantepec, south of Mexico, in mid-October 2015, Patricia was first classified a tropical depression on October 20. Initial development was slow, with only modest strengthening within the first day of its classification. The system later became a tropical storm and was named Patricia, the twenty-fourth named storm of the annual hurricane season. Exceptionally favorable environmental conditions fueled explosive intensification on October 22. A well-defined eye developed within an intense central dense overcast and Patricia grew from a tropical storm to a Category 5 hurricane in just 24 hours—a near-record pace. On October 23, the hurricane achieved its record peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 215 mph (345 km/h). This made it the most intense tropical cyclone on record in the Western Hemisphere and the strongest globally in terms of one-minute maximum sustained winds.

Hurricane Bud was a tropical cyclone that brought winds and severe flooding to Mexico throughout its existence as a tropical cyclone in June 2018. It was the second named storm, hurricane, and major hurricane of the 2018 Pacific hurricane season. Bud originated from a tropical wave that departed from Western Africa on May 29. It traveled across the Atlantic Ocean before entering the Northeast Pacific Ocean late on June 6. The system moved towards the northwest and steadily organized, becoming a tropical depression on June 9 and Tropical Storm Bud early the next day. Favorable upper-level winds, ample moisture aloft, and warm sea surface temperatures allowed the storm to rapidly intensify to a hurricane late on June 10, and further to a major hurricane on the following day. Bud ultimately peaked the next morning with maximum sustained winds of 140 mph (230 km/h) and a minimum central pressure of 943 mbar. Its track curved more northward while the storm rapidly succumbed to the effects of upwelling. Bud made landfall on Baja California Sur as a minimal tropical storm early on June 15. On the next day, land interaction and increasing wind shear caused Bud to degenerate into a post-tropical cyclone. It opened up into a trough of low-pressure on June 16. The remnants of Bud moved towards the Southwestern United States, bringing tropical moisture and gusty winds to the region.
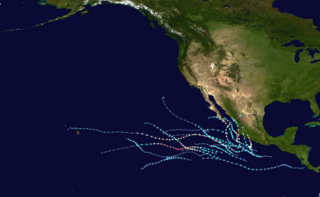
The 2021 Pacific hurricane season was a moderately active Pacific hurricane season, with above-average activity in terms of number of named storms, but below-average activity in terms of major hurricanes, as 19 named storms, 8 hurricanes, and 2 major hurricanes formed in all. It also had a near-normal accumulated cyclone energy (ACE). The season officially began on May 15, 2021 in the Eastern Pacific Ocean, and on June 1, 2021, in the Central Pacific in the Northern Hemisphere. The season ended in both regions on November 30, 2021. These dates historically describe the period each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in these regions of the Pacific and are adopted by convention. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year, as illustrated by the formation of Tropical Storm Andres on May 9, which was the earliest forming tropical storm on record in the Eastern Pacific. Conversely, 2021 was the second consecutive season in which no tropical cyclones formed in the Central Pacific.

The 2022 Pacific hurricane season was a slightly above average hurricane season in the eastern North Pacific basin, with nineteen named storms, ten hurricanes, and four major hurricanes. Two of the storms crossed into the basin from the Atlantic. In the central North Pacific basin, no tropical cyclones formed. The season officially began on May 15 in the eastern Pacific, and on June 1 in the central; both ended on November 30. These dates historically describe the period each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in these regions of the Pacific and are adopted by convention.

Hurricane Willa was a powerful tropical cyclone that brought torrential rains and destructive winds to southwestern Mexico, particularly the states of Sinaloa and Nayarit, during late October 2018. It was the twenty-fifth tropical cyclone, twenty-second named storm, thirteenth hurricane, tenth major hurricane, and record-tying third Category 5 hurricane of the 2018 Pacific hurricane season. Willa was the first major hurricane to make landfall in the Mexican state of Sinaloa since Lane in 2006.

Tropical Storm Narda was a short-lived tropical storm that remained close to the Pacific coast of Mexico, causing flash flooding and mudslides in southwestern Mexico and the Baja California Peninsula in late September 2019. The fourteenth named storm of the 2019 Pacific hurricane season, Narda developed from a broad area of low pressure that formed off the Central American Pacific coast on September 26. The broad low gradually organized as it moved west-northwestward, and it became Tropical Storm Narda early on September 29 while located off the southern coast of Mexico. The cyclone strengthened slightly before it moved inland near Manzanillo. Narda weakened to a tropical depression after moving inland, but restrengthened into a tropical storm on September 30 as it emerged over the Pacific Ocean just south of the Gulf of California. Narda quickly strengthened, and reached its peak intensity with winds of 50 mph (85 km/h) that day before making a second landfall along the northwestern coast of Mexico. The tropical cyclone weakened rapidly as it moved along the coastline, and it weakened to a tropical depression before dissipating just off the coast of Sonora on October 1.

Hurricane Genevieve was a strong tropical cyclone that almost made landfall on the Baja California Peninsula in August 2020. Genevieve was the twelfth tropical cyclone, seventh named storm, third hurricane, and second major hurricane of the 2020 Pacific hurricane season. The cyclone formed from a tropical wave that the National Hurricane Center (NHC) first started monitoring on August 10. The wave merged with a trough of low pressure on August 13, and favorable conditions allowed the wave to intensify into Tropical Depression Twelve-E at 15:00 UTC. Just six hours later, the depression became a tropical storm and was given the name Genevieve. Genevieve quickly became a hurricane by August 17, and Genevieve began explosive intensification the next day. By 12:00 UTC on August 18, Genevieve reached its peak intensity as a Category 4 hurricane, with maximum 1-minute sustained winds of 130 mph and a minimum central pressure of 950 millibars (28 inHg). Genevieve began to weaken on the next day, possibly due to cooler waters caused by Hurricane Elida earlier that month. Genevieve weakened below tropical storm status around 18:00 UTC on August 20, as it passed close to Baja California Sur. Soon afterward, Genevieve began to lose its deep convection and became a post-tropical cyclone by 21:00 UTC on August 21, eventually dissipating off the coast of Southern California late on August 24.

The 2023 Pacific hurricane season was an active and destructive Pacific hurricane season. In the Eastern Pacific basin, 17 named storms formed; 10 of those became hurricanes, of which 8 strengthened into major hurricanes – double the seasonal average. In the Central Pacific basin, no tropical cyclones formed for the fourth consecutive season, though four entered into the basin from the east. Collectively, the season had an above-normal accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) value of approximately 168 units. This season saw the return of El Niño and its associated warmer sea surface temperatures in the basin, which fueled the rapid intensification of several powerful storms. It officially began on May 15, 2023 in the Eastern Pacific, and on June 1 in the Central; both ended on November 30. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in these regions of the Pacific.

Tropical Storm Dolores was a strong tropical storm that made landfall in southwestern Mexico in June 2021. The fourth named storm of the 2021 Pacific hurricane season, Dolores developed from a low-pressure area that formed offshore the Mexican state of Oaxaca on June 16, 2021. The low steadily developed organized deep convection and a closed surface circulation, becoming Tropical Depression Four-E around 06:00 UTC June 18. The depression strengthened into a tropical storm nine hours later and was named Dolores. Gradually approaching the southwestern coast of Mexico, Dolores steadily intensified despite its close proximity to land. The storm reached its peak intensity around 15:00 UTC June 19 with maximum sustained winds of 115 km/h (70 mph) and a minimum barometric pressure of 29.2 inHg (989 mbar), just below hurricane strength. Shortly after reaching this intensity, Dolores made landfall just northwest of Punta San Telmo, near the Colima–Michoacán state border. The storm rapidly weakened as it moved inland over Mexico and dissipated early on June 20 over the state of Zacatecas.

Hurricane Enrique was a Category 1 Pacific hurricane that brought heavy rainfall and flooding to much of western Mexico in late June 2021. The fifth named storm and first hurricane of the 2021 Pacific hurricane season, Enrique developed from a tropical wave the entered the Pacific Ocean off the coast of Nicaragua on June 22. In an environment conducive for intensification, the disturbance moved west-northwestward and developed into a tropical storm by 6:00 UTC on June 25, as it was already producing winds of 40 mph (65 km/h), and received the name Enrique. Enrique strengthened steadily within an environment of warm waters and low-to-moderate wind shear while continuing its northwestward motion. By 12:00 UTC on June 26, Enrique had intensified into a Category 1 hurricane as the storm turned more northwestward. Nearing the coast of Mexico, Enrique reached its peak intensity around 6:00 UTC the following day, with maximum sustained winds of 90 mph (150 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 972 mbar (28.7 inHg). Enrique, passing closely offshore west-central Mexico, maintained its intensity for another 24 hours as it turned northward toward the Gulf of California. Turning back to the northwest on June 28, increasing wind shear and dry air caused the hurricane to weaken. Enrique dropped to tropical storm status at 18:00 UTC that day, and further weakened to a tropical depression on June 30 just to the northeast of Baja California. The depression was absorbed into a larger low pressure area to the southeast later that day.

Hurricane Nora was a large tropical cyclone that caused significant damage across the Pacific Coast of Mexico in late August 2021. The fourteenth named storm and fifth hurricane of the 2021 Pacific hurricane season, Nora was first monitored by the National Hurricane Center (NHC) as an area of low pressure near the coast of Mexico. On August 24, the low organized into tropical depression, but struggled to develop further due to wind shear in its surrounding environment. The depression eventually intensified into a tropical storm and was named Nora as it tracked to the west-northwest. Nora peaked as a strong Category 1 hurricane with maximum sustained winds of 85 miles per hour (140 km/h) on August 28. The storm then grazed the west coast of Mexico and made landfall two separate times, first in the state of Jalisco, followed by neighboring Nayarit. Nora weakened as it interacted with land, dissipating on August 30 just inland of the Mexican coast.

Hurricane Olaf was a Category 2 Pacific hurricane that struck the Baja California Peninsula in September 2021. The fifteenth named storm and sixth hurricane of the 2021 Pacific hurricane season, the cyclone formed from an area of low pressure that developed off the southwestern coast of Mexico on September 5, 2021. The disturbance developed within a favorable environment, acquiring more convection and a closed surface circulation. The disturbance developed into Tropical Depression Fifteen-E by 18:00 UTC on September 7. The depression strengthened into a tropical storm and was named Olaf at 12:00 UTC the next day. Olaf quickly strengthened as it moved to the north-northwest, and was upgraded to a hurricane 24 hours after being named. Hurricane Olaf continued to intensify and reached peak intensity while its center was just offshore the southwestern coast of Baja California Sur, with maximum sustained winds of 105 mph (169 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 975 mbar (28.8 inHg). Just after reaching peak intensity, the hurricane made landfall near San José del Cabo. Interaction with the mountainous terrain of the Baja California Peninsula caused Olaf to quickly weaken. It was downgraded to a tropical storm at 12:00 UTC on September 10. The system became devoid of convection later that day and degenerated to a remnant low by 06:00 UTC on September 11.

Hurricane Pamela was a Category 1 Pacific hurricane that caused significant damage across several northwestern and western states of Mexico in October 2021. The sixteenth named storm and seventh hurricane of the 2021 Pacific hurricane season, the storm originated from a tropical wave over the Atlantic basin, over the Caribbean Sea. It then quickly crossed into the Pacific Ocean, where it slowly consolidated, with a low-pressure area forming from the wave on October 9. Environmental conditions in the area were proved favorable for tropical cyclogenesis and developed into Tropical Depression Sixteen-E on the next day. It then organized further into Tropical Storm Pamela on that night. Despite wind shear and dry air affecting the cyclone, Pamela continued to strengthen and became a hurricane on October 12 before weakening back to a tropical storm as it continued to succumb onto these factors. However, as the system turned towards the coast of Mexico, Pamela restrengthened to a low-end hurricane before making landfall over Estacion Dimas, Sinaloa on 15:00 UTC on October 13 before rapidly weakening inland. It then dissipated over Coahuila on the early hours on the next day.

Hurricane Rick was a Category 2 Pacific hurricane that struck the southwestern coast of Mexico in late October 2021. Rick was the overall seventeenth named system and the eighth hurricane of the 2021 Pacific hurricane season, as well as the fifth named storm and fourth hurricane to make landfall along the Pacific coast of Mexico in 2021.

Hurricane Blas was a Category 1 hurricane that brought winds and flooding to several Mexican states in June 2022. The second named storm and second hurricane of the 2022 Pacific hurricane season, Blas developed from a low-pressure area off the coast of southwestern Mexico. It became a tropical depression on June 14. and strengthened into a tropical storm later that same day. Blas became a hurricane the next day, while paralleling the coast. The system reached its peak intensity on June 17, at 15:00 UTC, with maximum sustained winds of 80 knots and a central pressure of 976 mbar (28.82 inHg). Later, Blas turned to the west and weakened, becoming a tropical depression on June 20, before transitioning into a post-tropical cyclone on that same day.

Hurricane Roslyn was a powerful tropical cyclone that struck the Pacific coast of Mexico in October 2022. The nineteenth named storm, tenth hurricane, and fourth major hurricane of the 2022 Pacific hurricane season, Roslyn formed on October 20, from an area of low pressure that developed off the southwestern coast of Mexico. The system moved west-northwestward, paralleling the coast, where it became a hurricane at 00:00 UTC, on October 22, and, within 18 hours rapidly intensified to a Category 4 hurricane, with sustained winds of 130 mph (215 km/h). Roslyn made landfall on October 23 near Santa Cruz in northern Nayarit, at 11:20 UTC with 120 mph (195 km/h) winds. Inland, Roslyn weakened quickly to a tropical storm, and then dissipated over east-central Mexico on October 24.

Hurricane John was a powerful and devastating tropical cyclone that caused deadly flooding across southern Mexico for several days in September 2024. The eleventh named storm, fourth hurricane, and second major hurricane of the 2024 Pacific hurricane season, John originated from a low-pressure area offshore Southern Mexico. This low developed into Tropical Depression Ten‑E on the afternoon of September 22, strengthening into Tropical Storm John the following morning. Undergoing rapid intensification, John strengthened from a moderate tropical storm into a Category 3 hurricane on September 24. It was at that intensity that John made landfall in Marquelia, Guerrero, later that day. Once inland, John rapidly weakened, dissipating over Mexico later that day. However, the mid-level remnants of John moved back over the ocean, where favorable conditions enabled John to redevelop. On September 27, after again becoming a minimal hurricane, Tropical Storm John made its second landfall, this time near Tizupan, Michoacán. Hours later, it dissipated for a final time over the coastal mountains.























