
In probability theory and statistics, the exponential distribution or negative exponential distribution is the probability distribution of the distance between events in a Poisson point process, i.e., a process in which events occur continuously and independently at a constant average rate; the distance parameter could be any meaningful mono-dimensional measure of the process, such as time between production errors, or length along a roll of fabric in the weaving manufacturing process. It is a particular case of the gamma distribution. It is the continuous analogue of the geometric distribution, and it has the key property of being memoryless. In addition to being used for the analysis of Poisson point processes it is found in various other contexts.
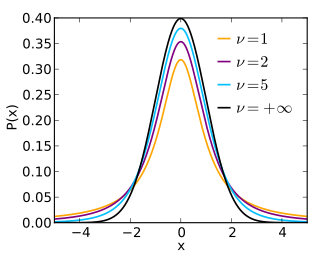
In probability theory and statistics, Student's t distribution is a continuous probability distribution that generalizes the standard normal distribution. Like the latter, it is symmetric around zero and bell-shaped.

In probability theory and statistics, the chi-squared distribution with degrees of freedom is the distribution of a sum of the squares of independent standard normal random variables.

In probability theory and statistics, the gamma distribution is a versatile two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. The exponential distribution, Erlang distribution, and chi-squared distribution are special cases of the gamma distribution. There are two equivalent parameterizations in common use:
- With a shape parameter k and a scale parameter θ
- With a shape parameter and an inverse scale parameter , called a rate parameter.
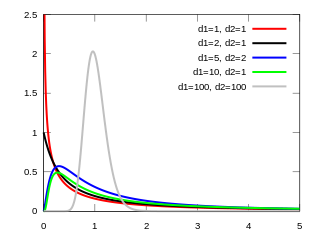
In probability theory and statistics, the F-distribution or F-ratio, also known as Snedecor's F distribution or the Fisher–Snedecor distribution, is a continuous probability distribution that arises frequently as the null distribution of a test statistic, most notably in the analysis of variance (ANOVA) and other F-tests.
In probability and statistics, an exponential family is a parametric set of probability distributions of a certain form, specified below. This special form is chosen for mathematical convenience, including the enabling of the user to calculate expectations, covariances using differentiation based on some useful algebraic properties, as well as for generality, as exponential families are in a sense very natural sets of distributions to consider. The term exponential class is sometimes used in place of "exponential family", or the older term Koopman–Darmois family. Sometimes loosely referred to as "the" exponential family, this class of distributions is distinct because they all possess a variety of desirable properties, most importantly the existence of a sufficient statistic.

In probability theory and statistics, the inverse gamma distribution is a two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions on the positive real line, which is the distribution of the reciprocal of a variable distributed according to the gamma distribution.
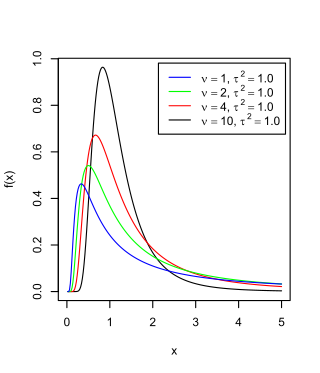
The scaled inverse chi-squared distribution, where is the scale parameter, equals the univariate inverse Wishart distribution with degrees of freedom .

The Pearson distribution is a family of continuous probability distributions. It was first published by Karl Pearson in 1895 and subsequently extended by him in 1901 and 1916 in a series of articles on biostatistics.

In probability theory and statistics, the generalized inverse Gaussian distribution (GIG) is a three-parameter family of continuous probability distributions with probability density function
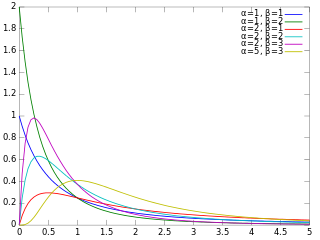
In probability theory and statistics, the beta prime distribution is an absolutely continuous probability distribution. If has a beta distribution, then the odds has a beta prime distribution.
Bayesian linear regression is a type of conditional modeling in which the mean of one variable is described by a linear combination of other variables, with the goal of obtaining the posterior probability of the regression coefficients and ultimately allowing the out-of-sample prediction of the regressandconditional on observed values of the regressors. The simplest and most widely used version of this model is the normal linear model, in which given is distributed Gaussian. In this model, and under a particular choice of prior probabilities for the parameters—so-called conjugate priors—the posterior can be found analytically. With more arbitrarily chosen priors, the posteriors generally have to be approximated.
In statistics, the multivariate t-distribution is a multivariate probability distribution. It is a generalization to random vectors of the Student's t-distribution, which is a distribution applicable to univariate random variables. While the case of a random matrix could be treated within this structure, the matrix t-distribution is distinct and makes particular use of the matrix structure.
In statistics, the inverse Wishart distribution, also called the inverted Wishart distribution, is a probability distribution defined on real-valued positive-definite matrices. In Bayesian statistics it is used as the conjugate prior for the covariance matrix of a multivariate normal distribution.
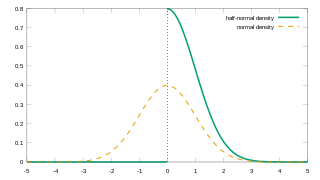
In probability theory and statistics, the half-normal distribution is a special case of the folded normal distribution.

In probability theory and statistics, the normal-inverse-gamma distribution is a four-parameter family of multivariate continuous probability distributions. It is the conjugate prior of a normal distribution with unknown mean and variance.

In probability theory and statistics, there are several relationships among probability distributions. These relations can be categorized in the following groups:
In statistical inference, the concept of a confidence distribution (CD) has often been loosely referred to as a distribution function on the parameter space that can represent confidence intervals of all levels for a parameter of interest. Historically, it has typically been constructed by inverting the upper limits of lower sided confidence intervals of all levels, and it was also commonly associated with a fiducial interpretation, although it is a purely frequentist concept. A confidence distribution is NOT a probability distribution function of the parameter of interest, but may still be a function useful for making inferences.
In Bayesian statistics, the posterior predictive distribution is the distribution of possible unobserved values conditional on the observed values.

The Kaniadakis Generalized Gamma distribution is a four-parameter family of continuous statistical distributions, supported on a semi-infinite interval [0,∞), which arising from the Kaniadakis statistics. It is one example of a Kaniadakis distribution. The κ-Gamma is a deformation of the Generalized Gamma distribution.














































