South West England, or the South West of England, is one of the nine official regions of England in the United Kingdom. It consists of the counties of Cornwall, Dorset, Devon, Gloucestershire, Somerset and Wiltshire. Cities and large towns in the region include Bath, Bristol, Bournemouth, Cheltenham, Exeter, Gloucester, Plymouth and Swindon. It is geographically the largest of the nine regions of England covering 9,200 square miles (23,800 km2), but the third-least populous, with approximately five million residents.

Bristol Temple Meads is the oldest and largest railway station in Bristol, England. It is located 118 miles 31 chains away from London Paddington. It is an important transport hub for public transport in the city; there are bus services to many parts of the city and surrounding districts, with a ferry to the city centre. Bristol's other major station, Bristol Parkway, is a more recent station on the northern outskirts of the conurbation.

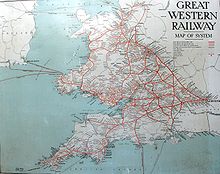
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran its first trains in 1838 with the initial route completed between London and Bristol in 1841. It was engineered by Isambard Kingdom Brunel, who chose a broad gauge of 7 ft —later slightly widened to 7 ft 1⁄4 in —but, from 1854, a series of amalgamations saw it also operate 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in standard-gauge trains; the last broad-gauge services were operated in 1892.

The Great Western Main Line (GWML) is a main line railway in England that runs westwards from London Paddington to Bristol Temple Meads. It connects to other main lines such as those from Reading to Penzance and Swindon to Swansea. Opened in 1841, it was the original route of the first Great Western Railway which was merged into the Western Region of British Railways in 1948. It is now a part of the national rail system managed by Network Rail with the majority of passenger services provided by the current Great Western Railway franchise.

The Wessex Main Line is the railway line from Bristol Temple Meads to Southampton Central. Diverging from this route is the Heart of Wessex Line from Westbury to Weymouth. The Wessex Main Line intersects the Reading to Taunton Line at Westbury and the West of England Main Line at Salisbury.

Taunton railway station is a junction station on the route from London to Penzance, 163 miles 12 chains (263 km) west of London Paddington station, measured via Box. It is situated in Taunton, Somerset, and is operated by Great Western Railway. The station is also served by CrossCountry trains and by the West Somerset Railway on special event days and by mainline steam excursions.

Bath Spa railway station is the principal station serving the city of Bath in South West England. It is on the Great Western Main Line, 106 miles 71 chains down the line from the zero point at London Paddington between Chippenham to the east and Oldfield Park to the west. Its three-letter station code is BTH.

St Austell station is a Grade II listed station which serves the town of St Austell, Cornwall, England. It is 286 miles 26 chains from the zero point at London Paddington measured via Box and Plymouth Millbay. The station is operated by Great Western Railway.

Bridgwater railway station serves town of Bridgwater in Somerset, England. It is on the Bristol to Taunton Line and is operated by Great Western Railway. It is 151 miles 47 chains from the zero point at London Paddington via Box.

Bradford-on-Avon railway station is a railway station on the Wessex Main Line in between Avoncliff and Trowbridge, serving the town of Bradford on Avon, in Wiltshire, England. The station is 9 miles 35 chains (15.2 km) south east of Bath Spa. The station was originally conceived by the Wilts, Somerset and Weymouth Railway, but was not built until after the company was purchased by the Great Western Railway in 1850 and did not open until 1857.

The Bristol and Exeter Railway (B&ER) was an English railway company formed to connect Bristol and Exeter. It was built on the broad gauge and its engineer was Isambard Kingdom Brunel. It opened in stages between 1841 and 1844. It was allied with the Great Western Railway (GWR), which built its main line between London and Bristol, and in time formed part of a through route between London and Cornwall.

The Berks and Hants Railway comprised two railway lines built simultaneously by the Great Western Railway (GWR) south and west from Reading in an attempt to keep the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) out of the area that it considered to be its territory in England.
The Langport and Castle Cary Railway is a railway line from Castle Cary railway station to Cogload Junction near Taunton, Somerset, England, which reduced the length of the journey from London to Penzance by 20+1⁄4 miles (32.6 km).

Western National was a bus company operating in South West England from 1929 until the 1990s.

Wootton Bassett Junction railway station, formerly Wootton Bassett railway station, was a junction station in Wootton Bassett where the Great Western and South Wales Main Lines diverge. Opened in 1841, it closed in 1965.
The South West Rugby League (SWRL) also known as the South West Men's League, is a rugby league competition for teams in the South West of England. It was formerly part of the Rugby League Conference.

The Reading–Taunton line is a major branch of the Great Western Main Line from which it diverges at Reading railway station. It runs to Cogload Junction where it joins the Bristol to Exeter and Penzance line.

The Bristol to Exeter line is a major branch of the Great Western Main Line in the West of England and runs from Bristol, to Exeter, from where it continues as the Exeter to Plymouth line. It was one of the principal routes of the pre-1948 Great Western Railway which were subsequently taken over by the Western Region of British Railways and are now part of the Network Rail system.

Heart West is a regional radio station owned and operated by Global as part of the Heart network. It broadcasts in South West England, South Wales, Herefordshire, Malvern and Malvern Hills from studios in Bristol.