Related Research Articles

In computer science, a data structure is a data organization, management, and storage format that enables efficient access and modification. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data.
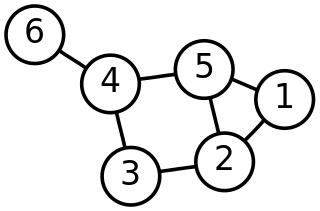
In mathematics, graph theory is the study of graphs, which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of vertices which are connected by edges. A distinction is made between undirected graphs, where edges link two vertices symmetrically, and directed graphs, where edges link two vertices asymmetrically; see Graph for more detailed definitions and for other variations in the types of graph that are commonly considered. Graphs are one of the prime objects of study in discrete mathematics.

Lisp is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation. Originally specified in 1958, Lisp is the second-oldest high-level programming language in widespread use today. Only Fortran is older, by one year. Lisp has changed since its early days, and many dialects have existed over its history. Today, the best-known general-purpose Lisp dialects are Racket, Common Lisp, Scheme and Clojure.
In computer science, a linked list is a linear collection of data elements whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, each element points to the next. It is a data structure consisting of a collection of nodes which together represent a sequence. In its most basic form, each node contains: data, and a reference to the next node in the sequence. This structure allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence during iteration. More complex variants add additional links, allowing more efficient insertion or removal of nodes at arbitrary positions. A drawback of linked lists is that access time is linear. Faster access, such as random access, is not feasible. Arrays have better cache locality compared to linked lists.
In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order. The term syntax is also used to refer to the study of such principles and processes. The goal of many syntacticians is to discover the syntactic rules common to all languages.

In computer science, a tree is a widely used abstract data type that simulates a hierarchical tree structure, with a root value and subtrees of children with a parent node, represented as a set of linked nodes.
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. The World Wide Web Consortium's XML 1.0 Specification of 1998 and several other related specifications—all of them free open standards—define XML.

The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance. A property listed in the National Register, or located within a National Register Historic District, may qualify for tax incentives derived from the total value of expenses incurred in preserving the property.

An organization, or organisation, is an entity – such as a company, an institution, or an association – comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.

A listed building, or listed structure, is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, Cadw in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland.

In astronomy, an astronomical object or celestial object is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms object and body are often used interchangeably. However, an astronomical body or celestial body is a single, tightly bound, contiguous entity, while an astronomical or celestial object is a complex, less cohesively bound structure, which may consist of multiple bodies or even other objects with substructures.
This is a list of lists of buildings and nonbuilding structures.

In crystallography, the cubiccrystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.

The Egyptian pyramids are ancient pyramid-shaped masonry structures located in Egypt. As of November 2008, sources cite either 118 or 138 as the number of identified Egyptian pyramids. Most were built as tombs for the country's pharaohs and their consorts during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods.

The U.S. National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) classifies its listings by various types of properties. Listed properties generally fall into one of five categories, though there are special considerations for other types of properties which do not fit into these five broad categories or fit into more specialized subcategories. The five general categories for NRHP properties are: building, district, object, site, and structure.