Argo Navis, or simply Argo, is one of Ptolemy's 48 constellations, now a grouping of three IAU constellations. It is formerly a single large constellation in the southern sky. The genitive is "Argus Navis", abbreviated "Arg". Flamsteed and other early modern astronomers called it Navis, genitive "Navis", abbreviated "Nav".

Antlia is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name means "pump" in Latin and Greek; it represents an air pump. Originally Antlia Pneumatica, the constellation was established by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille in the 18th century. Its non-specific (single-word) name, already in limited use, was preferred by John Herschel then welcomed by the astronomic community which officially accepted this. North of stars forming some of the sails of the ship Argo Navis, Antlia is completely visible from latitudes south of 49 degrees north.

A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer designations contained 1,564 stars. The brighter stars were assigned their first systematic names by the German astronomer Johann Bayer in 1603, in his star atlas Uranometria. Bayer catalogued only a few stars too far south to be seen from Germany, but later astronomers supplemented Bayer's catalog with entries for southern constellations.

A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.

Carina is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the keel of a ship, and it was the southern foundation of the larger constellation of Argo Navis until it was divided into three pieces, the other two being Puppis, and Vela.

Dorado is a constellation in the Southern Sky. It was named in the late 16th century and is now one of the 88 modern constellations. Its name refers to the mahi-mahi, which is known as dorado ("golden") in Spanish, although it has also been depicted as a swordfish. Dorado contains most of the Large Magellanic Cloud, the remainder being in the constellation Mensa. The South Ecliptic pole also lies within this constellation.

Pyxis is a small and faint constellation in the southern sky. Abbreviated from Pyxis Nautica, its name is Latin for a mariner's compass. Pyxis was introduced by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille in the 18th century, and is counted among the 88 modern constellations.

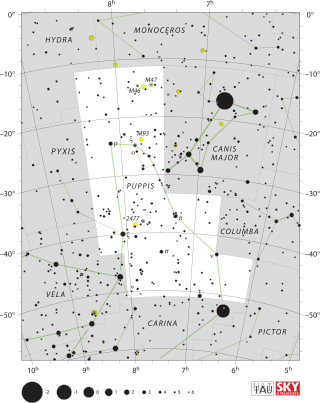
Puppis is a constellation in the southern sky. It was originally part of the traditional constellation of Argo Navis, which was divided into three parts, the other two being Carina, and Vela. Puppis is the largest of the three constellations in square degrees. It is one of the 88 modern constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union.

Sculptor is a faint constellation in the southern sky. It represents a sculptor. It was introduced by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in the 18th century. He originally named it Apparatus Sculptoris, but the name was later shortened.

Monoceros is a faint constellation on the celestial equator. Its definition is attributed to the 17th-century cartographer Petrus Plancius. It is bordered by Orion to the west, Gemini to the north, Canis Major to the south, and Hydra to the east. Other bordering constellations include Canis Minor, Lepus, and Puppis.

Volans is a constellation in the southern sky. It represents a flying fish; its name is a shortened form of its original name, Piscis Volans. Volans was one of twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman and it first appeared on a 35-cm (14") diameter celestial globe published in 1597 in Amsterdam by Plancius with Jodocus Hondius. The first depiction of this constellation in a celestial atlas was in Johann Bayer's Uranometria of 1603.

Columba is a faint constellation designated in the late sixteenth century, remaining in official use, with its rigid limits set in the 20th century. Its name is Latin for dove. It takes up 1.31% of the southern celestial hemisphere and is just south of Canis Major and Lepus.

In contemporary astronomy, 88 constellations are recognized by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Each constellation is a region of the sky bordered by arcs of right ascension and declination, together covering the entire celestial sphere. Their boundaries were officially adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1928 and published in 1930.

Noctua was a constellation near the tail of Hydra in the southern celestial hemisphere, but is no longer recognized. It was introduced by Alexander Jamieson in his 1822 work, A Celestial Atlas, and appeared in a derived collection of illustrated cards, Urania's Mirror. Now designated Asterism a, the owl was composed of the stars Sigma Librae, 4 Librae and 54–57 Hydrae, which range from 3rd to 6th magnitude.

Robur Carolinum was a constellation created by the English astronomer Edmond Halley in 1679. The name refers to the Royal Oak where Charles II was said to have hidden from the troops of Oliver Cromwell after the Battle of Worcester. It was between the constellations of Centaurus and Carina, extending into half of Vela.

Lochium Funis was a constellation created by Johann Bode in 1801 next to the constellation Pyxis, an earlier invention of Nicolas Louis de Lacaille. It represented the log and line used by seamen for measuring a ship's speed through the water. It was never used by other astronomers.

Former constellations are old historical Western constellations that for various reasons are no longer widely recognised or are not officially recognised by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Prior to 1930, many of these defunct constellations were traditional in one or more countries or cultures. Some only lasted decades but others were referred to over many centuries. All are now recognised only for having classical or historical value. Many former constellations had complex Latinised names after objects, people, or mythological or zoological creatures. Others with unwieldy names were shortened for convenience. For example, Scutum Sobiescianum was reduced to Scutum, Mons Mensae to Mensa, and Apparatus Sculptoris to Sculptor.

k Puppis is a Bayer designation given to an optical double star in the constellation Puppis, the two components being k1 Puppis and k2 Puppis.

Urania's Mirror; or, a view of the Heavens is a set of 32 astronomical star chart cards, first published in November 1824. They are illustrations based on Alexander Jamieson's A Celestial Atlas, but the addition of holes punched in them allow them to be held up to a light to see a depiction of the constellation's stars. They were engraved by Sidney Hall, and were said to be designed by "a lady", but have since been identified as the work of the Reverend Richard Rouse Bloxam, an assistant master at Rugby School.















