
Asparaginase is an enzyme that is used as a medication and in food manufacturing. As a medication, L-asparaginase is used to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and lymphoblastic lymphoma (LBL). It is given by injection into a vein, muscle, or under the skin. A pegylated version is also available. In food manufacturing it is used to decrease acrylamide.

Dickeya dadantii is a gram-negative bacillus that belongs to the family Pectobacteriaceae. It was formerly known as Erwinia chrysanthemi but was reassigned as Dickeya dadantii in 2005. Members of this family are facultative anaerobes, able to ferment sugars to lactic acid, have nitrate reductase, but lack oxidases. Even though many clinical pathogens are part of the order Enterobacterales, most members of this family are plant pathogens. D. dadantii is a motile, nonsporing, straight rod-shaped cell with rounded ends, much like the other members of the genus, Dickeya. Cells range in size from 0.8 to 3.2 μm by 0.5 to 0.8 μm and are surrounded by numerous flagella (peritrichous).

Oidium is a genus of Deuteromycetes, where traditionally most anamorphs of the order Erysiphales are included. Most of them are plant pathogens causing different forms of powdery mildew, for example:
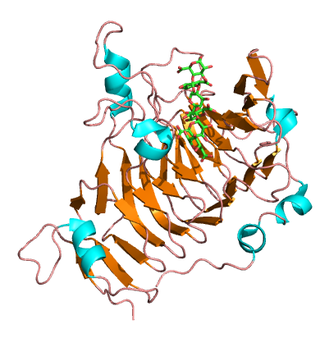
Pectinesterase (EC 3.1.1.11; systematic name pectin pectylhydrolase) is a ubiquitous cell-wall-associated enzyme that presents several isoforms that facilitate plant cell wall modification and subsequent breakdown. It catalyzes the following reaction:

The Castle of Canossa is a castle in Canossa, province of Reggio Emilia, northern Italy, especially known for being the location of the Road to Canossa, the meeting of Emperor Henry IV and Pope Gregory VII during the Investiture Controversy (1077).

Albert J. Friscia, was an Italian American sculptor. Initially interested in painting, Friscia studied art at the National Academy of Design in New York City in the Black Mountain College with Josef Albers, and in Paris with André Masson, then became Kinetic artist.
Coleophora chrysanthemi is a moth of the family Coleophoridae. It is found from Finland to Italy and Hungary.
Greek musical instruments were grouped under the general term "all developments from the original construction of a tortoise shell with two branching horns, having also a cross piece to which the stringser from an original three to ten or even more in the later period, like the Byzantine era". Greek musical instruments can be classified into the following categories:

The mantura or mandoura, is a Greek wind musical instrument of Cretan origin. It has 4 to 6 holes for the fingers and produces sound with the help of the tongue. Mantura is very widespread in Crete and the Greek islands.
Dickeya is a genus of the family Pectobacteriaceae that consists mainly of pathogens from herbaceous plants. Dickeya is the result of the reclassification of 75 strains of Pectobacterium chrysanthemi, as well as Brenneria paradisiaca CFBP 4178, into a new genus. The genus is named for American phytopathologist Robert S. Dickey. Several species in this genus, such as Dickeya dadantii, are known phytopathogens.

Godyris is a genus of clearwing (ithomiine) butterflies, named by Jean Baptiste Boisduval in 1870. They are in the brush-footed butterfly family, Nymphalidae.
Serralysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Giuseppe Capogrossi was an Italian painter.

Mantura obtusata is a species of Chrysomelidae family, that can be found nearly everywhere in Europe.

Mantura matthewsii is a species of Chrysomelidae family, that is common in Slovakia, Turkey.
Mantura rustica is a species of Chrysomelidae family.
Robert S. Dickey was an American phytopathologist, professor emeritus of Plant Pathology at the Cornell University and the namesake of the bacterial genus Dickeya.
Mantura floridana is a species of flea beetle in the family Chrysomelidae. It is found in North America. Larvae feed on Fallopia scandens. They appear yellow through the leaf epidermis, as the larvae are leaf miners.

Plagiognathus chrysanthemi, the trefoil plant bug, is a species of plant bug in the family Miridae. It is found across the entire Palearctic and in North America as an adventive.












