
McKees Rocks, also known as "The Rocks", is a borough in Allegheny County, in western Pennsylvania, along the south bank of the Ohio River. The borough population was 6,104 at the 2010 census.

Stowe Township is a township in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 6,362 at the 2010 census.

The Johnstown Inclined Plane is a 896.5-foot (273.3 m) funicular in Johnstown, Cambria County in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The incline and its two stations connect the city of Johnstown, situated in a valley at the confluence of the Stonycreek and the Little Conemaugh Rivers, to the borough of Westmont on Yoder Hill. The Johnstown Inclined Plane is billed as the "world's steepest vehicular inclined plane", as it is capable of carrying automobiles, in addition to passengers, up or down a slope with a grade of 70.9 percent. The travel time from one station to the other is 90 seconds.

The Pittsburgh and Lake Erie Railroad (P&LE), also known as the "Little Giant", was formed on May 11, 1875. Company headquarters were located in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The line connected Pittsburgh in the east with Youngstown, Ohio at nearby Haselton, Ohio in the west and Connellsville, Pennsylvania to the east. It did not reach Lake Erie until the formation of Conrail in 1976. The P&LE was known as the "Little Giant" since the tonnage that it moved was out of proportion to its route mileage. While it operated around one tenth of one percent of the nation's railroad miles, it hauled around one percent of its tonnage. This was largely because the P&LE served the steel mills of the greater Pittsburgh area, which consumed and shipped vast amounts of materials. It was a specialized railroad deriving much of its revenue from coal, coke, iron ore, limestone, and steel. The eventual closure of the steel mills led to the end of the P&LE as an independent line in 1992.

The Duquesne Incline is a funicular located near Pittsburgh's South Side neighborhood and scaling Mt. Washington in Pennsylvania, United States. Designed by Samuel Diescher, the incline was completed in 1877 and is 800 feet (244 m) long, 400 feet (122 m) in height, and is inclined at a 30-degree angle. It is an unusual track gauge of 5 ft.

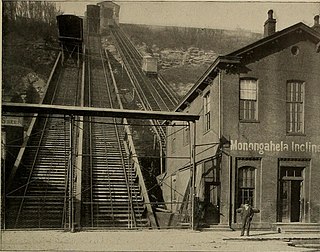
The Monongahela Incline is a funicular located near the Smithfield Street Bridge in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Built by John Endres in 1870, it is the oldest continuously operating funicular in the United States. It is also one of two surviving inclines from the original 17 passenger-carrying inclines built in Pittsburgh starting in the late 19th century. Its lower station is across the street from the Station Square shopping complex, and is easily accessible from the light rail system at the Station Square station.

The Pittsburgh and Ohio Central Railroad is a short-line railroad operating 35 miles of track over the Chartiers Branch in southwest Pennsylvania. It also operated a small portion of the former Panhandle Route until 2015, but Distributor Services, the Panhandle's only customer, decided to stop shipping by train. It is owned by the Ohio Central Railroad System, which is a division of the rail holding company Genesee & Wyoming Inc.

Chartiers Creek is a tributary of the Ohio River in Western Pennsylvania in the United States. The creek was named after Peter Chartier, a trapper of French and Native American parentage who established a trading post at the mouth of the creek in 1743.

The Knoxville Incline was a broad gauge inclined railway that ran between Pittsburgh's South Side and Allentown neighborhoods. The incline was constructed in 1890 and had a track gauge of 9 feet (2,700 mm). The charter was in planning as of January 1890, with a target filing date of February 8 of that year, and was originally to be called the Arlington Avenue Inclined Plane. The last day of service was December 3, 1960. It was demolished in 1960. It was designed by John H. McRoberts, with a length of 2644 feet. The Knoxville Incline briefly controlled the Pittsburgh, Knoxville & St. Clair Electric Railroad, while itself being later controlled by Pittsburgh Railways. During its operation, the incline ferried people and freight between the South Side and Knoxville. The Knoxville Incline and the nearby Mount Oliver Incline enabled the development of land in Allentown and surrounding communities on the hilltop. Like the Nunnery Hill Incline, the Knoxville Incline featured a curve, an unusual engineering feat for an incline.

The Castle Shannon Incline was a funicular railroad in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was originally part of the Pittsburgh and Castle Shannon Railroad route to the suburb of Castle Shannon. It replaced an earlier incline dating to 1825 that brought coal down from a mine in Mount Washington. Initially opened on 26 August 1890, the incline operated for only a few days before breaking down, the original machinery being unable to bear the strain of the large freight and passenger cars. After a second abortive run in October, it was decided that the machinery had to be replaced. The refitted incline opened on 7 March 1891. It ran from Bailey Avenue west of Haberman Avenue down to Carson Street just west of Arlington Avenue.
The Clifton Incline was a funicular that operated from 1889 to 1905 in what is now the Perry Hilltop neighborhood of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It extended from its base at Sarah Street at the intersection with Myrtle Street to its top landing at Clifton Park near the end of Clifton Street.

The Mount Oliver Incline was a funicular on the South Side of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was designed in 1871 by the Prussian engineer John Endres and his daughter Caroline Endres. Its track was 1600 feet long and gained 377 feet of elevation. It ran from the corner of Freyburg and South Twelfth Streets at its lower end to Warrington Avenue at its upper end. It was closed on 6 July 1951.

The Nunnery Hill Incline was a funicular in Allegheny City, Pennsylvania, in what is now the Fineview neighborhood of Pittsburgh. Designed by Samuel Diescher, it operated from 1888 until 1895 between its base station on Federal Street to its upper station on the currently named Meadville Street. It was one of a few inclines with a curve in the track. The name of the hill derived from a short-lived settlement of Poor Clares earlier in the century.
The St. Clair Incline, also known as the South Twenty-second Street Incline, was built in 1886–1888 and operated by St. Clair Incline Plane Company. It was a double track incline on the South Side Slopes of Pittsburgh from Josephine St. to Salisbury St. The lower station was near the intersection of S. 22nd Street and Josephine. The upper station was on Salisbury Street across from the former Fort Laughlin site eventually occupied by Arlington Playground. The incline was 2,060 ft (628 m) long, with a vertical rise of 361 ft (110 m). It was designed by engineer J. H. McRoberts. As it carried both freight and passengers over steep tracks laid on the ground, it could be considered to be a cable railway. Its path was not of constant slope but became progressively steeper toward the top, tracing a parabolic arc. It is uncertain exactly when the incline closed permanently, but it was reported as shut down in a 1932 Associated Press article about the "passing" of Pittsburgh's inclines. The structure was dismantled in 1934.
Ohio Valley Hospital is a not-for-profit hospital in Kennedy Township, Pennsylvania. Its postal address is 25 Heckel Road, McKees Rocks, Pennsylvania 15136. Ohio Valley serves Pittsburgh’s western suburbs, including the townships of Kennedy, Robinson, Moon and Findlay, and the municipalities of McKees Rocks, Oakdale, Crafton, Ingram, Imperial and Coraopolis. It is also described as being located in McKees Rocks.
The Monongahela Freight Incline was a funicular railway that scaled Mount Washington in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States.

The Troy Hill Incline, also known as the Mount Troy Incline, was a funicular railway located in old Allegheny, Pennsylvania, which is now the North Side of the city of Pittsburgh. Built by Gustav Lindenthal or Samuel Diescher, the incline was one of only a few funiculars constructed on the north side of Pittsburgh. It began construction in August 1887, and after considerable delay, opened on 20 September 1888. The incline ascended from Ohio Street near the end of the second 30th Street Bridge to Lowrie Street on the crest of Troy Hill. Never very profitable, it shut down in fall 1898 and was razed a decade later. A building now standing at 1733 Lowrie Street was long thought to have been the summit station, but later research found that the building did not appear on maps until well after the incline closed. The incline's length measured 370 feet (113 m), with a forty-seven percent (47%) gradient. The cost of construction was about $94,047.

The Penn Incline, also known as the 17th Street Incline, was a funicular railroad in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, in operation from 1884 to 1953. It ascended from 17th Street between Liberty and Penn avenues in the Strip District to Arcena (Ridgeway) Street near Ledlie Street in the Hill District.
The Ridgewood Incline was an inclined plane railroad in Allegheny City, Pennsylvania, in what is now the Perry South neighborhood of Pittsburgh. Built in 1886 and burned the next year, it was Allegheny's first and shortest-lived incline.




















