
Mixosaurus is an extinct genus of Middle Triassic ichthyosaur. Its fossils have been found near the Italy–Switzerland border and in South China.

Contectopalatus was a primitive ichthyosaur, an extinct fish-like marine reptile from the Middle Triassic of Germany and China. It was originally named Ichthyosaurus atavus by Quenstedt in 1852, and later reassigned to Mixosaurus. It was recognised as a separate genus by Maisch and Matzke in 1998, though other researchers have classified it as a species of Phalarodon instead.

Shastasaurus is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur from the middle and late Triassic. Specimens have been found in the United States, Canada, and China.

Himalayasaurus is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur from the Late Triassic Qulonggongba Formation of Tibet. The type species Himalayasaurus tibetensis was described in 1972 on the basis of fragmentary remains, including teeth, limb bones, and vertebrae. The entire body length of Himalayasaurus is estimated to have been over 15 metres (49 ft) in length. Himalayasaurus has since been considered a nomen dubium or "dubious name" because of the lack of features that set it apart from other ichthyosaurs, although the presence of distinct cutting edges on its teeth have more recently been proposed as a unique feature of the genus. Himalayasaurus belongs to the family Shastasauridae, which includes other large-bodied Triassic ichthyosaurs like Shonisaurus.

Omphalosaurus is an extinct genus of marine reptile from the Early Triassic to Middle Triassic, thought to be in the order of Ichthyosauria. Most of what is known about Omphalosaurus is based on multiple jaw fragments, ribs, and vertebrae. Specimens of Omphalosaurus have been described from the western United States, Poland, Austria and the island of Spitsbergen off the northern coast of Norway.
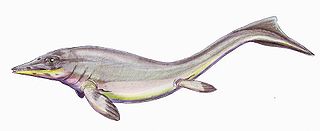
Grippia is a genus of early ichthyopterygian, an extinct group of reptiles that resembled dolphins. Its only species is Grippia longirostris. It was a relatively small ichthyopterygian, measuring around 1–1.5 metres (3.3–4.9 ft) long. Fossil remains from Svalbard from the specimen SVT 203 were originally assigned to G. longirostris but are now thought to have belonged to a non-ichthyopterygian diapsid related to Helveticosaurus.
Peltostega is an extinct genus of prehistoric trematosaurians. The type is the only known species, Peltostega erici It is known from the Early Triassic Kongressfjellet Formation of Svalbard and Jan Mayen.

Boreosomus is an extinct genus of Triassic ray-finned fish. It was first described from the Arctic island of Spitsbergen, but was later also discovered in other parts of the world. Boreosomus belongs to the family Ptycholepidae. Other genera of this family are Acrorhabdus (Spitsbergen), Ardoreosomus, Chungkingichthys (China), Ptycholepis (global) and Yuchoulepis (China).
Callawayia is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur. It contains the species Callawayia neoscapularis.
Isfjordosaurus is an extinct genus of ichthyopterygian marine reptile that lived during the Early Triassic. Fossils have been found on the island of Spitsbergen, part of the Svalbard archipelago off the northern coast of Norway. It was formally described by Ryosuke Motani in 1999 and contains the species Isfjordosaurus minor.
Parvinatator, from Latin, “parvus” little and “natator” swimmer, is an extinct genus of small ichthyopterygian marine reptile that lived during the Early to Middle Triassic. Its fossils have been found in British Columbia, Canada.

Phalarodon is an extinct genus of mixosaurid ichthyosaur known from the Middle Triassic. Its name is derived from the Greek φάλαρα (phálara) and odon ("tooth"). The genus has had a tumultuous history since its classification in 1910, with different workers describing species under different genera or declaring the genus to be a nomen dubium. Currently three species are recognized, but more have been identified in the past.
Wimanius is a genus of ichthyosaur from the Middle Triassic of Switzerland, containing a single species, Wimanius odontopalatus. It was described by Michael Maisch and Andreas Matzke in 1998 based on an incomplete skull from Monte San Giorgio, a mountain on the Swiss-Italian border. Wimanius possesses teeth on its palate, though whether they were located on the palatine or pterygoid is disputed. Other features of Wimanius include a large orbit and jugals with two rami of similar lengths. Different phylogenetic placements of Wimanius have been recovered by different studies, including it being a mixosaurid relative or a merriamosaur, and a monotypic family, Wimaniidae has been named for it. However, its validity has also been questioned, and synonymy with various other genera has been proposed.
Pessosaurus is an extinct genus of ichthyosaurs which existed during the Middle Triassic period.
Mixosauridae was an early group of ichthyosaurs, living between 247.2 and 235 million years ago, during the Triassic period. Fossils of mixosaurs have been found all over the world: China, Timor, Indonesia, Italy, Germany, Spitsbergen, Switzerland, Svalbard, Canada, Alaska, and Nevada.
Svalbardosaurus is a genus from the Lower Triassic, initially identified as an ichthyosaur but later reinterpretted as an amphibian.
Quasianosteosaurus is an extinct genus of basal ichthyosaur known from the late Early Triassic of Spitsbergen of the Svalbard archipelago, Norway. It was first named by Michael W. Maisch and Andreas T. Matzke in 2003 and the type species is Quasianosteosaurus vikinghoegdai. The generic name is derived from Latin quasi, "almost", and Greek anosteos, "boneless" and sauros, "lizard", regarding the preservation of the holotype which is almost exclusively a natural cast of the skull with very little original bone. The specific name is derived from Vikinghøgda, "Mount Viking", where the holotype was found. Quasianosteosaurus is known only from the holotype MNHN Nr. SVT 331, a partial three-dimensionally preserved skull consisting of the snout and orbital and postorbital regions. The skull is by far the largest Early Triassic ichthyosaur skull known, with an estimated cranial length of 50 cm (20 in). It was collected from the lowermost Grippia Niveau of the Sticky Keep Formation, Sassendalen Group at Mount Viking, Sassendalen. A phylogenetic analysis performed by Maisch & Matzke (2003) found it to be a basal ichthyosaur, sister taxon to Hueneosauria.

This timeline of ichthyosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on the ichthyosauromorphs, a group of secondarily aquatic marine reptiles whose later members superficially resembled dolphins, sharks, or swordfish. Scientists have documented ichthyosaur fossils at least as far back as the late 17th century. At that time, a scholar named Edward Lhwyd published a book on British fossils that misattributed some ichthyosaur vertebrae to actual fishes; their true nature was not recognized until the 19th century. In 1811, a boy named Joseph Anning discovered the first ichthyosaur fossils that would come to be scientifically recognized as such. His sister Mary would later find the rest of its skeleton and would go on to become a respected fossil collector and paleontologist in her own right.

Pachygonosaurus is a genus of ichthyosaur from Upper Silesia, Poland. It was described in 1916 by Friedrich von Huene and it has one single species, Pachygonosaurus robustus, based solely on the holotype, composed of two vertebral centra discovered in 1910, with a further three vertebrae also possibly belonging to the genus. Nowadays, Pachygonosaurus is considered a nomen dubium.

















