
Ichthyosauria is an order of large extinct marine reptiles sometimes referred to as "ichthyosaurs," although the term is also used for wider clades that the order resides in.

Shonisaurus is a genus of very large ichthyosaurs. At least 37 incomplete fossil specimens of the marine reptile have been found in the Luning Formation of Nevada, USA. This formation dates to the late Carnian age of the late Triassic period, about 237–227 million years ago.

Cymbospondylus is an extinct genus of large ichthyosaurs, of which he is among the oldest representatives, that lived during the Anisian stage of the Middle Triassic in what are now North America and Europe. The first known fossils of this taxon are a set of more or less complete vertebrae which were discovered in the 19th century in various mountain ranges of Nevada, in the United States, before being named and described by Joseph Leidy in 1868. It is in the beginning of the 20th century that more complete fossils were discovered through several expeditions launched by the University of California, and described in more detail by John Campbell Merriam in 1908, thus visualizing the overall anatomy of the animal. While many species have been assigned to the genus, only five are recognized as valid, the others being considered synonymous, doubtful or belonging to other genera. Cymbospondylus was formerly classified as a representative of the Shastasauridae, but more recent studies consider it to be more basal, view as the type genus of the Cymbospondylidae.

Lariosaurus is an extinct genus of nothosaurid from the Middle Triassic of central and western Europe and China. With a complete specimen of L. xingyiensis measuring 70.5 cm (2.3 ft) long and L. hongguoensis possibly measuring up to 80 cm (2.6 ft) long, it was one of the smallest known nothosaurs. First discovered at Perledo on the Lake Como in 1830, it was named in 1847 by Curioni, its name meaning "Lizard from Larius", the ancient name of the lake. This makes it one of the earliest studied reptiles from the Alps. It is known from an almost complete skeleton holotype and several other fairly complete fossils.

Chaohusaurus is an extinct genus of basal ichthyopterygian, depending on definition possibly ichthyosaur, from the Early Triassic of Chaohu and Yuanan, China.
Californosaurus is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur, an extinct marine reptile, from the Lower Hosselkus Limestone of California, and also the Muschelkalk of Germany.

Shastasaurus is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur from the middle and late Triassic. Specimens have been found in the United States, Canada, and China.

Thalattosauria is an extinct order of prehistoric marine reptiles that lived in the Middle to Late Triassic. Thalattosaurs were diverse in size and shape, and are divided into two superfamilies: Askeptosauroidea and Thalattosauroidea. Askeptosauroids were endemic to the Tethys Ocean, their fossils have been found in Europe and China, and they were likely semiaquatic fish eaters with straight snouts and decent terrestrial abilities. Thalattosauroids were more specialized for aquatic life and most had unusual downturned snouts and crushing dentition. Thalattosauroids lived along the coasts of both Panthalassa and the Tethys Ocean, and were most diverse in China and western North America. The largest species of thalattosaurs grew to over 4 meters (13 feet) in length, including a long, flattened tail utilized in underwater propulsion. Although thalattosaurs bore a superficial resemblance to lizards, their exact relationships are unresolved. They are widely accepted as diapsids, but experts have variously placed them on the reptile family tree among Lepidosauromorpha, Archosauromorpha, ichthyosaurs, and/or other marine reptiles.
Callawayia is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur. It contains the species Callawayia neoscapularis.

Guizhouichthyosaurus is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur which is known primarily from the Xiaowa Formation of the lower Carnian stage of the Late Triassic in southwest China. The type species of this genus is Guizhouichthyosaurus tangae, of which multiple skeletons are known. It has been reassigned as a species of the genus Shastasaurus in the past, though it has since been considered distinct. The ichthyosaurs Cymbospondylus asiaticus, named in 2002, and Panjiangsaurus epicharis, named in 2003, are junior synonyms of G. tangae. The genus is also known from the Ladinian-aged Middle Triassic Zhuganpo Formation; additionally, the species "Callawayia" wollongangense may belong to Guizhouichthyosaurus.
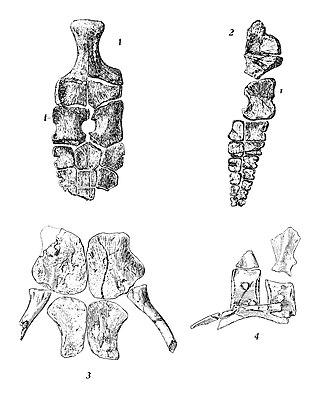
Toretocnemus is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur. Its remains have been found in California, United States, in Triassic layers of the Carnian Hosselkus Limestone.

Anshunsaurus is a genus of thalattosaurs within the family Askeptosauridae. Fossils have been found from Middle Triassic deposits in Guizhou, China. Three species are known: the type species A. huangguoshuensis, the slightly older species A. wushaensis, and the species A. huangnihensis.
Guanlingsaurus is an extinct genus of shastasaurid ichthyosaur from the Late Triassic of China. It grew up to 8.3 metres (27 ft) in length and has a wide, triangular skull with a short and toothless snout.

Yunguisaurus is an extinct genus of pistosaur known from the Guizhou Province of China.

Xinpusaurus is an extinct genus of thalattosaur from the Late Triassic of Guanling in Guizhou, China. Several species have been named since 2000: the type species X. suni along with the species X. bamaolinensis and X. kohi. A 2013 study proposed that all three species are synonymous with each other, in which case X. suni would be the only valid species, although a 2014 study argued that X. kohi was also valid. A fourth species, X. xingyiensis, was described in 2016.
Litorosuchus is a genus of armored, semiaquatic archosauriform reptile from the Middle Triassic of China, closely related to the morphologically similar Vancleavea. It contains one species, L. somnii.
The Xiaowa Formation is a Carnian-age geological formation found in southern China. It is a sequence of limestone and marls from the Carnian stage of the Triassic. Its lower section was previously known as the Wayao Formation or Wayao Member of the Falang Formation. In 2002, the Wayao Member was renamed and raised to the Xiaowa Formation to prevent confusion with an Eocene unit of the same name. Crinoids and marine reptiles are abundant in the Xiaowa Formation, forming a lagerstätte known as the Guanling biota. Ammonoids and conodonts found in the formation constrain its age to the early Carnian. Reptiles of the Guanling biota include ichthyosaurs, thalattosaurs, placodonts, and Odontochelys. Sedimentary events within this formation have been tied to the Carnian Pluvial Event.
The Zhuganpo Formation is a Triassic geologic unit found in southern China. It has historically been known as the Zhuganpo Member of the Falang Formation. A diverse fossil assemblage known as the Xingyi biota or Xingyi Fauna can be found in the upper part of the Zhuganpo Formation. Fossils of the Xingyi biota include articulated skeletons of marine reptiles, abundant fish, and a plentiful assortment of invertebrates indicating a Ladinian to Carnian age for the sediments of the formation.





















