Related Research Articles
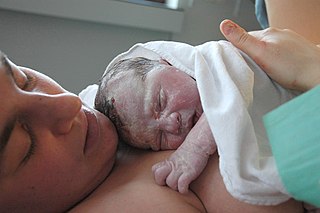
Childbirth, also known as labour, parturition and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million human births globally. In the developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in the developing countries most are home births.

Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition.
Uterine contractions are muscle contractions of the uterine smooth muscle that can occur at various intensities in both the non-pregnant and pregnant uterine state. The non-pregnant uterus undergoes small, spontaneous contractions in addition to stronger, coordinated contractions during the menstrual cycle and orgasm. Throughout gestation, the uterus enters a state of uterine quiescence due to various neural and hormonal changes. During this state, the uterus undergoes little to no contractions, though spontaneous contractions still occur for the uterine myocyte cells to experience hypertrophy. The pregnant uterus only contracts strongly during orgasms, labour, and in the postpartum stage to return to its natural size.

Braxton Hicks is the fourth studio album by Australian alternative rock band Jebediah. It was recorded between January and February 2004 and released on 12 July 2004 by record label Redline, a defunct independent record label that was co-owned by the band, making it the band's first independent release.
Labor induction is the process or treatment that stimulates childbirth and delivery. Inducing (starting) labor can be accomplished with pharmaceutical or non-pharmaceutical methods. In Western countries, it is estimated that one-quarter of pregnant women have their labor medically induced with drug treatment. Inductions are most often performed either with prostaglandin drug treatment alone, or with a combination of prostaglandin and intravenous oxytocin treatment.
Braxton Hicks contractions, also known as practice contractions or false labor, are sporadic uterine contractions that may start around six weeks into a pregnancy. However, they are usually felt in the second or third trimester of pregnancy.

John Braxton Hicks was a 19th-century English medical doctor who specialised in obstetrics.
False pregnancy is the appearance of clinical or subclinical signs and symptoms associated with pregnancy although the individual is not physically carrying a fetus. The mistaken impression that one is pregnant includes signs and symptoms such as tender breasts with secretions, abdominal growth, delayed menstrual periods, and subjective feelings of a moving fetus. Examination, ultrasound, and pregnancy tests can be used to rule out false pregnancy.
Cervical dilation is the opening of the cervix, the entrance to the uterus, during childbirth, miscarriage, induced abortion, or gynecological surgery. Cervical dilation may occur naturally, or may be induced surgically or medically.

Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.

Yokel is one of several derogatory terms referring to the stereotype of unsophisticated country people. The term is of uncertain etymology and is only attested from the early 19th century on.

Prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM), previously known as premature rupture of membranes, is breakage of the amniotic sac before the onset of labour. Women usually experience a painless gush or a steady leakage of fluid from the vagina. Complications in the baby may include premature birth, cord compression, and infection. Complications in the mother may include placental abruption and postpartum endometritis.
A contraction stress test (CST) is performed near the end of pregnancy to determine how well the fetus will cope with the contractions of childbirth. The aim is to induce contractions and monitor the fetus to check for heart rate abnormalities using a cardiotocograph. A CST is one type of antenatal fetal surveillance technique.
Postterm pregnancy is when a woman has not yet delivered her baby after 42 weeks of gestation, two weeks beyond the typical 40-week duration of pregnancy. Postmature births carry risks for both the mother and the baby, including fetal malnutrition, meconium aspiration syndrome, and stillbirths. After the 42nd week of gestation, the placenta, which supplies the baby with nutrients and oxygen from the mother, starts aging and will eventually fail. Postterm pregnancy is a reason to induce labor.
An object of the mind is an object that exists in the mind, but which, in the real world, can only be represented or modeled. Some such objects are abstractions, literary concepts, or fictional scenarios.
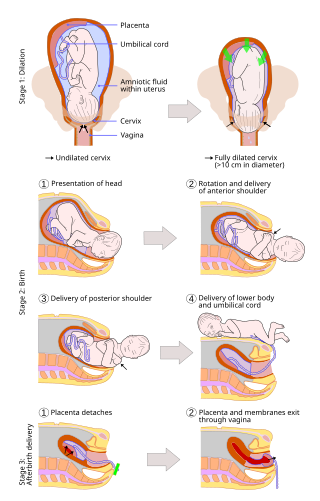
A vaginal delivery is the birth of offspring in mammals through the vagina. It is the most common method of childbirth worldwide. It is considered the preferred method of delivery, as it is correlated with lower morbidity and mortality than caesarean sections (C-sections), though it is not clear whether this is causal.

Labor Pains is a 2009 American romantic comedy film directed by Lara Shapiro and written by Stacy Kramer. It stars Lindsay Lohan, Luke Kirby, Bridgit Mendler, Chris Parnell, Cheryl Hines, and Kevin Covais. The film was released theatrically on June 19, 2009, only in Europe, Latin America, and United Arab Emirates. In United States, the film premiered on ABC Family on July 19, 2009. It drew 2.1 million viewers, a better-than-average prime-time audience for ABC Family; according to the network, it was the week's top cable film among coveted female demographic groups. Labor Pains was released on DVD and Blu-ray on August 4 and 31 in the United States and United Kingdom, respectively.
A false positive is an error in binary classification in which a test result incorrectly indicates the presence of a condition, while a false negative is the opposite error, where the test result incorrectly indicates the absence of a condition when it is actually present. These are the two kinds of errors in a binary test, in contrast to the two kinds of correct result. They are also known in medicine as a false positivediagnosis, and in statistical classification as a false positiveerror.

Prolonged labor is the inability of a woman to proceed with childbirth upon going into labor. Prolonged labor typically lasts over 20 hours for first time mothers, and over 14 hours for women that have already had children. Failure to progress can take place during two different phases; the latent phase and active phase of labor. The latent phase of labor can be emotionally tiring and cause fatigue, but it typically does not result in further problems. The active phase of labor, on the other hand, if prolonged, can result in long term complications.

Pain management during childbirth is the partial treatment and a way of reducing any pain that a woman may experience during labor and delivery. The amount of pain a woman feels during labor depends partly on the size and position of her baby, the size of her pelvis, her emotions, the strength of the contractions, and her outlook. Tension increases pain during labor. Virtually all women worry about how they will cope with the pain of labor and delivery. Childbirth is different for each woman and predicting the amount of pain experienced during birth and delivery can not be certain.