Related Research Articles

In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle.
In medicine, prolapse is a condition in which organs fall down or slip out of place. It is used for organs protruding through the vagina, rectum, or for the misalignment of the valves of the heart. A spinal disc herniation is also sometimes called "disc prolapse". Prolapse means "to fall out of place", from the Latin prolabi meaning "to fall out".

Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus. It may also involve removal of the cervix, ovaries (oophorectomy), Fallopian tubes (salpingectomy), and other surrounding structures.

A pessary is a prosthetic device inserted into the vagina for structural and pharmaceutical purposes. It is most commonly used to treat stress urinary incontinence to stop urinary leakage and to treat pelvic organ prolapse to maintain the location of organs in the pelvic region. It can also be used to administer medications locally in the vagina or as a method of contraception. Pessaries come in different shapes and sizes, so it is important that individuals be fitted for them by health care professionals to avoid any complications. However, there are a few instances and circumstances that allow individuals to purchase pessaries from a store without a prescription or without seeking help from a health care professional. Some side effects may occur if pessaries are not sized properly or regularly maintained, but with the appropriate care, pessaries are generally safe and well tolerated.

The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is composed of muscle fibers of the levator ani, the coccygeus muscle, and associated connective tissue which span the area underneath the pelvis. The pelvic diaphragm is a muscular partition formed by the levatores ani and coccygei, with which may be included the parietal pelvic fascia on their upper and lower aspects. The pelvic floor separates the pelvic cavity above from the perineal region below. Both males and females have a pelvic floor. To accommodate the birth canal, a female's pelvic cavity is larger than a male's.
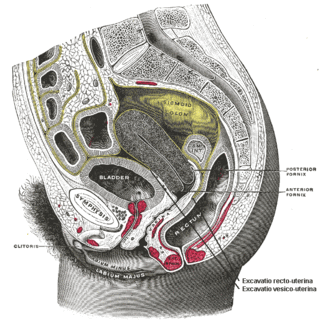
A rectocele or posterior vaginal wall prolapse results when the rectum herniates into or forms a bulge in the vagina. Two common causes of this defect are childbirth and hysterectomy. Rectocele also tends to occur with other forms of pelvic organ prolapse such as enterocele, sigmoidocele and cystocele.

Vaginoplasty is any surgical procedure that results in the construction or reconstruction of the vagina. It is a type of genitoplasty. Pelvic organ prolapse is often treated with one or more surgeries to repair the vagina. Sometimes a vaginoplasty is needed following the treatment or removal of malignant growths or abscesses in order to restore a normal vaginal structure and function. Surgery to the vagina is done to correct congenital defects to the vagina, urethra and rectum. It will correct protrusion of the urinary bladder into the vagina (cystocele) and protrusion of the rectum (rectocele) into the vagina. Often, a vaginoplasty is performed to repair the vagina and its attached structures due to trauma or injury. Labiaplasty, which alters the appearance of the vulva, can be performed as a discrete surgery, or as a subordinate procedure within a vaginoplasty.
A cystocele, also known as a prolapsed bladder, is a medical condition in which a woman's bladder bulges into her vagina. Some may have no symptoms. Others may have trouble starting urination, urinary incontinence, or frequent urination. Complications may include recurrent urinary tract infections and urinary retention. Cystocele and a prolapsed urethra often occur together and is called a cystourethrocele. Cystocele can negatively affect quality of life.
Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is characterized by descent of pelvic organs from their normal positions. In women, the condition usually occurs when the pelvic floor collapses after gynecological cancer treatment, childbirth or heavy lifting.
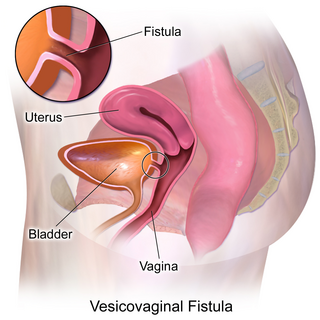
Vesicovaginal fistula (VVF) is a subtype of female urogenital fistula (UGF).

Uterine prolapse is when the uterus descends towards or through the opening of the vagina. Symptoms may include vaginal fullness, pain with sex, trouble urinating, urinary incontinence, and constipation. Often it gets worse over time. Low back pain and vaginal bleeding may also occur.

A pelvic examination is the physical examination of the external and internal female pelvic organs. It is frequently used in gynecology for the evaluation of symptoms affecting the female reproductive and urinary tract, such as pain, bleeding, discharge, urinary incontinence, or trauma. It can also be used to assess a woman's anatomy in preparation for procedures. The exam can be done awake in the clinic and emergency department, or under anesthesia in the operating room. The most commonly performed components of the exam are 1) the external exam, to evaluate the external genitalia 2) the internal exam with palpation to examine the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes, and 3) the internal exam using the speculum to visualize the vaginal walls and cervix. During the pelvic exam, sample of cells and fluids may be collected to screen for sexually transmitted infections or cancer.
Urogynecology or urogynaecology is a surgical sub-specialty of urology and gynecology.

Perineoplasty denotes the plastic surgery procedures used to correct clinical conditions of the vagina and the anus. Among the vagino-anal conditions resolved by perineoplasty are vaginal looseness, vaginal itching, damaged perineum, incontinence, genital warts, dyspareunia, vaginal stenosis, vaginismus, vulvar vestibulitis, and decreased sexual sensation. Depending upon the vagino-anal condition to be treated, there are two variants of the perineoplasty procedure: the first, to tighten the perineal muscles and the vagina; the second, to loosen the perineal muscles.

Surgical mesh is a loosely woven sheet which is used as either a permanent or temporary support for organs and other tissues during surgery. Surgical mesh is created from both inorganic and biological materials and is used in a variety of surgeries. Though hernia repair surgery is the most common application, it can also be used for reconstructive work, such as in pelvic organ prolapse.
A well-woman examination is an exam offered to women to review elements of their reproductive health. The exam includes a breast examination, a pelvic examination and a Pap smear but may also include other procedures. Hospitals employ strict policies relating to the provision of consent by the patient, the availability of chaperones at the examination, and the absence of other parties.
Genitoplasty is plastic surgery to the genitals. Genitoplasties may be reconstructive to repair injuries, and damage arising from cancer treatment, or congenital disorders, endocrine conditions, or they may be cosmetic.
A urogenital fistula is an abnormal tract that exists between the urinary tract and bladder, ureters, or urethra. A urogenital fistula can occur between any of the organs and structures of the pelvic region. A fistula allows urine to continually exit through and out the urogenital tract. This can result in significant disability, interference with sexual activity, and other physical health issues, the effects of which may in turn have a negative impact on mental or emotional state, including an increase in social isolation. Urogenital fistulas vary in etiology. Fistulas are usually caused by injury or surgery, but they can also result from malignancy, infection, prolonged and obstructed labor and deliver in childbirth, hysterectomy, radiation therapy or inflammation. Of the fistulas that develop from difficult childbirth, 97 percent occur in developing countries. Congenital urogenital fistulas are rare; only ten cases have been documented. Abnormal passageways can also exist between the vagina and the organs of the gastrointestinal system, and these may also be termed fistulas.

Vaginal anomalies are abnormal structures that are formed during the prenatal development of the female reproductive system and are rare congenital defects that result in an abnormal or absent vagina. When present, they are often found with uterine, skeletal and urinary abnormalities. This is because these structures, like the vagina, are most susceptible to disruption during crucial times of organ-genesis. Many of these defects are classified under the broader term Müllerian duct anomalies. Müllerian duct anomalies are caused by a disturbance during the embryonic time of genitourinary development. The other isolated incidents of vaginal anomalies can occur with no apparent cause. Oftentimes vaginal anomalies are part of a cluster of defects or syndromes. In addition, inheritance can play a part as can prenatal exposure to some teratogens. Many vaginal anomalies are not detected at birth because the external genitalia appear to be normal. Other organs of the reproductive system may not be affected by an abnormality of the vagina. The uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries can be functional despite the presence of a defect of the vagina and external genitalia. A vaginal anomaly may not affect fertility. Though it depends on the extent of the vaginal defect, it is possible for conception to occur. In instances where a functional ovary exists, IVF may be successful. Functioning ovaries in a woman with a vaginal defect allows the implantation of a fertilized ovum into the uterus of an unaffected gestational carrier, usually another human. A successful conception and can occur. Vaginal length varies from 6.5 to 12.5 cm. Since this is slightly shorter than older descriptions, it may impact the diagnosis of women with vaginal agenesis or hypoplasia who may unnecessarily be encouraged to undergo treatment to increase the size of the vagina. Vaginal anomalies may cause difficulties in urination, conception, pregnancy, impair sex. Psychosocial effects can also exist.
Transvaginal mesh, also known as vaginal mesh implant, is a net-like surgical tool that is used to treat pelvic organ prolapse (POP) and stress urinary incontinence (SUI) among female patients. The surgical mesh is placed transvaginally to reconstruct weakened pelvic muscle walls and to support the urethra or bladder.
References
- ↑ Baggish, Michael (2016). Atlas of pelvic anatomy and gynecologic surgery. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier. ISBN 9780323225526; Access provided by the University of Pittsburgh
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link)