Related Research Articles
Clitoridectomy or clitorectomy is the surgical removal, reduction, or partial removal of the clitoris. It is rarely used as a therapeutic medical procedure, such as when cancer has developed in or spread to the clitoris. It is often performed on intersex newborns. Commonly, non-medical removal of the clitoris is performed during female genital mutilation (FGM).

In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle.
In medicine, prolapse is a condition in which organs fall down or slip out of place. It is used for organs protruding through the vagina, rectum, or for the misalignment of the valves of the heart. A spinal disc herniation is also sometimes called "disc prolapse". Prolapse means "to fall out of place", from the Latin prolabi meaning "to fall out".

The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is an anatomical location in the human body, which has an important role in urinary and anal continence, sexual function and support of the pelvic organs. The pelvic floor includes muscles, both skeletal and smooth, ligaments and fascia. and separates between the pelvic cavity from above, and the perineum from below. It is formed by the levator ani muscle and coccygeus muscle, and associated connective tissue.
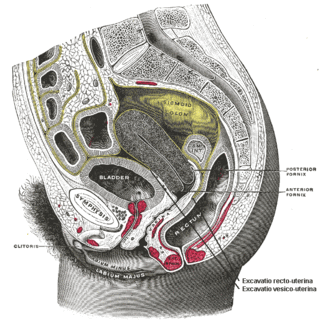
In gynecology, a rectocele or posterior vaginal wall prolapse results when the rectum bulges (herniates) into the vagina. Two common causes of this defect are childbirth and hysterectomy. Rectocele also tends to occur with other forms of pelvic organ prolapse, such as enterocele, sigmoidocele and cystocele.

Vaginoplasty is any surgical procedure that results in the construction or reconstruction of the vagina. It is a type of genitoplasty. Pelvic organ prolapse is often treated with one or more surgeries to repair the vagina. Sometimes a vaginoplasty is needed following the treatment or removal of malignant growths or abscesses in order to restore a normal vaginal structure and function. Surgery to the vagina is done to correct congenital defects to the vagina, urethra and rectum. It will correct protrusion of the urinary bladder into the vagina (cystocele) and protrusion of the rectum (rectocele) into the vagina. Often, a vaginoplasty is performed to repair the vagina and its attached structures due to trauma or injury. Labiaplasty, which alters the appearance of the vulva, can be performed as a discrete surgery, or as a subordinate procedure within a vaginoplasty.
Genital reconstructive surgery may refer to:

Intersex medical interventions, also known as intersex genital mutilations (IGM), are surgical, hormonal and other medical interventions performed to modify atypical or ambiguous genitalia and other sex characteristics, primarily for the purposes of making a person's appearance more typical and to reduce the likelihood of future problems. The history of intersex surgery has been characterized by controversy due to reports that surgery can compromise sexual function and sensation, and create lifelong health issues. Timing, evidence, necessity and indications for surgeries in infancy, adolescence or adult age have been controversial, associated with issues of consent.

The history of intersex surgery is intertwined with the development of the specialities of pediatric surgery, pediatric urology, and pediatric endocrinology, with our increasingly refined understanding of sexual differentiation, with the development of political advocacy groups united by a human qualified analysis, and in the last decade by doubts as to efficacy, and controversy over when and even whether some procedures should be performed.

The cystocele, also known as a prolapsed bladder, is a medical condition in which a woman's bladder bulges into her vagina. Some may have no symptoms. Others may have trouble starting urination, urinary incontinence, or frequent urination. Complications may include recurrent urinary tract infections and urinary retention. Cystocele and a prolapsed urethra often occur together and is called a cystourethrocele. Cystocele can negatively affect quality of life.

Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is characterized by descent of pelvic organs from their normal positions into the vagina. In women, the condition usually occurs when the pelvic floor collapses after gynecological cancer treatment, childbirth or heavy lifting. Injury incurred to fascia membranes and other connective structures can result in cystocele, rectocele or both. Treatment can involve dietary and lifestyle changes, physical therapy, or surgery.

Vaginectomy is a surgery to remove all or part of the vagina. It is one form of treatment for individuals with vaginal cancer or rectal cancer that is used to remove tissue with cancerous cells. It can also be used in gender-affirming surgery. Some people born with a vagina who identify as trans men or as nonbinary may choose vaginectomy in conjunction with other surgeries to make the clitoris more penis-like (metoidioplasty), construct of a full-size penis (phalloplasty), or create a relatively smooth, featureless genital area.

Uterine prolapse is a form of pelvic organ prolapse in which the uterus and a portion of the upper vagina protrude into the vaginal canal and, in severe cases, through the opening of the vagina. It is most often caused by injury or damage to structures that hold the uterus in place within the pelvic cavity. Symptoms may include vaginal fullness, pain with sexual intercourse, difficulty urinating, and urinary incontinence. Risk factors include older age, pregnancy, vaginal childbirth, obesity, chronic constipation, and chronic cough. Prevalence, based on physical exam alone, is estimated to be approximately 14%.

Disorders of sex development (DSDs), also known as differences in sex development, diverse sex development and variations in sex characteristics (VSC), are congenital conditions affecting the reproductive system, in which development of chromosomal, gonadal, or anatomical sex is atypical.
Cervical agenesis is a congenital disorder of the female genital system that manifests itself in the absence of a cervix, the connecting structure between the uterus and vagina. Milder forms of the condition, in which the cervix is present but deformed and nonfunctional, are known as cervical atresia or cervical dysgenesis.
A retropubic paravaginal repair is the surgical procedure to reattach the anterior lateral vaginal wall and its connective tissue to its normal position in the pelvis to correct pelvic organ prolapse. It may be necessary to preserve normal function of pelvic organs after the vagina has detached from its normal position and has moved along with underlying tissues away from the pelvic sidewall. A common finding in repairing this condition is that the arcus tendineus fasciae has become detached. The procedure is usually performed by a gynecological surgeon using pelvic surgery techniques.

Vaginal anomalies are abnormal structures that are formed during the prenatal development of the female reproductive system and are rare congenital defects that result in an abnormal or absent vagina.
Vaginal rugae are structures of the vagina that are transverse ridges formed out of the supporting tissues and vaginal epithelium in females. Some conditions can cause the disappearance of vaginal rugae and are usually associated with childbirth and prolapse of pelvic structures. The rugae contribute to the resiliency and elasticity of the vagina and its ability to distend and return to its previous state. These structures not only allow expansions and an increase in surface area of the vaginal epithelium, they provide the space necessary for the vaginal microbiota. The shape and structure of the rugae are supported and maintained by the lamina propria of the vagina and the anterior and posterior rugae.
Vaginal stenosis is an abnormal condition in which the vagina becomes narrower and shorter due to the formation of fibrous tissue. Vaginal stenosis can contribute to sexual dysfunction, dyspareunia and make pelvic exams difficult and painful. The lining of the vagina may also be thinner and drier and contain scar tissue. This condition can result in pain during sexual intercourse or a pelvic exam. Vaginal stenosis is often caused by radiation therapy to the pelvis, an episiotomy, or other forms of surgical procedures. Chemotherapy can also increase the likelihood of developing vaginal stenosis. Vaginal stenosis can also result from genital reconstructive surgery in people with congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Sexual anomalies, also known as sexual abnormalities, are a set of clinical conditions due to chromosomal, gonadal and/or genitalia variation. Individuals with congenital (inborn) discrepancy between sex chromosome, gonadal, and their internal and external genitalia are categorised as individuals with a disorder of sex development (DSD). Afterwards, if the family or individual wishes, they can partake in different management and treatment options for their conditions.
References
- ↑ Ruth A. Hannon (2010). Porth pathophysiology : concepts of altered health states (1st Canadian ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 128. ISBN 9781605477817.
- 1 2 Baggish, Michael (2016). Atlas of pelvic anatomy and gynecologic surgery. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier. ISBN 9780323225526.
- 1 2 Gundeti, Mohan (2012). Pediatric Robotic and Reconstructive Urology a Comprehensive Guide. City: Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 9781444335538; Access provided by the University of Pittsburgh
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ↑ Horbach, Sophie E.R.; Bouman, Mark-Bram; Smit, Jan Maerten; Özer, Müjde; Buncamper, Marlon E.; Mullender, Margriet G. (2015). "Outcome of Vaginoplasty in Male-to-Female Transgenders: A Systematic Review of Surgical Techniques". The Journal of Sexual Medicine. 12 (6): 1499–1512. doi:10.1111/jsm.12868. ISSN 1743-6095. PMID 25817066.
- ↑ Pooler, Charlotte (2009-10-01). Porth Pathophysiology: Concepts of Altered Health States. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9781605477817.
- ↑ Entry "hypospadias" in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary .
- ↑ OED 2nd edition, 1989 as /hɪpəʊˈspeɪdɪəs/~/haɪpəʊˈspeɪdɪəs/
- ↑ Eberhard Nieschlag; Hermann M. Behre; Susan Nieschlag (July 2009). Andrology: Male Reproductive Health and Dysfunction. Springer. pp. 328–. ISBN 978-3-540-78354-1.
- ↑ Hiort, O (2014). Understanding differences and disorders of sex development (DSD. Basel: Karger. ISBN 9783318025590.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "2016 ICD-10-PCS Procedure Code 0UQG0ZZ : Repair Vagina, Open Approach". ICD10Data.com. Retrieved 2016-03-03.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Hoffman, Barbara (2012). Williams gynecology. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. ISBN 9780071716727.
- 1 2 Baggish, Michael (2016). Atlas of pelvic anatomy and gynecologic surgery. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier. ISBN 9780323225526; Access provided by the University of Pittsburgh
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ↑ "Online ICD9/ICD9CM codes". World Health Organization. Retrieved 2016-03-06.
- ↑ Lee, Peter A.; Nordenström, Anna; Houk, Christopher P.; Ahmed, S. Faisal; Auchus, Richard; Baratz, Arlene; Baratz Dalke, Katharine; Liao, Lih-Mei; Lin-Su, Karen; Looijenga, Leendert H.J.; Mazur, Tom; Meyer-Bahlburg, Heino F.L.; Mouriquand, Pierre; Quigley, Charmian A.; Sandberg, David E.; Vilain, Eric; Witchel, Selma; and the Global DSD Update Consortium (2016-01-28). "Global Disorders of Sex Development Update since 2006: Perceptions, Approach and Care". Hormone Research in Paediatrics. 85 (3): 158–180. doi: 10.1159/000442975 . ISSN 1663-2818. PMID 26820577.