| Part of a series on |
| Machine learning and data mining |
|---|
In natural language processing, a sentence embedding is a representation of a sentence as a vector of numbers which encodes meaningful semantic information. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7]
State of the art embeddings are based on the learned hidden layer representation of dedicated sentence transformer models. BERT pioneered an approach involving the use of a dedicated [CLS] token prepended to the beginning of each sentence inputted into the model; the final hidden state vector of this token encodes information about the sentence and can be fine-tuned for use in sentence classification tasks. In practice however, BERT's sentence embedding with the [CLS] token achieves poor performance, often worse than simply averaging non-contextual word embeddings. SBERT later achieved superior sentence embedding performance [8] by fine tuning BERT's [CLS] token embeddings through the usage of a siamese neural network architecture on the SNLI dataset.
Other approaches are loosely based on the idea of distributional semantics applied to sentences. Skip-Thought trains an encoder-decoder structure for the task of neighboring sentences predictions; this has been shown to achieve worse performance than approaches such as InferSent or SBERT.
An alternative direction is to aggregate word embeddings, such as those returned by Word2vec, into sentence embeddings. The most straightforward approach is to simply compute the average of word vectors, known as continuous bag-of-words (CBOW). [9] However, more elaborate solutions based on word vector quantization have also been proposed. One such approach is the vector of locally aggregated word embeddings (VLAWE), [10] which demonstrated performance improvements in downstream text classification tasks.
In recent years, sentence embedding has seen a growing level of interest due to its applications in natural language queryable knowledge bases through the usage of vector indexing for semantic search. LangChain for instance utilizes sentence transformers for purposes of indexing documents. In particular, an indexing is generated by generating embeddings for chunks of documents and storing (document chunk, embedding) tuples. Then given a query in natural language, the embedding for the query can be generated. A top k similarity search algorithm is then used between the query embedding and the document chunk embeddings to retrieve the most relevant document chunks as context information for question answering tasks. This approach is also known formally as retrieval-augmented generation [11]
Though not as predominant as BERTScore, sentence embeddings are commonly used for sentence similarity evaluation which sees common use for the task of optimizing a Large language model's generation parameters is often performed via comparing candidate sentences against reference sentences. By using the cosine-similarity of the sentence embeddings of candidate and reference sentences as the evaluation function, a grid-search algorithm can be utilized to automate hyperparameter optimization [ citation needed ].
A way of testing sentence encodings is to apply them on Sentences Involving Compositional Knowledge (SICK) corpus [12] for both entailment (SICK-E) and relatedness (SICK-R).
In [13] the best results are obtained using a BiLSTM network trained on the Stanford Natural Language Inference (SNLI) Corpus. The Pearson correlation coefficient for SICK-R is 0.885 and the result for SICK-E is 86.3. A slight improvement over previous scores is presented in: [14] SICK-R: 0.888 and SICK-E: 87.8 using a concatenation of bidirectional Gated recurrent unit.
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related to information retrieval, knowledge representation and computational linguistics, a subfield of linguistics. Typically data is collected in text corpora, using either rule-based, statistical or neural-based approaches in machine learning and deep learning.
A language model is a probabilistic model of a natural language. In 1980, the first significant statistical language model was proposed, and during the decade IBM performed ‘Shannon-style’ experiments, in which potential sources for language modeling improvement were identified by observing and analyzing the performance of human subjects in predicting or correcting text.

Distributional semantics is a research area that develops and studies theories and methods for quantifying and categorizing semantic similarities between linguistic items based on their distributional properties in large samples of language data. The basic idea of distributional semantics can be summed up in the so-called distributional hypothesis: linguistic items with similar distributions have similar meanings.

In machine learning (ML), feature learning or representation learning is a set of techniques that allow a system to automatically discover the representations needed for feature detection or classification from raw data. This replaces manual feature engineering and allows a machine to both learn the features and use them to perform a specific task.
In natural language processing, a word embedding is a representation of a word. The embedding is used in text analysis. Typically, the representation is a real-valued vector that encodes the meaning of the word in such a way that the words that are closer in the vector space are expected to be similar in meaning. Word embeddings can be obtained using language modeling and feature learning techniques, where words or phrases from the vocabulary are mapped to vectors of real numbers.
Word2vec is a technique in natural language processing (NLP) for obtaining vector representations of words. These vectors capture information about the meaning of the word based on the surrounding words. The word2vec algorithm estimates these representations by modeling text in a large corpus. Once trained, such a model can detect synonymous words or suggest additional words for a partial sentence. Word2vec was developed by Tomáš Mikolov and colleagues at Google and published in 2013.
Neural machine translation (NMT) is an approach to machine translation that uses an artificial neural network to predict the likelihood of a sequence of words, typically modeling entire sentences in a single integrated model.
Semantic folding theory describes a procedure for encoding the semantics of natural language text in a semantically grounded binary representation. This approach provides a framework for modelling how language data is processed by the neocortex.
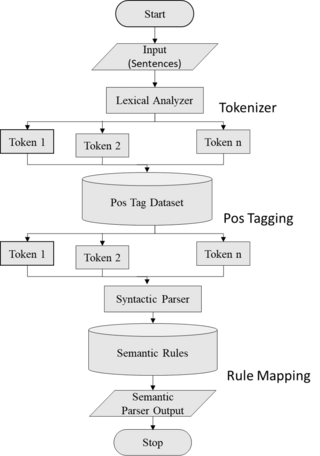
Semantic parsing is the task of converting a natural language utterance to a logical form: a machine-understandable representation of its meaning. Semantic parsing can thus be understood as extracting the precise meaning of an utterance. Applications of semantic parsing include machine translation, question answering, ontology induction, automated reasoning, and code generation. The phrase was first used in the 1970s by Yorick Wilks as the basis for machine translation programs working with only semantic representations. Semantic parsing is one of the important tasks in computational linguistics and natural language processing.
Spark NLP is an open-source text processing library for advanced natural language processing for the Python, Java and Scala programming languages. The library is built on top of Apache Spark and its Spark ML library.
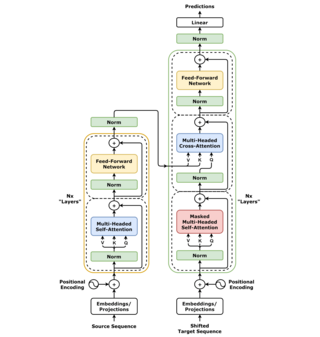
A transformer is a deep learning architecture that was developed by researchers at Google and is based on the multi-head attention mechanism, which was proposed in the 2017 paper "Attention Is All You Need". Text is converted to numerical representations called tokens, and each token is converted into a vector via lookup from a word embedding table. At each layer, each token is then contextualized within the scope of the context window with other (unmasked) tokens via a parallel multi-head attention mechanism, allowing the signal for key tokens to be amplified and less important tokens to be diminished.
Bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) is a language model introduced in October 2018 by researchers at Google. It learns to represent text as a sequence of vectors using self-supervised learning. It uses the encoder-only transformer architecture. It is notable for its dramatic improvement over previous state-of-the-art models, and as an early example of a large language model. As of 2020, BERT is a ubiquitous baseline in natural language processing (NLP) experiments.

ELMo is a word embedding method for representing a sequence of words as a corresponding sequence of vectors. It was created by researchers at the Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence, and University of Washington and first released in February, 2018. It is a bidirectional LSTM which takes character-level as inputs and produces word-level embeddings, trained on a corpus of about 30 million sentences and 1 billion words.

Attention is a machine learning method that determines the relative importance of each component in a sequence relative to the other components in that sequence. In natural language processing, importance is represented by "soft" weights assigned to each word in a sentence. More generally, attention encodes vectors called token embeddings across a fixed-width sequence that can range from tens to millions of tokens in size.

A vision transformer (ViT) is a transformer designed for computer vision. A ViT decomposes an input image into a series of patches, serializes each patch into a vector, and maps it to a smaller dimension with a single matrix multiplication. These vector embeddings are then processed by a transformer encoder as if they were token embeddings.
Perceiver is a variant of the Transformer architecture, adapted for processing arbitrary forms of data, such as images, sounds and video, and spatial data. Unlike previous notable Transformer systems such as BERT and GPT-3, which were designed for text processing, the Perceiver is designed as a general architecture that can learn from large amounts of heterogeneous data. It accomplishes this with an asymmetric attention mechanism to distill inputs into a latent bottleneck.
Prompt engineering is the process of structuring an instruction that can be interpreted and understood by a generative artificial intelligence (AI) model.
DisCoCat is a mathematical framework for natural language processing which uses category theory to unify distributional semantics with the principle of compositionality. The grammatical derivations in a categorial grammar are interpreted as linear maps acting on the tensor product of word vectors to produce the meaning of a sentence or a piece of text. String diagrams are used to visualise information flow and reason about natural language semantics.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique that grants generative artificial intelligence models information retrieval capabilities. It modifies interactions with a large language model (LLM) so that the model responds to user queries with reference to a specified set of documents, using this information to augment information drawn from its own vast, static training data. This allows LLMs to use domain-specific and/or updated information. Use cases include providing chatbot access to internal company data or giving factual information only from an authoritative source.

"Attention Is All You Need" is a 2017 landmark research paper in machine learning authored by eight scientists working at Google. The paper introduced a new deep learning architecture known as the transformer, based on the attention mechanism proposed in 2014 by Bahdanau et al. It is considered a foundational paper in modern artificial intelligence, as the transformer approach has become the main architecture of large language models like those based on GPT. At the time, the focus of the research was on improving Seq2seq techniques for machine translation, but the authors go further in the paper, foreseeing the technique's potential for other tasks like question answering and what is now known as multimodal Generative AI.