Related Research Articles

The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.

The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle.

The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI and anterior to cranial nerve VIII.

The pons is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.

The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest.

Afferent nerve fibers are axons of sensory neurons that carry sensory information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system. Many afferent projections arrive at a particular brain region.

Efferent nerve fibers refer to axonal projections that exit a particular region; as opposed to afferent projections that arrive at the region. These terms have a slightly different meaning in the context of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and central nervous system (CNS). The efferent fiber is a long process projecting far from the neuron's body that carries nerve impulses away from the central nervous system toward the peripheral effector organs. A bundle of these fibers is called an efferent nerve. The opposite direction of neural activity is afferent conduction, which carries impulses by way of the afferent nerve fibers of sensory neurons.

A reflex arc is a neural pathway that controls a reflex. In vertebrates, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord. This allows for faster reflex actions to occur by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of routing signals through the brain. The brain will receive the input while the reflex is being carried out and the analysis of the signal takes place after the reflex action.

A cranial nerve nucleus is a collection of neurons in the brain stem that is associated with one or more of the cranial nerves. Axons carrying information to and from the cranial nerves form a synapse first at these nuclei. Lesions occurring at these nuclei can lead to effects resembling those seen by the severing of nerve(s) they are associated with. All the nuclei except that of the trochlear nerve supply nerves of the same side of the body.
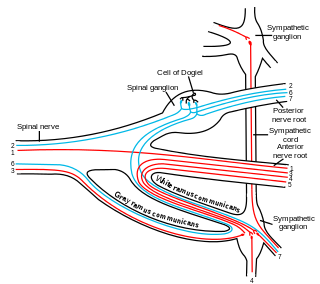
The white ramus communicans from Latin ramus (branch) and communicans (communicating) is the preganglionic sympathetic outflow nerve tract from the spinal cord.

General visceral efferent fibers (GVE) or visceral efferents or autonomic efferents, are the efferent nerve fibers of the autonomic nervous system that provide motor innervation to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands through postganglionic varicosities.

The inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve is one of the two sensory ganglia of each vagus nerve. It contains neuron cell bodies of general visceral afferent fibers and special visceral afferent fibers. It is situated within the jugular fossa just below the skull. It is situated just below the superior ganglion of vagus nerve.
Pelvic splanchnic nerves or nervi erigentes are splanchnic nerves that arise from sacral spinal nerves S2, S3, S4 to provide parasympathetic innervation to the organs of the pelvic cavity.

The esophageal plexus is formed by nerve fibers from two sources, branches of the vagus nerve, and visceral branches of the sympathetic trunk. The esophageal plexus and the cardiac plexus contain the same types of fibers and are both considered thoracic autonomic plexus.

The general somatic afferent fibers afferent fibers arise from neurons in sensory ganglia and are found in all the spinal nerves, except occasionally the first cervical, and conduct impulses of pain, touch and temperature from the surface of the body through the dorsal roots to the spinal cord and impulses of muscle sense, tendon sense and joint sense from the deeper structures.

The general visceral afferent (GVA) fibers conduct sensory impulses from the internal organs, glands, and blood vessels to the central nervous system. They are considered to be part of the visceral nervous system, which is closely related to the autonomic nervous system, but 'visceral nervous system' and 'autonomic nervous system' are not direct synonyms and care should be taken when using these terms. Unlike the efferent fibers of the autonomic nervous system, the afferent fibers are not classified as either sympathetic or parasympathetic.

The general (spinal) somatic efferent neurons, arise from motor neuron cell bodies in the ventral horns of the gray matter within the spinal cord. They exit the spinal cord through the ventral roots, carrying motor impulses to skeletal muscle through a neuromuscular junction.
Special visceral efferent fibers (SVE) are the efferent nerve fibers that provide motor innervation to the muscles of the pharyngeal arches in humans, and the branchial arches in fish.
Special visceral afferent fibers (SVA) are afferent fibers that develop in association with the gastrointestinal tract. They carry the special sense of taste (gustation). The cranial nerves containing SVA fibers are the facial nerve (VII), the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX), and the vagus nerve (X). The facial nerve receives taste from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue; the glossopharyngeal from the posterior 1/3, and the vagus nerve from the epiglottis. The sensory processes, using their primary cell bodies from the inferior ganglion, send projections to the medulla, from which they travel in the tractus solitarius, later terminating at the rostral nucleus solitarius.
References
- ↑ Drake et al. (2010), Gray's Anatomy for Students, 2nd Ed., Churchill Livingstone.
- ↑ Standring, Susan, ed. (2016). "Overview of the nervous system". Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (41 ed.). Elsevier. p. 232. ISBN 978-0-7020-5230-9.