
Arizona Airways was an Arizona intrastate airline that operated 1946–1948, making substantial losses. About the time it ceased operations, it was federally certificated as a local service carrier to fly smaller routes in Arizona, New Mexico and Texas by the Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB), the now-defunct US federal agency that at the time tightly regulated almost all air transportation in the United States. However, the company was unable to resume service and ultimately, as a non-operating airline, contributed its routes and other assets to a 1 June 1950 three-way merger with Monarch Air Lines and Challenger Airlines to create the original Frontier Airlines.

The Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB) was an agency of the federal government of the United States, formed in 1940 from a split of the Civil Aeronautics Authority and abolished in 1985, that regulated aviation services and, until the establishment of the National Transportation Safety Board in 1967, conducted air accident investigations. The agency was headquartered in Washington, D.C.

Capital Airlines was a United States trunk carrier, a scheduled airline serving the eastern, southern, southeastern, and midwestern United States. Capital's headquarters were located at Washington National Airport across the Potomac river from Washington, D.C., where crew training and aircraft overhauls were also accomplished. In the 1950s Capital was the fifth largest United States domestic carrier by passenger count after the Big Four air carriers.
Marquette Airlines was a brief-lived trunk air carrier, a United States scheduled airline that operated between St. Louis to Detroit from 1938 to 1940 before merging into Transcontinental & Western Air (TWA).

Cleveland Burke Lakefront Airport is a city-owned airport on the shore of Lake Erie, in the northeast part of downtown Cleveland, Ohio, United States. It is classified as a general aviation airport and is an FAA designated reliever to Cleveland Hopkins International Airport (CLE), which is Greater Cleveland's primary airport. In 2018, based on FAA data, Burke Lakefront was the seventh busiest airport in the state of Ohio. It is named after former Cleveland mayor and U.S. senator Thomas A. Burke.

Wiggins Airways is a long-lived American aviation company that pursued many lines of business during its existence, including:

Northeast Airlines was an American trunk carrier, a scheduled airline based in Boston, Massachusetts, originally founded as Boston-Maine Airways that chiefly operated in the northeastern United States, and later to Canada, Florida, the Bahamas, Bermuda and other cities. It was notably small and unprofitable relative to other trunk carriers, being less than half the size, by revenue, than the next biggest trunk in 1971. Northeast was acquired by and merged into Delta Air Lines in August 1972.

Ohio State University Airport is a public airport six miles (10 km) northwest of downtown Columbus, in Franklin County, Ohio, United States. It is owned and operated by Ohio State University in Columbus. It is also known as the OSU Don Scott Airport, named after Donald E. Scott, an OSU alumnus who died during his training as a pilot in the United Kingdom during World War II. The airport's main entrance is located on Case Road, and is easily accessible from OH-315 and Interstate 270.

Bonanza Air Lines was a local service carrier, a US scheduled airline focused on smaller routes in the Western United States from 1949 until it merged with two other local service airlines to form Air West in 1968. Its headquarters was initially Las Vegas, Nevada, and moved to Phoenix, Arizona in 1966.

Air New England (ANE) was a US regional airline in New England during the 1970s and early 1980s. It was headquartered at Logan International Airport in the East Boston area of Boston, Massachusetts. ANE was noneconomic for most of its existence. From 1975 through its last year, 1981, ANE depended heavily on government subsidies. Depending on the year, these accounted for 17 to 25% of operating revenues, despite which the airline was generally unprofitable. ANE collapsed in the early years of US airline deregulation.

Trans Caribbean Airways (TCA) was an irregular air carrier until 1957, when it was certificated by the Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB) as an international air carrier to fly from New York City to San Juan, Puerto Rico. TCA thereafter operated as a small scheduled airline specializing in flying from New York to the Caribbean, adding a small number of additional routes over time until it was purchased by American Airlines in 1971.

Chicago and Southern Air Lines (C&S) was a United States trunk carrier, a scheduled airline that started life as Pacific Seaboard Air Lines in California and was organized on June 15, 1933. Following the move from California, the airline's headquarters were initially located in St. Louis, Missouri, and were then moved to Memphis, Tennessee, which also served as a hub for the carrier. C&S was merged into Delta Air Lines in 1953, thus providing Delta with its first international routes.

On the surface, Wright Air Lines was no different than many other many other small turboprop airlines that collapsed in the early years of the deregulated US airline industry. What set Wright apart was:
Challenger Airlines was a local service carrier, a United States scheduled airline certificated to fly smaller routes by the Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB), the now defunct US Federal agency that, at the time, tightly regulated almost all air transport. Challenger merged with two other local service carriers, Monarch Air Lines and Arizona Airways, in 1950 to form the first Frontier Airlines.

South Pacific Air Lines (SPAL) was a small US international carrier that flew from Hawaii to Tahiti from 1960 to 1963, later adding American Samoa to its small network. The airline was controlled by the Dollar family. SPAL was tiny, unable to compete with jet carriers and not able to secure sufficient route authority from the Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB) to expand. The airline transferred its routes to Pan Am at the end of 1963 and merged into Pan Am in 1964.
Florida Airways was a brief-lived United States local service carrier, also known as a feeder airline. On March 28, 1946, the US Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB), the now defunct federal agency that, at that time, tightly regulated almost all US commercial air transportation, certificated Thomas E. Gordon, dba Orlando Airlines to provide air service from Orlando, Florida to points in central and north Florida for a three-year period. Gordon beat out competition from trunk carrier National Airlines and from another local service carrier, Southern Airways, for the routes. Gordon owned a fixed-base operator at Orlando Cannon Mills Airport.
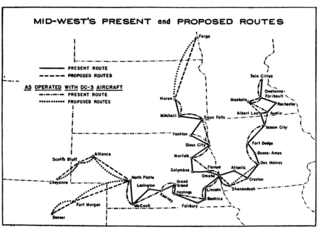
Mid-West Airlines was a Des Moines, Iowa-based local service carrier, a scheduled airline certificated by the Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB), the now-defunct Federal agency that at the time tightly regulated almost all US air transportation, to fly smaller routes in Iowa, Minnesota, Nebraska, and South Dakota. It was briefly owned by a Purdue University affiliate before being liquidated after the CAB refused to extend the airline's initial certification. It was one of three local service carriers that failed to have initial certification extended by the CAB, the other two being Florida Airways and Wiggins Airways.
Wilmington-Catalina Airline, Ltd. (WCA) was a US scheduled airline founded in 1931 by the Wrigley family of chewing gum fame to provide air transportation with amphibious aircraft on the 30-mile flight from Wilmington, California to Santa Catalina Island. In 1941, the name of the company changed to Catalina Air Transport (CAT) in anticipation of changing to land-based aircraft, but it ceased operation in June 1942 as a result of World War II. After the war, United Air Lines provided service to the island under contract to CAT until 1954. In 1955 CAT formally lost its airline certificate and the company dissolved in 1956.

United States Overseas Airlines (USOA) was a supplemental air carrier founded and controlled by Dr. Ralph Cox Jr, a dentist turned aviator, based at Cape May County Airport in Wildwood, New Jersey, where it had a substantial operation. It was one of the larger and more capable of the supplemental airlines, also known as irregular air carriers, during a period where such airlines were not simply charter carriers but could also provide a limited amount of scheduled service. USOA's operations included scheduled flights that spanned the Pacific. However, in the early 1960s USOA fell into significant financial distress leading to its 1964 shuttering by the Civil Aeronautics Board, the defunct federal agency that, at the time, controlled almost all commercial air transportation in the United States.

Mackey International (MI) was a US airline, initially flying under commuter regulations until it was certificated in 1978 as an international scheduled airline by the Civil Aeronautics Board (CAB), the now-defunct Federal agency that, until 1979, tightly regulated almost all commercial US air transportation. MI's founder was Joseph C. Mackey, who earlier founded Mackey Airlines, which flew similar routes until sold to Eastern Air Lines in 1967. Through 1978, MI flew between Florida, the Bahamas, Turks and Caicos and Haiti under a number of names, including Mackey International Air Taxi, Mackey International Air Commuter and Mackey International Airlines. However, the legal name remained Mackey International. MI grew during the early 1970s but never achieved profitability. In 1977, its offices were destroyed by a terrorist bomb.


















