
Robert Theodore Stafford was an American politician from Vermont. In his lengthy political career, he served as the 71st governor of Vermont, a United States representative, and a U.S. Senator. A Republican, Stafford was generally considered a liberal, or "Rockefeller Republican".

Frederick Holbrook was an American farmer, businessman, and Governor of the State of Vermont. Active in politics and government, first as a Whig, and later as a Republican, he was most notable for his service as the 27th governor of Vermont from 1861 to 1863.

Peter Thacher Washburn was a Vermont lawyer, politician and soldier. A veteran of the American Civil War, he served as the 31st governor of Vermont as a Republican from 1869 to 1870, and was the second Vermont Governor to die in office.

Ebenezer J. Ormsbee was an American attorney and politician from Vermont. A Republican, he served as lieutenant governor from 1884 to 1886, and governor from 1886 to 1888.

Josiah Grout Jr. was an American lawyer and politician from Vermont. A Republican, he served multiple terms in the Vermont House of Representatives and Vermont Senate, including holding the leadership post of Speaker from 1874 to 1876 and 1886 to 1890. He served as governor from 1896 to 1898.

Levi Underwood was a lawyer and politician from Vermont. Originally a Democrat, Underwood's antislavery views caused him to join the new Republican Party when it was founded. Underwood was most notable for his service as the 23rd lieutenant governor of Vermont from 1860 to 1862.

The 1852 Vermont gubernatorial election was held on Tuesday, September 7. Incumbent governor Charles K. Williams, a Whig, was not a candidate for reelection. In the voting, Whig Erastus Fairbanks received 49.2 percent, Democrat John S. Robinson 31.3 percent, and Free Soil Party nominee Lawrence Brainerd 19.6 percent.

The 1853 Vermont gubernatorial election took place on September 6. The same three candidates who ran for governor of Vermont in 1852 ran again in 1853: Whig and incumbent Erastus Fairbanks, Democratic candidate John S. Robinson, and Lawrence Brainerd, the nominee of the Free Soil Party. The results showed that Fairbanks had received 43.9 percent of the vote, with Robinson receiving 38.5 percent, and Brainerd 17.6 percent.

The 1854 Vermont gubernatorial election for governor of Vermont took place on September 5. The Whig nominee was Stephen Royce, former Chief Justice of the Vermont Supreme Court. The Democratic nominee was Merritt Clark, and Lawrence Brainerd ran as the nominee of the Free Soil Party even as he was one of the organizers of the new anti-slavery Republican Party and appeared as a Whig candidate for the Vermont Senate on the ballot in Franklin County. Whig William C. Kittredge was nominated for governor against his wishes by advocates of the Temperance movement and Democrat Horatio Needham also attracted the support of some Free Soil advocates.

The 1856 Vermont gubernatorial election for governor of Vermont was held on Tuesday, September 2. In keeping with the "Mountain Rule", incumbent Republican Stephen Royce was not a candidate for a third one-year term. The Republican nomination was won by Ryland Fletcher, the incumbent lieutenant governor. The Democratic nominee was Henry Keyes, a former member of the Vermont House of Representatives and Vermont Senate.

The 1857 Vermont gubernatorial election for governor of Vermont was held on Tuesday, September 1. In keeping with the "Mountain Rule", incumbent Republican Ryland Fletcher was a candidate for a second one-year term. The Democratic nominee was Henry Keyes, a former member of the Vermont House of Representatives and Vermont Senate who had run against Fletcher in 1856.

The 1858 Vermont gubernatorial election for governor of Vermont was held on Tuesday, September 7. In keeping with the "Mountain Rule", incumbent Republican Ryland Fletcher was not a candidate for a third one-year term. The Republican nominee was Hiland Hall. The Democratic nominee was Henry Keyes, who was also the Democratic nominee in 1856 and 1857.

The 1859 Vermont gubernatorial election for governor of Vermont was held on Tuesday, September 6. In keeping with the "Mountain Rule", incumbent Republican Hiland Hall was a candidate for a second one-year term. The Democratic nominee was John Godfrey Saxe, former State's Attorney of Chittenden County.
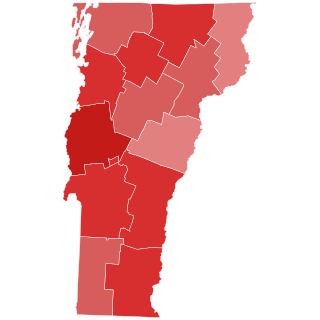
The 1860 Vermont gubernatorial election for governor of Vermont was held on Tuesday, September 4. In keeping with the "Mountain Rule", incumbent Republican Hiland Hall was not a candidate for a third one-year term. The Republican nominee was former Governor Erastus Fairbanks. With the Democratic Party fracturing nationally over the slavery issue, John Godfrey Saxe, the Democratic nominee against Hall in 1859, appeared on the ballot as a supporter of Stephen A. Douglas for president. Robert Harvey appeared as a supporter of Democratic presidential candidate John C. Breckinridge.

The 1862 Vermont gubernatorial election for governor of Vermont was held on Tuesday, September 2. In keeping with the "Mountain Rule", incumbent Republican Frederick Holbrook was a candidate for a second one-year term. The Democratic nominee was Benjamin H. Smalley, who had been on the ballot in 1861 as the gubernatorial candidate of the "Peace Democrats," who favored compromise with the Confederacy.

The 1830 Vermont gubernatorial election took place in September and October, and resulted in the election of Samuel C. Crafts to a one-year term as governor.

The 1832 Vermont gubernatorial election took place in September and October, and resulted in the election of William A. Palmer to a one-year term as governor.

The 1846 Vermont gubernatorial election took place on September 1, 1846, and resulted in the election of Whig Party candidate Horace Eaton to a one-year term as governor.

Charles N. Davenport was an American attorney, businessman, and political candidate from Vermont. A Democrat during the American Civil War and post-war era when Republicans won every election for statewide office, Davenport was an unsuccessful candidate for offices including governor and U.S. representative. He was a delegate to many local, state, and county Democratic conventions, and was the founder of the Brattleboro Reformer newspaper.





















