
The 12th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1811, to March 4, 1813, during the third and fourth years of James Madison's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the 1800 United States census. Both chambers had a Democratic-Republican majority.
These are tables of congressional delegations from Vermont to the United States Senate and United States House of Representatives.
Since Illinois became a U.S. state in 1818, it has sent congressional delegations to the United States Senate and United States House of Representatives. Each state elects two senators to serve for six years, and members of the House to two-year terms. Before becoming a state, the Illinois Territory elected a non-voting delegate at-large to Congress from 1812 to 1818.

Vermont has been represented in the United States House of Representatives by a single at-large congressional district since the 1930 census, when the state lost its second seat, obsoleting its 1st and 2nd congressional districts. There were once six districts in Vermont, all of which were eliminated after various censuses.
The 1906 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 6, 1906, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They occurred in the middle of President Theodore Roosevelt's second term. Elections were held for 386 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 60th United States Congress.
The 1902 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 4, 1902, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They occurred in the middle of President Theodore Roosevelt's first term, about a year after the assassination of William McKinley in September 1901. Elections were held for 386 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 58th United States Congress.

The 1896 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 3, 1896, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They coincided with the election of President William McKinley. Elections were held for 357 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 55th United States Congress. The size of the House increased by one seat after Utah gained statehood on January 4, 1896. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1872–73 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 4, 1872, and April 7, 1873. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 43rd United States Congress convened on December 1, 1873. They coincided with the re-election of United States President Ulysses S. Grant. The congressional reapportionment based on the 1870 United States census increased the number of House seats to 292.

The 1822–23 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 1, 1822, and August 14, 1823. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 18th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1823. They occurred during President James Monroe's second term.

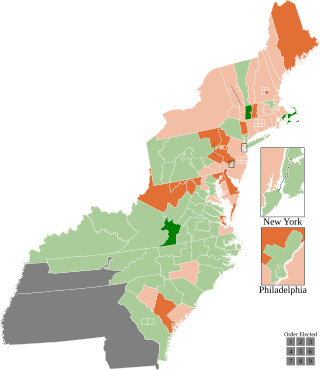
The 1812–13 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 3, 1812, and April 30, 1813. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 13th United States Congress convened on May 24, 1813. They coincided with James Madison being re-elected president.

The 1802–03 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1802 and December 14, 1803. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, either before or after the first session of the 8th United States Congress convened on October 17, 1803. They occurred during President Thomas Jefferson's first term in office.
The 1796–97 United States House of Representatives elections took place in the various states took place between August 12, 1796, and October 15, 1797. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. The size of the House increased to 106 seats after Tennessee became the 16th state to join the union. The first session of the 5th United States Congress was convened on May 15, 1797, at the proclamation of the new President of the United States, John Adams. Since Kentucky and Tennessee had not yet voted, they were unrepresented until the second session began on November 13, 1797.

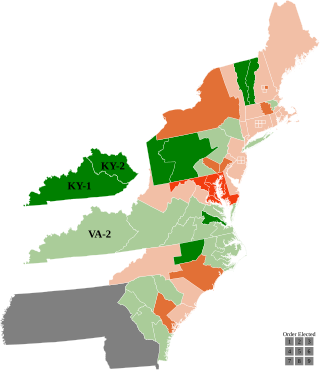
The 1792–93 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 27, 1792, and September 6, 1793. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 3rd United States Congress convened on December 2, 1793. With the addition of the new state of Kentucky's representatives, and the congressional reapportionment based on the 1790 United States census, the size of the House increased to 105 seats.
The 1790–91 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 27, 1790, and October 11, 1791. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 2nd United States Congress convened on October 24, 1791. This was the first midterm election cycle, which took place in the middle of President George Washington's first term. The size of the House increased to 67 seats after the new state of Vermont elected its first representatives.

Elections in Vermont are authorized under Chapter II of the Vermont State Constitution, articles 43–49, which establishes elections for the state level officers, cabinet, and legislature. Articles 50–53 establish the election of county-level officers.

Vermont lost one seat in reapportionment following the 1820 United States census. For the 1822 election, Vermont switched back to using a single at-large district. This would be the last year that Vermont would use an at-large district until 1932, when its representation was reduced to a single seat. Vermont elected its members September 3, 1822.

The 1810 census revealed dramatic population growth in Ohio since 1800, resulting in its representation increasing from a single Representative to six, resulting in the State being broken up into 6 districts, abolishing the at-large district. Jeremiah Morrow (Democratic-Republican), who had served since Ohio achieved statehood in 1803, retired to run for U.S. Senator, so that all six seats were open. Its elections were held October 13, 1812.
Georgia gained two seats after the 1810 census.

New Jersey kept its delegation at six seats but changed from electing its Representatives on a statewide general ticket to using three plural districts of two seats each. These districts were used only for the 1812 election, and the state returned to using a single at-large district in 1814. This was only the second time that New Jersey used districts.

Vermont elected its members September 7, 1824. Congressional districts were re-established in Vermont for the 1824 election. Vermont had used an at-large district 1812-1818 and 1822. A majority was required for election, which was not met in the 1st district, necessitating a second election December 6, 1824.













