
The 1824–25 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 7, 1824, and August 30, 1825. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 19th United States Congress convened on December 5, 1825. Elections were held for all 213 seats, representing 24 states.

The 1822–23 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 1, 1822, and August 14, 1823. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 18th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1823. They occurred during President James Monroe's second term.

The 1802–03 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1802 and December 14, 1803. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, either before or after the first session of the 8th United States Congress convened on October 17, 1803. They occurred during President Thomas Jefferson's first term in office.

The 1800–01 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1800, and August 1, 1801. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 7th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1801. They were held at the same time as the 1800 presidential election, in which Vice President Thomas Jefferson, a Democratic Republican, defeated incumbent President John Adams, a Federalist. Elections were held for all 106 seats, representing 15 states.
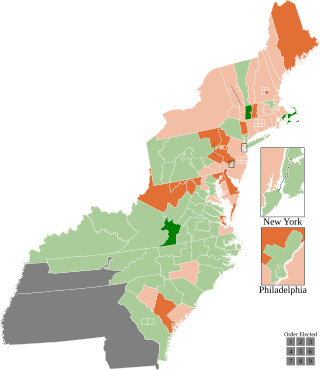
The 1796–97 United States House of Representatives elections took place in the various states took place between August 12, 1796, and October 15, 1797. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. The size of the House increased to 106 seats after Tennessee became the 16th state to join the union. The first session of the 5th United States Congress was convened on May 15, 1797, at the proclamation of the new President of the United States, John Adams. Since Kentucky and Tennessee had not yet voted, they were unrepresented until the second session began on November 13, 1797.

The 1792–93 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 27, 1792, and September 6, 1793. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 3rd United States Congress convened on December 2, 1793. With the addition of the new state of Kentucky's representatives, and the congressional reapportionment based on the 1790 United States census, the size of the House increased to 105 seats.
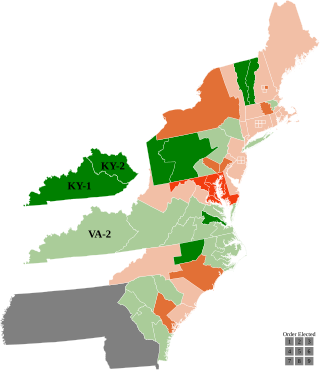
The 1790–91 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 27, 1790, and October 11, 1791. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 2nd United States Congress convened on October 24, 1791. This was the first midterm election cycle, which took place in the middle of President George Washington's first term. The size of the House increased to 67 seats after the new state of Vermont elected its first representatives.

Elections in Vermont are authorized under Chapter II of the Vermont State Constitution, articles 43–49, which establishes elections for the state level officers, cabinet, and legislature. Articles 50–53 establish the election of county-level officers.

The 1790–91 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. These U.S. Senate elections occurred during the first midterm election cycle, which took place in the middle of President George Washington's first term. As these elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1790 and 1791, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the nine senators in Class 1.

Vermont was admitted at the end of the First Congress, with the admission taking effect at the start of the Second Congress. Vermont was entitled to elect two representatives. Vermont law at the time required a majority to win an office. In the 1st district, no candidate won a majority, necessitating a run-off.

Due to Vermont's election law requiring a majority to secure a congressional seat, the 1st district required three ballots to choose a winner.

Vermont increased its apportionment from 2 seats to 4 after the 1800 census. Vermont law at the time required a majority of votes to win an office, which frequently necessitated additional ballots.

Vermont law required a majority for election, which frequently mandated runoff elections. The 2nd, and 3rd districts both required second elections in this election cycle, and the 3rd district required a third election.

Majority vote required to win, necessitating a run-off election in the 1st (Western) district.

Only 1 of the 2 Vermont incumbents were re-elected.

The 1988 United States House of Representatives election in Vermont was held on November 8, 1988. Republican nominee Peter Plympton Smith defeated Independent candidate Bernie Sanders and Democratic nominee Paul N. Poirier.

Following is a table of United States presidential elections in Vermont, ordered by year. Since its admission to statehood in 1791, Vermont has participated in every U.S. presidential election.

Only one of the two Vermont incumbents was re-elected.

The 1843 Vermont gubernatorial election was held on September 5, 1843.

The 1845 Vermont gubernatorial election was held on September 2, 1845.














