
North Lanarkshire is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland. It borders the north-east of the Glasgow City council area and contains many of Glasgow's suburbs, commuter towns, and villages. It also borders East Dunbartonshire, Falkirk, Stirling, South Lanarkshire, and West Lothian. The council area covers parts of the historic counties of Dunbartonshire, Lanarkshire, and Stirlingshire. The council is based in Motherwell.

Peterborough, or the City of Peterborough, is a local government district with city status in the ceremonial county of Cambridgeshire, England. Its council is a unitary authority, being a district council which also performs the functions of a county council. The district is named after its largest settlement, Peterborough, but also covers a wider area of outlying villages and hamlets.
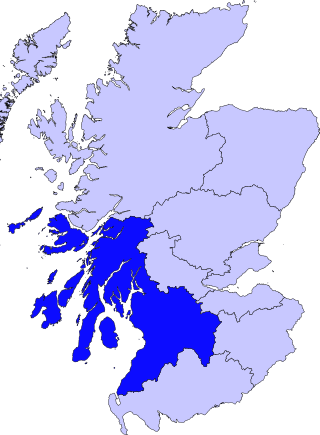
Strathclyde was one of nine former local government regions of Scotland created in 1975 by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973 and abolished in 1996 by the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994. The Strathclyde region had 19 districts. The region was named after the early medieval Kingdom of Strathclyde centred on Govan, but covered a broader geographic area than its namesake.

The Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that created the current local government structure of 32 unitary authorities covering the whole of Scotland.

Referendums in the United Kingdom are occasionally held at a national, regional or local level. Historically, national referendums are rare due to the long-standing principle of parliamentary sovereignty. There is no constitutional requirement to hold a national referendum for any purpose or on any issue however the UK Parliament is free to legislate through an Act of Parliament for a referendum to be held on any question at any time.

The North East England devolution referendum was an all postal ballot referendum that took place on 4 November 2004 throughout North East England on whether or not to establish an elected assembly for the region. Devolution referendums in the regions of Northern England were initially proposed under provisions of the Regional Assemblies (Preparations) Act 2003. Initially, three referendums were planned, but only one took place. The votes concerned the question of devolving limited political powers from the UK Parliament to elected regional assemblies in North East England, North West England and Yorkshire and the Humber respectively. Each were initially planned to be held on 4 November 2004, but on 22 July 2004 the planned referendums in North West England and in Yorkshire and the Humber were postponed, due to concerns raised about the use of postal ballots, but the referendum in North East England was allowed to continue, particularly as it was assumed that the region held the most support for the proposed devolution.

British Rail was the brand image of the nationalised railway owner and operator in Great Britain, the British Railways Board, used from 1965 until its breakup and sell-off from 1993 onwards.

Inverclyde Council is one of the 32 local authorities of Scotland, covering the Inverclyde council area. In its current form the council was created in 1996, replacing the previous Inverclyde District Council which existed from 1975 to 1996.

Scotland has elections to several bodies: the Scottish Parliament, the United Kingdom Parliament, local councils and community councils. Before the United Kingdom left the European Union, Scotland elected members to the European Parliament.

Northumbrian Water Group plc (NWG) is the holding company for several companies in the water supply, sewerage and waste water industries. Its largest subsidiary is Northumbrian Water Limited (NWL), which is one of ten companies in England and Wales that are regulated water supply and sewerage utilities. NWL is the principal water supplier in the north-east of England, where it trades as Northumbrian Water, and also supplies water to part of eastern England, as Essex and Suffolk Water. In 2011 it was acquired by Cheung Kong Infrastructure Holdings.
Public water supply and sanitation in the United Kingdom are characterized by universal access and generally good service quality. Unlike many other developed countries, the United Kingdom features diverse institutional arrangements across its constituent parts:. In England and Wales, water services are primarily provided by privatized companies, while in Scotland and Northern Ireland, these services are managed by publicly owned entities. Each region's unique approach is explored in separate articles, while this article is devoted to some common issues across the United Kingdom.
The Passenger Transport Executive (PTE) bus operations were the bus operating divisions of the passenger transport executives in the United Kingdom. In 1986 they underwent a process of deregulation and privatisation, forming some of the largest private bus companies in the UK outside London, with all being sold to their employees or management. Despite their relative size and lucrative operating areas, none of the companies survived beyond the late 1990s, with all falling into the hands of the major bus groups, who had their origins in privatised regional subsidiaries of the former National Bus Company and the Scottish Bus Group.

The water privatisation in England and Wales involved the transfer of the provision of water and wastewater services in England and Wales from the state to the private sector in 1989, through the sale of the ten regional water authorities (RWA). The potable water supply as well as the sewerage and sewage disposal functions of each RWA were transferred to privately-owned companies.
Public water supply and sanitation in Scotland is characterised by universal access and generally good service quality. Water and sewerage services are provided by a single public company, Scottish Water. The economic water industry regulator is the Water Industry Commission for Scotland. It "promotes the interests of water and sewerage customers in Scotland by making sure that householders and businesses receive a high-quality service and value for money by setting prices, monitoring Scottish Water's performance and facilitating competition in the water industry". The environmental regulator is the Scottish Environment Protection Agency. Drinking water standards and wastewater discharge standards are determined by the EU.

Public water supply and sanitation in England and Wales has been characterised by universal access and generally good service quality. In both England and Wales, water companies became privatised in 1989, although Dwr Cymru operates as a not-for-profit organisation. Whilst independent assessments place the cost of water provision in Wales and England as higher than most major countries in the EU between 1989 and 2005, the government body responsible for water regulation, together with the water companies, have claimed improvements in service quality during that period.
A regional water authority, commonly known as a water board, was one of a group of public bodies that came into existence in England and Wales in April 1974, as a result of the Water Act 1973 coming into force. This brought together in ten regional units a diverse range of bodies involved in water treatment and supply, sewage disposal, land drainage, river pollution and fisheries. They lasted until 1989, when the water industry was privatised and the water supply and sewerage and sewage disposal parts became companies and the regulatory arm formed the National Rivers Authority. Regional water authorities were also part of the Scottish water industry when three bodies covering the North, West and East of Scotland were created in 1996, to take over responsibilities for water supply and sewage treatment from the regional councils, but they only lasted until 2002, when they were replaced by the publicly owned Scottish Water.

The Electricity Act 1989 provided for the privatisation of the electricity supply industry in Great Britain, by replacing the Central Electricity Generating Board in England and Wales and by restructuring the South of Scotland Electricity Board and the North of Scotland Hydro-Electric Board. The Act also established a licensing regime and a regulator for the industry called the Office of Electricity Regulation (OFFER), which has since become the Office of Gas and Electricity Markets (OFGEM).
The politics of Glasgow, Scotland's largest city by population, are expressed in the deliberations and decisions of Glasgow City Council, in elections to the council, the Scottish Parliament and the UK Parliament.

The Water Act 1989 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reorganised the bodies responsible for all aspects of water within England and Wales. Whereas previous legislation, particularly the Water Act 1973, had focused on providing a single unifying body with responsibility for all water-related functions within a river basin or series of river basins, this legislation divided those functions up again, with water supply, sewerage and sewage disposal being controlled by private companies, and the river management, land drainage and pollution functions becoming the responsibility of the National Rivers Authority.
The sixth and last election to Tayside Regional Council was held on 5 May 1994 as part of the wider 1994 Scottish regional elections. The election saw the Scottish National Party overtaking Labour to become the council's largest party, and following the election the SNP formed a minority administration. The Conservatives lost 10 seats and became the third largest party. 8 weeks later, leader of the council Lena Graham resigned 'for personal reasons' and Ewan Dow took over as council leader.













