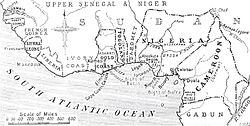
The Adubi War (known locally as Ogun Adubi or Egba Uprising) was a conflict in June and July 1918 in the British Colony and Protectorate of Nigeria ostensibly because of the imposition of colonial taxation. [1] Direct taxes were introduced by the colonial government along with existing forced labour obligations and fees. On 7 June, the British arrested 70 Egba chiefs and issued an ultimatum that resisters should lay down their arms, pay the taxes and obey the local leadership.