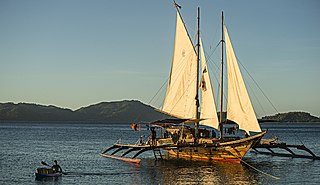A ship burial or boat grave is a burial in which a ship or boat is used either as the tomb for the dead and the grave goods, or as a part of the grave goods itself. If the ship is very small, it is called a boat grave. This style of burial was practiced by various seafaring cultures in Asia and Europe. Notable ship burial practices include those by the Germanic peoples, particularly by Viking Age Norsemen, as well as the pre-colonial ship burials described in the Boxer Codex in the Philippines.

A pump boat is an outrigger canoe powered by a small gasoline or diesel engine. Smaller pump boats might be powered by the sort of small single-cylinder engine used to drive a water pump. Larger ones are often powered by recycled automobile engines.

Okir, also spelled okil or ukkil, is the term for rectilinear and curvilinear plant-based designs and folk motifs that can be usually found among the Moro and Lumad people of the Southern Philippines, as well as parts of Sabah. It is particularly associated with the artwork of the Maranao and Sama (Badjao) tribes, although it can also be found to a lesser extent among the Maguindanao, Iranun, Tausug, Yakan, and Lumad groups. The design elements vary among these ethnic groups, with the greatest refinement being found among the Maranao.

The Sama-Bajau include several Austronesian ethnic groups of Maritime Southeast Asia. The name collectively refers to related people who usually call themselves the Sama or Samah ; or are known by the exonym Bajau. They usually live a seaborne lifestyle and use small wooden sailing vessels such as the perahu, djenging (balutu), lepa, and vinta (pilang). Some Sama-Bajau groups native to Sabah are also known for their traditional horse culture.

The vinta is a traditional outrigger boat from the Philippine island of Mindanao. The boats are made by Sama-Bajau, Tausug and Yakan peoples living in the Sulu Archipelago, Zamboanga peninsula, and southern Mindanao. Vinta are characterized by their colorful rectangular lug sails (bukay) and bifurcated prows and sterns, which resemble the gaping mouth of a crocodile. Vinta are used as fishing vessels, cargo ships, and houseboats. Smaller undecorated versions of the vinta used for fishing are known as tondaan.

Pangalay is the traditional "fingernail" dance of the Tausūg people of the Sulu Archipelago and eastern coast Bajau of Sabah.

The Sama–Bajaw languages are a well-established group of languages spoken by the Sama-Bajau peoples of the Philippines, Indonesia and Malaysia.
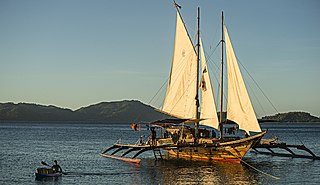
A balangay, or barangay, is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines and were used largely as trading ships up until the colonial era. The oldest known balangay are the Butuan boats, which have been carbon-dated to 320 AD and were recovered from several sites in Butuan, Agusan del Norte.

Lepa, also known as lipa or lepa-lepa, are indigenous ships of the Sama-Bajau people in the Philippines and Malaysia. They were traditionally used as houseboats by the seagoing Sama Dilaut. Since most Sama have abandoned exclusive sea-living, modern lepa are instead used as fishing boats and cargo vessels.

Bangka are various native watercraft of the Philippines. It originally referred to small double-outrigger dugout canoes used in rivers and shallow coastal waters, but since the 18th century, it has expanded to include larger lashed-lug ships, with or without outriggers. Though the term used is the same throughout the Philippines, "bangka" can refer to a very diverse range of boats specific to different regions. Bangka was also spelled as banca, panca, or panga in Spanish. It is also known archaically as sakayan.
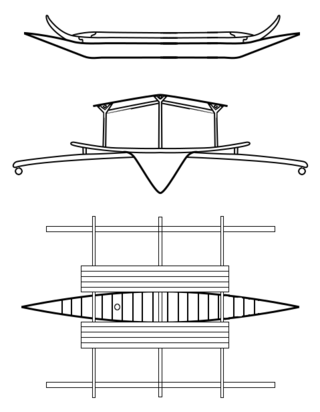
Djenging is a type of large double-outrigger plank boat built by the Sama-Bajau people of the Philippines. It is typically used as a houseboat, though it can be converted to a sailing ship. It was the original type of houseboat used by the Sama-Bajau before it was largely replaced by the lepa after World War II. Larger versions of djenging were also known as balutu or kubu, often elaborately carved with bifurcated extensions on the prow and stern.

Birau, is a type of small dugout canoe of the Sama-Bajau people of the Philippines. They are made from a single log hollowed into a canoe with a rounded bottom. The prow and stern of the vessel usually has knob-like protrusions. A smaller wider variant without these knobs is known as bitok. Birau are usually around 1.5 to 4.5 m long. They are sometimes equipped with two outrigger floats. They are very similar to the buggoh, differing only in that the prow and the stern of the birau slope inward.

Junkun, is a type of small dugout canoe of the Sama-Bajau people of the Philippines. They are usually made from a single log, though a single plank can be added to the sides, and longer boats can include ribs that support a deck made of planks. They are around 2.5 to 8 m long. They have knob-like protrusions on the tip of the prow and the stern, which also sweep upwards from the waterline. They are sometimes equipped with double outriggers. They are used for fishing and short-distance travel.
Ontang is a type of raft of the Sama-Bajau people of the Philippines. They resemble a miniature catamaran, with two bamboo floats about 1 m (3.3 ft) long connected by two bow-shaped booms. A platform made split bamboo is built on top of the booms. Ontang can be used for fishing, but they can also hold lanterns during night-time fishing. They are typically towed behind Sama-Bajau houseboats during travel, with the towing line commonly strung with baited fish hooks.
Bangka anak-anak are very small dugout canoes among the Sama-Bajau people of the Philippines. They are typically made by Sama-Bajau fathers for their children and are patterned after the larger Sama-Bajau dugout canoes. They can be used for transportation between the Sama-Bajau houseboats, but are more commonly used for playing. They are typically no longer than around 1.5 m (4.9 ft) long. Children as young as three or four can use these boats, which allows them to learn valuable maritime skills.
Awang are traditional dugout canoes of the Maranao and Maguindanao people in the Philippines. They are used primarily in Lake Lanao, the Pulangi River, and the Liguasan Marsh for fishing or for transporting goods. They have long low hulls that are carved from single trunks of lauan and apitong trees. They have no outriggers but have a single sail or a paddle. The prow and the stern are commonly elaborately decorated with painted designs and okir carvings, usually of the piyako and potiyok a rabong motifs. Some awang are also decorated with a carved prow extension known as the panolong or kalandapon.

Tiririt, also known as taririt or papet, is a type of small dinghy of the Sama-Bajau and Tausug people of the Philippines. It is commonly motorized. It is usually carried aboard larger motherships and assists in transporting passenger and cargo to the shore, as well as in towing the boat to port. However, it can also be used as a small inter-island transport. It is roughly leaf-shaped in outline with a distinctive hump-backed side-profile. The prow and stern can sometimes rise up into arcs. It normally has no outriggers.
Tempel, also known as temper or kurikong, is a type of wooden motorized boat used by the Yakan, Tausug, and Sama-Bajau people of the Philippines. It is commonly used in the Sulu Archipelago and the Zamboanga Peninsula. It is around 48 ft (15 m) long, 11 ft (3.4 m) deep, and around 5 ft (1.5 m) at the widest point. It has a V-shaped cross-section at the front, though it is flat-bottomed on the stern for stability. It is commonly made from thick marine lauan plywood attached to ribs and caulked with epoxy. Tempel can also be made from fiberglass, though wood is preferred. Tempel are larger than the junkung but smaller than the kumpit. They are usually used as cargo ships.
Junkung, also spelled jungkung or jungkong, is a small wooden motorized boat used by Tausug, Sama-Bajau, and Yakan people of the Philippines. It is a fast cargo ship and is commonly used as a smuggling vessel in the maritime borders of the Philippines, Sabah, Malaysia and Eastern Indonesia. They are also sometimes used by pirates and Abu Sayyaf terrorists in and around the Sulu Sea.

Lashed-lug boats are built using a long-standing traditional boat-building technique found in Maritime Southeast Asia. It dates back at least to early in the first millennium CE and its use has continued into the 20th century. Lashed lug construction is closely associated with Austronesian maritime activity.