
A jukung or kano, also known as cadik is a small wooden Indonesian outrigger canoe. It is a traditional fishing boat, but newer uses include "Jukung Dives", using the boat as a vehicle for small groups of SCUBA divers.

Literally, the word pinisi refers to a type of rigging of Indonesian sailing vessels. A pinisi carries seven to eight sails on two masts, arranged like a gaff-ketch with what is called 'standing gaffs' — i.e., unlike most Western ships using such a rig, the two main sails are not opened by raising the spars they are attached to, but the sails are 'pulled out' like curtains along the gaffs which are fixed at around the centre of the masts.

The term lambo or lamba refer to two types of traditional boats from Indonesia.

A Sandeq is a type of outrigger sailboat or trimaran used by the Mandarese people for fishing and as a means of transportation between islands. The size of Sandeq varies, with hulls ranging from 5 to 15 metres long and 0.5 to 1.5 metres wide. Its carrying capacity ranges from a few hundred kilograms to over 2 tons. The sleek shape of the Sandeq makes it more agile and faster than other sailboats. The name of the vessel comes from a word in the Mandar language that means pointy, referring to the bow's shape.

Padewakang were traditional boats used by the Bugis, Mandar, and Makassar people of South Sulawesi. Padewakang were used for long distance voyages serving the south Sulawesi kingdoms.

Pencalang is a traditional merchant ship from Nusantara. Historically it was called as pantchiallang or pantjalang. It was originally built by Malay people from the area of Riau and the Malay Peninsula, but has been copied by Javanese shipwrights. By the end of the 17th century this ship has been built by Javanese and Chinese shipbuilders in and around Rembang. However it was a popular choice for Balinese skippers followed by Sulawesian skippers.

A chialoup was a type of sloop used in the East Indies, a combination of western (Dutch) and Nusantaran (Indonesian) technologies and techniques. Many of these "boat-ships" were produced by VOC shipwrights in Rembang and Juwana, where the majority of the workers were local Javanese. Chialoups were used by the Dutch East India Company and private merchant-sailors of western and Nusantaran origin.

Toop is a type of boat-ship produced in East Indies. Appeared at the end of the 18th century, and built in local shipyards, this type of boat is one of the results of the incorporation of 'Western' and 'Nusantaran' technologies that began in the shipyards of the 17th and 18th European trading companies. This type of boat is commonly used for long-distance shipping. In the first half of the 19th century, this was the most common type of boat used by sailors and traders in Nusantara. Majority of toop is owned by merchants from the western area of Nusantara.

Patorani is a traditional fishing boat from Makassar, Indonesia. It is used by Macassan people for fishing, transport, and trading since at least 17th century A.D. Historically this type of boat was used by Gowa Sultanate as war boat.

Golekan is a type of traditional boat from Madura, Indonesia. They once plied as far as Singapore, where they are referred to as Madurese traders. In the present this type of boat is only known locally, especially near Bangkalan in Western Madura and around the Kangean islands.

Leti leti is a type of traditional transport vessel from East Madura, Indonesia, especially from the administrative district of Sumenep. The leti leti is a recent development, the hull form and sail were developed in the 19th century. In 1979 sailing leti leti was numbered about 1000, but this was reduced in the next decades when more modern, motorized vessel appeared.

Lis-alis is a type of traditional boat of Madura, Indonesia. Lis-alis usually present in canals that provide salt evaporation service in southern part of Madura and around Surabaya. Until the present, lis-alis remained overwhelmingly popular as a fishing craft in Bangkalan and Sukolilo, while a larger version, the kroman, has been used in this area for at least a century for inshore transport work.

Janggolan refers to two different type of perahu from Indonesia. One is from Madura, and the other from Bali. The Madurese janggolan is a type of indigenously constructed boat, meanwhile Balinese janggolan is an indigenous boat with western-styled hull construction.

Palari is a type of Indonesian sailing vessel from South Sulawesi. It was mainly used by the people of Ara and Lemo Lemo, for transporting goods and people. This vessel is rigged with pinisi rig, which often makes it better known as "Pinisi" instead of its name. In Singapore, palari is known as "Makassartrader".

Pajala is a type of traditional perahu from western South Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is used mainly for fishing, but in the present it's a Bugis/Makassar name for small to medium-sized boat hull.

A bago is a traditional boat built by the Mandar people of Sulawesi, Indonesia. The hull is of the pajala-type, lightly built and allowing for shallow displacement. The boat is long, with the mast only making up a quarter of its length. A bago can be readily identified as Mandarese boat by its rudderpost style. Smaller-sized bagos are often used as fishing boats from which fishermen cast their nets. The Mandar people prefer using a bago over an outrigger canoe.
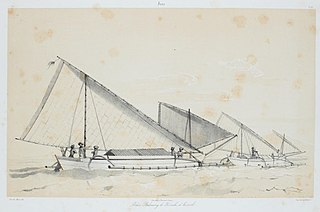
Paduwang is a traditional double-outrigger vessel from Madura, Indonesia. It is built with planks instead of single log, and used for fishing, trading and transport of people and goods near Madura island. In the 19th century, Paduwang was a popular fishing craft in East Java.

Bagan or bagang is a fishing instrument that uses nets and lights so that it can be used for light fishing, originating from Indonesia. Bagan is floated out to the sea to catch fishes, squids, and shrimps, and remain in the sea for several days or even months. The catch would be transported to land using other boats.

Perahu payang or simply payang is a traditional Malay open fishing boat. They are usually found in Terengganu, and to a lesser extent, Kelantan, Pahang, and Johor coasts. A few examples normally come down to Singapore to operate during the period of the north-east monsoon in the South China Sea.

A lancang is a type of sailing ship from Maritime Southeast Asia. It is used as warship, lighter, and as royal ship, particularly used by the people of Sumatran east coast, but can also be found in the coast of Kalimantan.






























