In the game of chess, an endgame study, or just study, is a composed position—that is, one that has been made up rather than played in an actual game—presented as a sort of puzzle, in which the aim of the solver is to find the essentially unique way for one side to win or draw, as stipulated, against any moves the other side plays. If the study does not end in a mate or stalemate, it should be obvious that the game is either won or drawn, and White can have a selection of many different moves. There is no limit to the number of moves which are allowed to achieve the win; this distinguishes studies from the genre of direct mate problems. Such problems also differ qualitatively from the very common genre of tactical puzzles based around the middlegame, often based on an actual game, where a decisive tactic must be found.
Stalemate is a situation in the game of chess where the player whose turn it is to move is not in check and has no legal move. Stalemate results in a draw. During the endgame, stalemate is a resource that can enable the player with the inferior position to draw the game rather than lose. In more complex positions, stalemate is much rarer, usually taking the form of a swindle that succeeds only if the superior side is inattentive. Stalemate is also a common theme in endgame studies and other chess problems.

Ulf Andersson is a leading Swedish chess player. FIDE awarded him the International Master title in 1970 and the Grandmaster title in 1972.

Kasparov versus the World was a game of chess played in 1999 over the Internet. It was a consultation game, in which a World Team of thousands decided each move for the black pieces by plurality vote, while Garry Kasparov conducted the white pieces by himself. More than 50,000 people from over 75 countries participated in the game.
In chess, a passed pawn is a pawn with no opposing pawns to prevent it from advancing to the eighth rank; i.e. there are no opposing pawns in front of it on either the same file or adjacent files. A passed pawn is sometimes colloquially called a passer. Passed pawns are advantageous because only the opponent's pieces can stop them from promoting.

In chess, promotion is the replacement of a pawn with a new queen, rook, bishop, or knight of the same color. It occurs immediately when the pawn moves to its last rank, with the player choosing the piece of promotion. The new piece does not have to be a previously captured piece. Promotion is mandatory; the pawn cannot remain as a pawn.
In chess, a fortress is an endgame drawing technique in which the side behind in material sets up a zone of protection that the opponent cannot penetrate. This might involve keeping the enemy king out of one's position, or a zone the enemy cannot force one out of. An elementary fortress is a theoretically drawn position with reduced material in which a passive defense will maintain the draw.
In chess, a desperado piece is a piece that is either en prise or trapped, but captures an enemy piece before it is itself captured, or is used as a sacrifice that will result in stalemate if it is captured. The former case can arise in a situation where both sides have hanging pieces, in which case these pieces are used to win material prior to being captured. A desperado in the latter case is usually a rook or a queen; such a piece is sometimes also called crazy or mad.
The chess endgame of a queen versus pawn is usually an easy win for the side with the queen. However, if the pawn has advanced to its seventh rank it has possibilities of reaching a draw, and there are some drawn positions with the pawn on the sixth rank. This endgame arises most often from a race of pawns to promote.

In chess, a swindle is a ruse by which players in a losing position trick their opponent and thereby achieve a win or draw instead of the expected loss. It may also refer more generally to obtaining a win or draw from a clearly losing position. I. A. Horowitz and Fred Reinfeld distinguish among "traps", "pitfalls", and "swindles". In their terminology, a "trap" refers to a situation where players go wrong through their own efforts. In a "pitfall", the beneficiary of the pitfall plays an active role, creating a situation where a plausible move by the opponent will turn out badly. A "swindle" is a pitfall adopted by a player who has a clearly lost game. Horowitz and Reinfeld observe that swindles, "though ignored in virtually all chess books", "play an enormously important role in over-the-board chess, and decide the fate of countless games".
A pawnless chess endgame is a chess endgame in which only a few pieces remain, and no pawns. The basic checkmates are types of pawnless endgames. Endgames without pawns do not occur very often in practice except for the basic checkmates of king and queen versus king, king and rook versus king, and queen versus rook. Other cases that occur occasionally are (1) a rook and minor piece versus a rook and (2) a rook versus a minor piece, especially if the minor piece is a bishop.

Deep Blue versus Garry Kasparov was a pair of six-game chess matches between the world chess champion Garry Kasparov and an IBM supercomputer called Deep Blue. The first match was played in Philadelphia in 1996 and won by Kasparov by 4–2. A rematch was played in New York City in 1997 and won by Deep Blue by 3½–2½. The second match was the first defeat of a reigning world chess champion by a computer under tournament conditions, and was the subject of a documentary film, Game Over: Kasparov and the Machine.

Nikalai (Nikolay) Dmitrievich Grigoriev was a Russian chess player and a composer of endgame studies. He was born on 14 August 1895 in Moscow, and he died there in 1938.

The World Chess Championship 1889 was the second official World Chess Championship, and was between Wilhelm Steinitz and Mikhail Chigorin. It took place in Havana, Cuba. Steinitz successfully defended his world title, by being the first of the two players to reach 10½. He won the match 10½-6½.

The 1960 World Chess Championship was played between Mikhail Botvinnik and Mikhail Tal in Moscow from March 15 to May 7, 1960. Botvinnik was the reigning champion, after winning the World Chess Championship 1958, while Tal qualified by winning the Candidates tournament. Tal won by a margin of 4 points.
The queen and pawn versus queen endgame is a chess endgame in which both sides have a queen and one side has a pawn, which one tries to promote. It is very complicated and difficult to play. Cross-checks are often used as a device to win the game by forcing the exchange of queens. It is almost always a draw if the defending king is in front of the pawn.

Chess is a poem written by Jan Kochanowski, first published in 1564 or 1565. Inspired by Marco Girolamo Vida's Scacchia Ludus, it is a narrative poetry work that describes a game of chess between two men, Fiedor and Borzuj, who fight for the right to marry Anna, princess of Denmark. The poem anthropomorphises the pieces, presenting the game as a battle between two armies, in a style reminiscent of battle scenes in the works of Homer and Virgil.
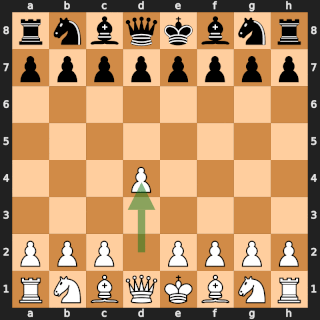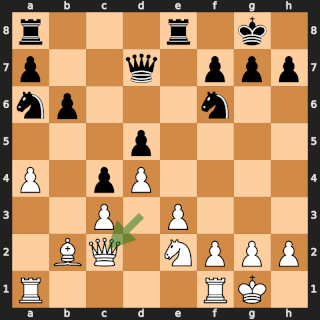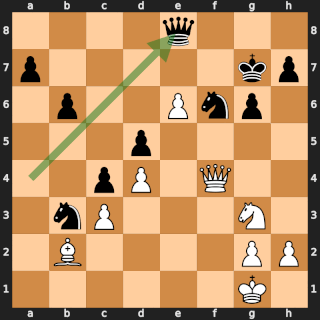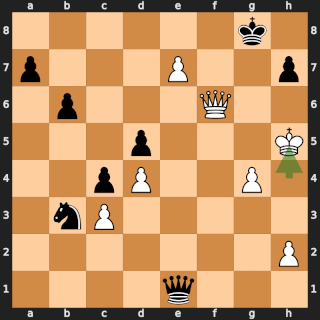
In Rotterdam on 22 November 1938, then future World Chess Champion Mikhail Botvinnik defeated former World Champion José Raúl Capablanca in round 11 of the AVRO tournament in one of the most famous games in chess history. Garry Kasparov wrote:
[...] Botvinnik played what was altogether the "game of his life" against Capablanca. It was not just that it was judged the most brilliant in the tournament and to be worth two first prizes, but it was even suggested that, by analogy with the "immortal" and "evergreen" games, it should be called "peerless" or "classical"!
The 14th season of the Top Chess Engine Championship took place between 17 November 2018 and 24 February 2019. Stockfish was the defending champion, having defeated Komodo in the previous season's superfinal.
The staircase maneuver is a tactical motif which tends to occur in queen and pawn endgames, where the defender has advanced pawns on the seventh rank. The tactic employs the idea of alternation, with the attacking queen alternating between black and white squares until it reaches an open file, where the opponent's queening square is not controlled by one of the opponent's pawns. Thus the attacking queen alternates between a series of pins and checks until it delivers the final mate.














