
Noodle soup refers to a variety of soups with noodles and other ingredients served in a light broth. Noodle soup is a common dish across East Asia, Southeast Asia and the Himalayan states of South Asia. Various types of noodles are used, such as rice noodles, wheat noodles and egg noodles.
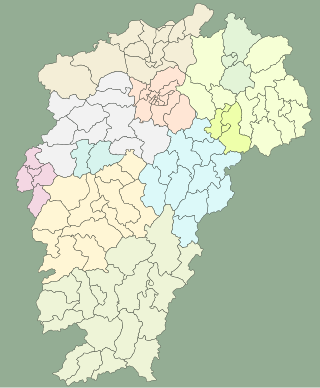
Jiangxi cuisine, also known as Gan cuisine, is a style of Chinese cuisine derived from the native cooking styles of Jiangxi province in southern China. According to the East China Travel Guide published in 1983, Jiangxi cuisine has its unique taste which can be described in four Chinese idioms: 原汁原味(aim to bring out the own flavor of the cooking material),油厚不腻(dishes contained a significant amount of oil but the taste are not greasy),口味浓厚(dishes have really thick taste),咸鲜兼辣(always come with spicy solid, salty flavor). Jiangxi cuisine is widely popular within the ordinary family because most of the notable dishes from Jiangxi cuisine are the extension of homely dishes with solid local flavor.

White cut chicken or white sliced chicken is a type of siu mei. Unlike most other meats in the siu mei category, this particular dish is not roasted, but poached. The dish is common to the cultures of Southern China, including Guangdong, Fujian and Hong Kong. In Hawaii, this popular dish is known as cold ginger chicken.

Kyrgyz cuisine is the cuisine of the Kyrgyz, who comprise a majority of the population of Kyrgyzstan. The cuisine is similar in many aspects to that of their neighbors.

Uyghur cuisine is the cuisine of the Uyghur people, which are mainly situated in the autonomous region of Xinjiang.

Javanese cuisine is the cuisine of Javanese people, a major ethnic group in Indonesia, more precisely the province of Central Java, Yogyakarta and East Java.

Mixian is a type of rice noodle from Yunnan Province, China. These noodles are typically distinguished by their round shape, moderate thickness, and smooth, silky texture. They are normally used fresh and are commonly seen in stir-fry recipes, often served with rich broths and sauces.
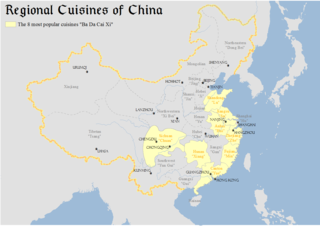
Chinese regional cuisines are amongst the many different cuisines found in different provinces and prefectures of China as well as from larger overseas Chinese communities.

Dandan noodles is a Chinese noodle dish originating from Sichuan cuisine. It consists of a spicy sauce, usually containing pickled vegetables such as zha cai or ya cai, as well as chili oil, Sichuan pepper, minced pork, and scallions served over noodles. The dish can either be served dry or as a noodle soup.

Hot and sour soup is a popular example of Chinese cuisine. Although it is said to be originated in Sichuan, this is actually a variant of hulatang or "pepper hot soup" (胡辣汤) with added vinegar to enhance the sourness. This variation is found in Henan province, and in Henan cuisine itself. Also popular in Southeast Asia, India, Pakistan and the United States, it is a flexible soup which allows ingredients to be substituted or added depending on availability. For example, the American-Chinese version can be thicker as it commonly includes corn starch, while in Japan, sake is often added.

Kung Pao chicken, also transcribed Gong Bao or Kung Po, is a spicy, stir-fried Chinese dish made with cubes of cooked chicken, peanuts, vegetables and chili peppers, and Sichuan peppercorns. From its origins in Sichuan cuisine, the dish's popularity has spread throughout China, spawning a number of regional variations—some of which are less spicy than the classic version.

Mala is a spicy and numbing seasoning made from Sichuan peppercorn and chilli. Most commonly, mala is made into a sauce by simmering it in oil and other spices. Characteristic of Sichuan cuisine, particularly Chongqing cuisine, it has become one of the most popular ingredients in Chinese cuisine, spawning many regional variants.

Hot pot or hotpot, also known as steamboat, is a dish of soup/stock kept simmering in a pot by a heat source on the table, accompanied by an array of raw meats, vegetables and soy-based foods which diners quickly cook by dip-boiling in the broth.

A stew is a combination of solid food ingredients that have been cooked in liquid and served in the resultant gravy. Ingredients can include any combination of vegetables and may include meat, especially tougher meats suitable for slow-cooking, such as beef, pork, venison, rabbit, lamb, poultry, sausages, and seafood. While water can be used as the stew-cooking liquid, stock is also common. A small amount of red wine or other alcohol is sometimes added for flavour. Seasonings and flavourings may also be added. Stews are typically cooked at a relatively low temperature, allowing flavours to mingle.

Hot and sour noodles is a dish which comes from Sichuan, China and is a popular part of Sichuan cuisine. The noodles are made from starch derived from peas, potato, sweet potato, or rice.

Laghman is a dish of meat, vegetables and pulled noodles from Uyghur cuisine and Central Asian cuisine. In Chinese, the noodle is known as latiaozi or bànmiàn.

Indonesian noodles are a significant aspect of Indonesian cuisine which is itself very diverse. Indonesian cuisine recognizes many types of noodles, with each region of the country often developing its own distinct recipes.

















