
A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. A speaker system, also often simply referred to as a speaker or loudspeaker, comprises one or more such speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections possibly including a crossover network. The speaker driver can be viewed as a linear motor attached to a diaphragm which couples that motor's movement to motion of air, that is, sound. An audio signal, typically from a microphone, recording, or radio broadcast, is amplified electronically to a power level capable of driving that motor in order to reproduce the sound corresponding to the original unamplified electronic signal. This is thus the opposite function to the microphone; indeed the dynamic speaker driver, by far the most common type, is a linear motor in the same basic configuration as the dynamic microphone which uses such a motor in reverse, as a generator.
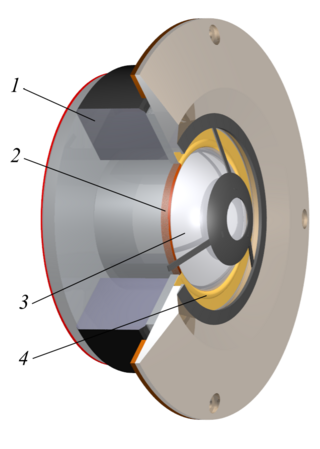
A tweeter or treble speaker is a special type of loudspeaker that is designed to produce high audio frequencies, typically deliver high frequencies up to 100 kHz. The name is derived from the high pitched sounds made by some birds (tweets), especially in contrast to the low woofs made by many dogs, after which low-frequency drivers are named (woofers).
A woofer or bass speaker is a technical term for a loudspeaker driver designed to produce low frequency sounds, typically from 20 Hz up to 80 Hz. The name is from the onomatopoeic English word for a dog's bark, "woof". The most common design for a woofer is the electrodynamic driver, which typically uses a stiff paper cone, driven by a voice coil surrounded by a magnetic field.

JBL is an American audio equipment manufacturer headquartered in Los Angeles, California, United States. JBL serves the customer home and professional market. The professional market includes studios, installed/tour/portable sound, cars, music production, DJ, cinema markets, etc. JBL is owned by Harman International, itself a subsidiary of Samsung Electronics.
Altec Lansing, Inc. is an American audio electronics company founded in 1927. Their primary products are loudspeakers and associated audio electronics for professional, home, automotive and multimedia applications.

A voice coil is the coil of wire attached to the apex of a loudspeaker cone. It provides the motive force to the cone by the reaction of a magnetic field to the current passing through it.
Celestion is a British designer and exporter of professional loudspeakers.
Wharfedale is a Chinese audio equipment manufacturer best known for loudspeakers. It is currently part of the International Audio Group.

Magnepan is a private high-end audio loudspeaker manufacturer in White Bear Lake, Minnesota, United States. Their loudspeaker technology was conceived and implemented by engineer Jim Winey in 1969.

A ferrite is a ceramic material made by mixing and firing iron(III) oxide with one or more additional metallic elements, such as strontium, barium, manganese, nickel, and zinc. They are ferrimagnetic, meaning they are attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetized to become permanent magnets. Unlike other ferromagnetic materials, most ferrites are not electrically conductive, making them useful in applications like magnetic cores for transformers to suppress eddy currents. Ferrites can be divided into two families based on their resistance to being demagnetized.
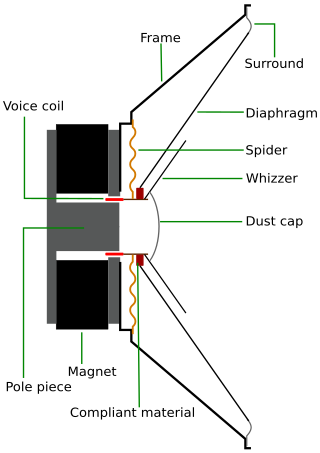
A full-range loudspeaker drive unit is defined as a driver which reproduces as much of the audible frequency range as possible, within the limitations imposed by the physical constraints of a specific design. The frequency range of these drivers is maximized through the use of a whizzer cone and other means. Most single driver systems, such as those in radios, or small computer speaker designs, cannot reproduce all of the audible frequencies or the entire audible audio range.

Infinity Systems is an American manufacturer of loudspeakers founded in Los Angeles in 1968 and headquartered in Stamford, Connecticut. Since 1983, Infinity has been part of Harman International Industries, which became a subsidiary of Samsung Electronics in 2017.
Jensen Loudspeakers is a company that manufactures speakers in many different models and sizes. Originally located in Chicago, Illinois, the company built a reputation during the 50s and 60s providing speakers used mainly in guitar and bass amplifiers. Although the American company is long out of business, "reissue" guitar speakers are currently made in Italy by SICA Altoparlanti and distributed in the United States by CE Distribution. Jensen and Rola were, for a time both under common ownership, and shared various design similarities. Their 8" and 15" baskets appeared to utilize the same tooling. Rola locations took over Jensen product manufacturing when the Chicago plant closed.
Uni-ball and Uni are brands of pens and pencils, made by the Mitsubishi Pencil Company Limited of Japan. The brand was introduced in 1979 as a rollerball pen model, then expanding to the rest of Mitsubishi Pencil products.

Plasma speakers or ionophones are a form of loudspeaker which varies air pressure via an electrical plasma instead of a solid diaphragm. The plasma arc heats the surrounding air causing it to expand. Varying the electrical signal that drives the plasma and connected to the output of an audio amplifier, the plasma size varies which in turn varies the expansion of the surrounding air creating sound waves.
Technics is a Japanese brand name of Panasonic for audio equipment. Since 1965, Panasonic has produced a variety of hi-fi and audio products under the brand name, such as turntables, amplifiers, radio receivers, tape recorders, CD players, speakers, and digital pianos. Technics products were available for sale in various countries. The brand was originally conceived as a line of high-end audio equipment to compete against brands such as Nakamichi.

An electrodynamic speaker driver, often called simply a speaker driver when the type is implicit, is an individual transducer that converts an electrical audio signal to sound waves. While the term is sometimes used interchangeably with the term speaker (loudspeaker), it is usually applied to specialized transducers which reproduce only a portion of the audible frequency range. For high fidelity reproduction of sound, multiple loudspeakers are often mounted in the same enclosure, each reproducing a different part of the audible frequency range. In this case the individual speakers are referred to as drivers and the entire unit is called a loudspeaker. Drivers made for reproducing high audio frequencies are called tweeters, those for middle frequencies are called mid-range drivers, and those for low frequencies are called woofers, while those for very low bass range are subwoofers. Less common types of drivers are supertweeters and rotary woofers.

Focal-JMlab is a French company that has been designing and selling high fidelity audio systems since 1979. Based in Saint-Étienne, the company manufactures loudspeakers for the home, speaker drivers for automobiles, headphones, and professional monitor loudspeakers.

DUPLEX was the trade name given by Altec Lansing to its line of coaxial loudspeakers, beginning with the first model 601 in 1943. However, the name was most commonly associated with the subsequent model 604 which was a seminal loudspeaker that became a milestone in loudspeaker development. Well over a dozen different models carried the Duplex name over a near 50-year period. The vast majority consisted of a high frequency (HF) compression driver mounted to the back of a large diameter paper cone low frequency (LF) driver. However, there were also a few models with small diameter LF cones and direct radiator tweeters.
Vifa is a Danish consumer electronics company that designs and manufactures audio products. The brand name stems from "Videbæk Højttalerfabrik", originally founded in 1933 by N.C.Madsen, which manufactured electrodynamic loudspeaker drive units in the town of Videbæk. From 1981, operating under the acronym Vifa, the company quickly grew to become a respected OEM supplier for many high-end loudspeaker brands, until production seized in 2009.











