
Chelidae is one of three living families of the turtle/tortoise suborder Pleurodira, and are commonly called Austro-South American side-neck turtles. The family is distributed in Australia, New Guinea, parts of Indonesia, and throughout most of South America. It is a large family of turtles with a significant fossil history dating back to the Cretaceous. The family is entirely Gondwanan in origin, with no members found outside Gondwana, either in the present day or as a fossil.

Irwin's turtle is a rare species of freshwater turtle in the family Chelidae. The species is endemic to Australia, originating from the lower region of the Burdekin River area.
The Namoi River snapping turtle, also commonly known as Bell's turtle, the Namoi River elseya, or Bell's saw-shelled turtle, is a species of turtle in the family Chelidae. The species is endemic to New South Wales, Australia.

Elseya is a genus of large side-necked turtles, commonly known as Australian snapping turtles, in the family Chelidae. Species in the genus Elseya are found in river systems in northern and northeastern Australia and throughout the river systems of New Guinea. They are identified by the presence of alveolar ridges on the triturating surfaces of the mouth and the presence of a complex bridge strut.

Elseya branderhorsti, also known commonly as Branderhorst's turtle and Branderhorst's snapping turtle, is a species of freshwater turtle in the family Chelidae. The species is endemic to southern New Guinea, in West Papua Indonesia and Western Province of Papua New Guinea. Until recently it has been a confusing species due to its lost holotype and its sympatry with another, undescribed, species. E. branderhorsti is currently listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN RedList in part due to its vulnerability to the Asian turtle trade.

The Bellinger River turtle, is a species of turtle in the family Chelidae. The species is of moderate size, and is endemic to Australia with a highly restricted distribution to the small coastal drainage of the Bellinger River in New South Wales. In the past the species was considered locally abundant. The species' preferred habitat is the deeper pools of the clear-water upstream reaches of the river, where water flows continuously in most months over a bedrock basement and a stream bed of boulders, pebbles, and gravel. A captive breeding program has been under way since a 2015 virus outbreak came close to wiping out the entire species; most remaining individuals are currently housed in quarantine, though a small number have been reintroduced to the original habitat.

The Western New Guinea stream turtle or New Guinea snapping turtle is a species of freshwater turtle in the Chelidae family. It is found in the Bird's Head Peninsula and the Bomberai Peninsula west of Cenderawasih Bay, and on the island of Waigeo of West Papua, Indonesia.

Emydura, the Australian short-necked turtles, are a genus of turtles in the family Chelidae. It was paraphyletic with Elseya. Consequently, it was split into two genera Myuchelys and Elseya by Thomson & Georges, 2009. They can grow quite large, 30 cm or more is not unusual and have a life span of around 20–30 years. They generally do not hibernate as their warmer climate lets them remain active all year round; they also spend more time in the water than other varieties. They are considered omnivore but rely on a constant supply of meat to remain healthy, feeding on basically anything that will fit into their mouth.

Elseya uberrima is an Eocene species of extinct Australian snapping turtle.
The Bluff Downs giant python is an extinct species of snake from Queensland, Australia, that lived during the Early Pliocene.

The Myuchelys is a genus of turtles, the Australian saw-shelled turtles, in the family Chelidae and subfamily Chelodininae. They inhabit the headwaters and tributaries of rivers within their range and this led to the name Myuchelys, which is formed from the Aboriginal word myuna meaning clear water and the Greek chelys meaning turtle. They have a short neck and the intergular scute completely separates the gular scutes. They have no alveolar ridge separating them from the snapping turtles of the genus Elseya.
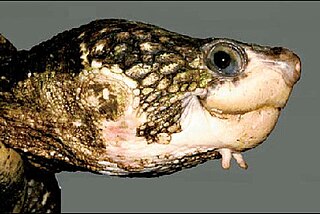
Elseya albagula, commonly known as the white-throated snapping turtle, is one of the largest species of chelid turtles in the world, growing to about 45 cm (18 in) carapace length.

The Gulf snapping turtle or Lavaracks' turtle is a large species of freshwater turtle in the sidenecked family Chelidae. The species is endemic to northern Australia in northwest Queensland and northeast Northern Territory. The species, similar to other members of the Australian snapping turtles in genus Elseya, only comes ashore to lay eggs and bask. The Gulf snapping turtle is a herbivore and primarily consumes Pandanus and figs.

Elseya dentata, the northern snapping turtle, is a large aquatic turtle found throughout many rivers in northern Western Australia and the Northern Territory. It is one of three species in the nominate subgenus Elseya.

The Bluff Downs fossil site is a paleontological site of Pliocene age in northern Queensland, Australia. It is one of the most significant fossil sites of Pliocene age in Australia due to its unique fauna and specific dating. The fossil site lies on the banks of the Allingham Creek on the pastoral property of Bluff Downs Station, northwest of Charters Towers on the Cape York Peninsula

Rheodytes devisi is a Pleistocene fossil turtle from the Darling Downs of Queensland, Australia. It was described from material originally included in the description of Elseya uberima.

Chelodina insculpta is an extinct species of snake-necked turtle that was described in 1897 from material gathered in Darling Downs, Queensland, Australia, restricted. It is a member of the Chelidae; Pleurodira. The fossil has been dated as Pliocene to Pleistocene.

Elseya rhodini, the southern New Guinea stream turtle, is a recently described aquatic species of chelid turtle found south of the central ranges of New Guinea. It inhabits small streams that flow into the major river drainage's south of the ranges.
Elseya flaviventralis, the yellow bellied snapping turtle, is a species of large river snapping turtles from the Arnhem Land region of the Northern Territory of Australia. It is a member of the nominate subgenus Elseya.

Scott A. Thomson is an Australian paleontologist, taxonomist, and herpetologist specialising in turtles of the family Chelidae.















