
Guam is an unincorporated and organized territory of the United States in Micronesia in the western Pacific Ocean. It is the easternmost point and territory of the United States, along with the Northern Mariana Islands. The capital city of Guam is Hagåtña and the most populous city is Dededo. The inhabitants of Guam are called Guamanians, and they are American citizens by birth. Indigenous Guamanians are the Chamorros, who are related to other Austronesian natives of Eastern Indonesia and Philippines and Taiwan. Guam has been a member of the Pacific Community since 1983.

Micronesia is a subregion of Oceania, composed of thousands of small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a shared cultural history with two other island regions: Polynesia to the east and Melanesia to the south.

Palmyra Atoll is one of the Northern Line Islands, located almost due south of the Hawaiian Islands, roughly one-third of the way between Hawaii and American Samoa. The nearest continent is almost 3,355 miles to the northeast. The atoll is 4.6 sq mi (12 km2), and it is located in the equatorial Northern Pacific Ocean. Its 9 mi (14 km) of coastline has one anchorage known as West Lagoon.

The United States Minor Outlying Islands are a statistical designation defined by the International Organization for Standardization's ISO 3166-1 code. The entry code is ISO 3166-2:UM. The minor outlying islands and groups of islands consist of eight United States insular areas in the Pacific Ocean and one in the Caribbean Sea.
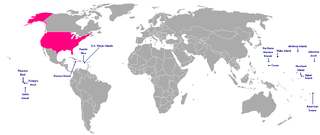
An insular area of the United States is a U.S. territory that is neither a part of one of the 50 states nor of a Federal district. Article IV, Section 3, Clause 2 of the United States Constitution grants to United States Congress the responsibility of overseeing these territories, of which there are currently 14—three in the Caribbean Sea and 11 in the Pacific Ocean. These territories are classified by whether they are incorporated and whether they have an organized territorial government established by the U.S. Congress through an Organic Act. All territories but one are unincorporated, and all but four are considered to be unorganized. Five U.S. territories have a permanent, nonmilitary population. Each of them has a civilian government, a constitution, and enjoys some degree of local political autonomy.

Territories of the United States are sub-national administrative divisions overseen by the federal government. They differ from U.S. states and Native American tribes, which have limited sovereignty. The territories are classified by incorporation and whether they have an "organized" government through an organic act passed by Congress.

The Office of Insular Affairs (OIA) is a unit of the United States Department of the Interior that oversees federal administration of several United States insular areas. It is the successor to the Bureau of Insular Affairs of the War Department, which administered certain territories from 1902 to 1939, and the Office of Territorial Affairs in the Interior Department, which was responsible for certain territories from the 1930s to the 1990s. The word "insular" comes from the Latin word insula ("island").
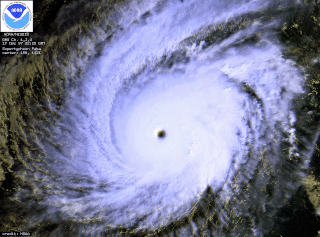
Typhoon Paka, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Rubing, was the last tropical cyclone of the 1997 Pacific hurricane and typhoon season, and was among the strongest Pacific typhoons in the month of December. Paka, which is the Hawaiian name for Pat, developed on November 28 from a trough well to the southwest of Hawaii. The storm tracked generally westward for much of its duration, and on December 7 it crossed into the western Pacific Ocean. Much of its track was characterized by fluctuations in intensity, and on December 10 the cyclone attained typhoon status as it crossed the Marshall Islands. On December 16, Paka struck Guam and Rota with winds of 230 km/h (145 mph), and it strengthened further to reach peak winds on December 18 over open waters as the final super typhoon of the year. Subsequently, it underwent a steady weakening trend, and on December 23 Paka dissipated.
This overview contains the flags of dependent territories and other areas of special sovereignty.

It has been estimated that before European settlement, forests in the United States covered nearly 1 billion acres (4,000,000 km2). The arrival of Europeans, however, caused a decline in native populations, and since the natives were largely agricultural, this caused reforestation of agricultural lands.

The District of Columbia and United States Territories Quarter Program was a one-year coin program of the United States Mint that saw quarters being minted in 2009 to honor the District of Columbia and the unincorporated United States insular areas of Puerto Rico, Guam, United States Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and the Northern Mariana Islands. The islands commonly grouped together as the United States Minor Outlying Islands were not featured, as the law defined the word "territory" as being limited to the areas mentioned above. It followed the completion of the 50 State Quarters program. The coins used the same George Washington obverse as with the quarters of the previous ten years. The reverse of the quarters featured a design selected by the Mint depicting of the federal district and each territory. Unlike on the 50 State quarters, the motto "E Pluribus Unum" preceded and was the same size as the mint date on the reverse.

Source: JTF-HD PAO
i-Tree is a collection of urban and rural forestry analysis and benefits assessment tools. It was designed and developed by the United States Forest Service to quantify and value ecosystem services provided by trees including pollution removal, carbon sequestration, avoided carbon emissions, avoided stormwater runoff, and more. i-Tree provides baseline data so that the growth of trees can be followed over time, and is used for planning purposes. Different tools within the i-Tree Suite use different types of inputs and provide different kinds of reports; some tools use a 'bottom up' approach based on tree inventories on the ground, while other tools use a 'top down' approach based on remote sensing data. i-Tree is peer-reviewed and has a process of ongoing collaboration to improve it.

Tropical Storm Bavi, known in the Philippines as Tropical Storm Betty, influenced the trade winds over the Pacific Ocean and was partially responsible for one of the strongest trade wind reversals ever observed. The system was first noted as a tropical disturbance during March 8, while it was located to the southeast of Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands. Over the next couple of days the system moved north-westwards through the Marshall Islands, before it was classified as a tropical depression during March 10. The system subsequently moved north-westwards and continued to develop further, before it was classified as the third tropical storm of the 2015 Pacific typhoon season and named Bavi by the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) during March 11. After continuing its north-westwards movement, the system peaked as a tropical storm during March 14, before it started to weaken as it approached the Mariana Islands. The system subsequently passed over Guam during the next day, before continuing its west-northwestwards movement as it gradually weakened over the next few days. The system entered the Philippine area of responsibility, where it was named Betty by PAGASA during March 17 as the system weakened into a tropical depression. The system was subsequently last noted during March 21, as it dissipated over the Philippines.












