
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain and the spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the limbs and organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the vertebral column and skull, or by the blood–brain barrier, which leaves it exposed to toxins.

The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, its force of contraction, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. This system is the primary mechanism in control of the fight-or-flight response.

The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.
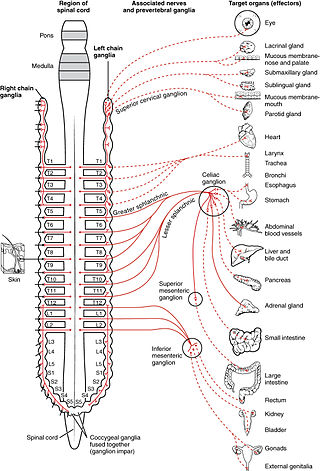
The sympathetic nervous system is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.

The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI and anterior to cranial nerve VIII.

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.
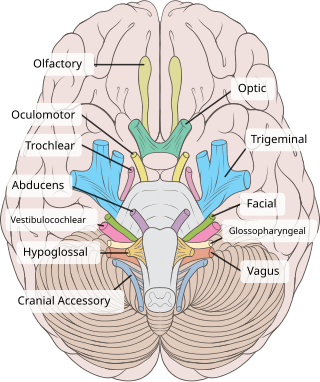
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most movements of the eye and that raise the eyelid. The nerve also contains fibers that innervate the intrinsic eye muscles that enable pupillary constriction and accommodation. The oculomotor nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic midbrain. Cranial nerves IV and VI also participate in control of eye movement.

The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest.

The somatic nervous system (SNS), also known as voluntary nervous system, is a part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) that links brain and spinal cord to skeletal muscles under conscious control, as well as to sensory receptors in the skin. The other part complementary to the somatic nervous system is the autonomic nervous system (ANS).

Efferent nerve fibers are the axons of efferent neurons that exit a particular region. These terms have a slightly different meaning in the context of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and central nervous system (CNS). The efferent fiber is a long process projecting far from the neuron's body that carries nerve impulses away from the central nervous system toward the peripheral effector organs. A bundle of these fibers constitute an efferent nerve. The opposite direction of neural activity is afferent conduction, which carries impulses by way of the afferent nerve fibers of sensory neurons.

The solitary nucleus(SN) (nucleus of the solitary tract, nucleus solitarius, or nucleus tractus solitarii) is a series of neurons whose cell bodies form a roughly vertical column of grey matter in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem. Their axons form the bulk of the enclosed solitary tract. The solitary nucleus can be divided into different parts including dorsomedial, dorsolateral, and ventrolateral subnuclei.

The submandibular ganglion is part of the human autonomic nervous system. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck..

The lesser petrosal nerve is the general visceral efferent (GVE) nerve conveying pre-ganglionic parasympathetic secretomotor fibers for the parotid gland from the tympanic plexus to the otic ganglion. It passes out of the tympanic cavity through the petrous part of the temporal bone into the middle cranial fossa of the cranial cavity, then exits the cranial cavity through its own canaliculus to reach the infratemporal fossa.

The sympathetic ganglia, or paravertebral ganglia, are autonomic ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system. Ganglia are 20,000 to 30,000 afferent and efferent nerve cell bodies that run along on either side of the spinal cord. Afferent nerve cell bodies bring information from the body to the brain and spinal cord, while efferent nerve cell bodies bring information from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. The cell bodies create long sympathetic chains that are on either side of the spinal cord. They also form para- or pre-vertebral ganglia of gross anatomy.

The lateral grey column is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord ; the others being the anterior and posterior grey columns. The lateral grey column is primarily involved with activity in the sympathetic division of the autonomic motor system. It projects to the side as a triangular field in the thoracic and upper lumbar regions of the postero-lateral part of the anterior grey column.
Pelvic splanchnic nerves or nervi erigentes are splanchnic nerves that arise from sacral spinal nerves S2, S3, S4 to provide parasympathetic innervation to the organs of the pelvic cavity.
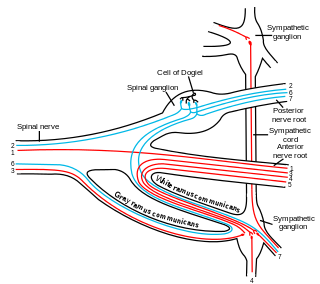
The general visceral afferent (GVA) fibers conduct sensory impulses from the internal organs, glands, and blood vessels to the central nervous system. They are considered to be part of the visceral nervous system, which is closely related to the autonomic nervous system, but 'visceral nervous system' and 'autonomic nervous system' are not direct synonyms and care should be taken when using these terms. Unlike the efferent fibers of the autonomic nervous system, the afferent fibers are not classified as either sympathetic or parasympathetic.

The general (spinal) somatic efferent neurons arise from motor neuron cell bodies in the ventral horns of the gray matter within the spinal cord. They exit the spinal cord through the ventral roots, carrying motor impulses to skeletal muscle through a neuromuscular junction.
Special visceral efferent fibers (SVE) are the efferent nerve fibers that provide motor innervation to the muscles of the pharyngeal arches in humans, and the branchial arches in fish.

The salivatory nuclei are pre-ganglionic parasympathetic neurons in the caudal pons representing the general visceral efferent (GVE) cranial nerve nuclei giving rise to axons which join the facial nerve and glossopharyngeal nerve to reach and innervate the salivary as well as lacrimal glands. The nuclei may also be involved in parasympathetic control of head vasculature.



















