Contents

This page list topics related to French Polynesia.

This page list topics related to French Polynesia.
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |

French Polynesia is an overseas collectivity of France and its sole overseas country. It comprises 121 geographically dispersed islands and atolls stretching over more than 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) in the South Pacific Ocean. The total land area of French Polynesia is 3,521 square kilometres (1,359 sq mi), with a population of 278,786 of which at least 205,000 live in the Society Islands and the remaining population lives in the rest of the archipelago.
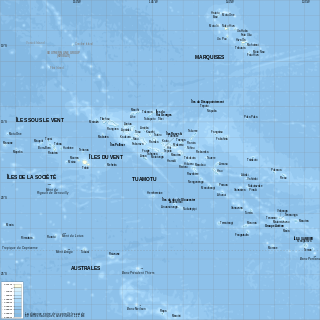
French Polynesia is located in Oceania. It is a group of six archipelagos in the South Pacific Ocean, about halfway between South America and Australia. Its area is about 4,167 km2, of which 3,827 km2 is land and 340 km2 is (inland) water. It has a coastline of 2,525 km but no land borders with other countries.

The Marquesas Islands are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in the southern Pacific Ocean. Their highest point is the peak of Mount Oave on Ua Pou island, at 1,230 m (4,035 ft) above sea level.

Air Tahiti Nui is the flag carrier of the French overseas collectivity of French Polynesia, with its head office and daily operations office in Faaa, Tahiti. It operates long-haul flights from its home base at Faa'a International Airport, with a fleet consisting of four Boeing 787 Dreamliners.

The Tuamotu Archipelago or the Tuamotu Islands are a French Polynesian chain of just under 80 islands and atolls in the southern Pacific Ocean. They constitute the largest chain of atolls in the world, extending over an area roughly the size of Western Europe. Their combined land area is 850 square kilometres. This archipelago's major islands are Anaa, Fakarava, Hao and Makemo.

The Gambier Islands are an archipelago in French Polynesia, located at the southeast terminus of the Tuamotu archipelago. They cover an area of 27.8 km2 or 10.7 sq mi, and are made up of the Mangareva Islands, a group of high islands remnants of a caldera along with islets on the surrounding fringing reef, and the uninhabited Temoe atoll, which is located 45 km south-east of the Mangareva Islands. The Gambiers are generally considered a separate island group from Tuamotu both because their culture and language (Mangarevan) are much more closely related to those of the Marquesas Islands, and because, while the Tuamotus comprise several chains of coral atolls, the Mangareva Islands are of volcanic origin with central high islands.
Air Tahiti is a French airline company which operates in French Polynesia. Its main hub is Faa'a International Airport. It is the largest private employer in French Polynesia.

The Leeward Islands are the western part of the Society Islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France, in the South Pacific Ocean. They lie south of the Line Islands, east of the Cooks and north of the Austral Islands. Their area is 404 km2 and their population is over 36,000.

The Society Islands are an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean that includes the major islands of Tahiti, Moʻorea, Raiatea, Bora Bora and Huahine. Politically, they are part of French Polynesia, an overseas country of the French Republic. Geographically, they form part of Polynesia.
Mangareva, Mangarevan is a Polynesian language spoken by about 600 people in the Gambier Islands of French Polynesia and by Mangarevians emigrants on the islands of Tahiti and Moorea, located 1,650 kilometres (1,030 mi) to the North-West of the Gambier Islands.

Bora Bora Airport, also known as Motu Mute Airport, is an airport serving the island of Bora Bora in French Polynesia. It is located on the islet of Motu Mute.

Moorea Airport is an airport serving the island of Moorea in French Polynesia, France. It is also known as Temae Airport or Moorea Temae Airport for its location near the village of Temae in northeastern Moorea. The airport is located 7.5 km (4.0 NM) northeast of Afareitu, the island's main village. It is also 15 km (8.1 NM) west of the island of Tahiti. The airport opened on October 6, 1967.

Vaitape is the largest city of Bora Bora Island in French Polynesia. It has a population of 4,927, about half of the island's population which is about 10,605. It is located about 210 km (130 mi) northwest of Papeete, the capital of French Polynesia. The main language of Vaitape is French, although 20 percent of the population speaks Tahitian.
The Pōmare dynasty was the reigning family of the Kingdom of Tahiti between the unification of the islands by Pōmare I in 1788 and Pōmare V's cession of the kingdom to France in 1880. Their influence once spanned most of the Society Islands, the Austral Islands and the Tuamotu Archipelago.

Tahiti and Society Islands mythology comprises the legends, historical tales, and sayings of the ancient people of the Society Islands, consisting of Tahiti, Bora Bora, Raiatea, Huahine, Moorea and other islands. It is considered a variant of a more general Polynesian mythology, developing its own unique character for several centuries. The religion was officially suppressed in the 19th century, and ultimately abandoned by the natives in favor of Christianity.

The Franco-Tahitian War or French–Tahitian War (1844–1847) was a conflict between the Kingdom of France and the Kingdom of Tahiti and its allies in the South Pacific archipelago of the Society Islands in modern-day French Polynesia.

French Polynesia's 2nd constituency is a French legislative constituency in French Polynesia. It is currently represented by Nicole Sanquer of A here ia Porinetia.

The annexation of the Leeward Islands or the Leewards War was a series of diplomatic and armed conflicts between the French Third Republic and the native kingdoms of Raiatea-Tahaa, Huahine and Bora Bora, which resulted in the conquest of the Leeward Islands, in the South Pacific archipelago of the Society Islands in modern-day French Polynesia.