
The common gamma chain (γc), also known as interleukin-2 receptor subunit gamma or IL-2RG, is a cytokine receptor sub-unit that is common to the receptor complexes for at least six different interleukin receptors: IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15 and interleukin-21 receptor. The γc glycoprotein is a member of the type I cytokine receptor family expressed on most lymphocyte populations, and its gene is found on the X-chromosome of mammals.

Interleukin-23 subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL23A gene. IL-23 is produced by dendritic cells and macrophages.
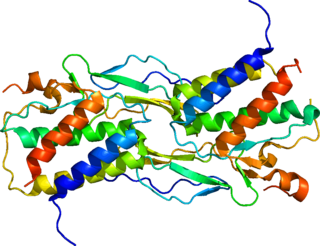
Interleukin-15 (IL-15) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL15 gene. IL-15 is an inflammatory cytokine with structural similarity to Interleukin-2 (IL-2). Like IL-2, IL-15 binds to and signals through a complex composed of IL-2/IL-15 receptor beta chain (CD122) and the common gamma chain. IL-15 is secreted by mononuclear phagocytes following infection by virus(es). This cytokine induces the proliferation of natural killer cells, i.e. cells of the innate immune system whose principal role is to kill virally infected cells.

Interleukin 21 (IL-21) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL21 gene.
Type I cytokine receptors are transmembrane receptors expressed on the surface of cells that recognize and respond to cytokines with four α-helical strands. These receptors are also known under the name hemopoietin receptors, and share a common amino acid motif (WSXWS) in the extracellular portion adjacent to the cell membrane. Members of the type I cytokine receptor family comprise different chains, some of which are involved in ligand/cytokine interaction and others that are involved in signal transduction.

The interleukin 4 receptor is a type I cytokine receptor. IL4R is its human gene.
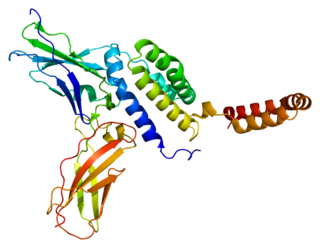
Interleukin 10 receptor, alpha subunit is a subunit for the interleukin-10 receptor. IL10RA, is its human gene.

Interleukin-12 receptor, beta 1, or IL-12Rβ1 in short, is a subunit of the interleukin 12 receptor. IL12RB1, is the name of its human gene. IL-12Rβ1 is also known as CD212.

Interleukin 5 receptor, alpha (IL5RA) also known as CD125 is a subunit of the Interleukin-5 receptor. IL5RA also denotes its human gene.

Interleukin 9 receptor (IL9R) also known as CD129 is a type I cytokine receptor. IL9R also denotes its human gene.

Interleukin 17 receptor A, also known as IL17RA and CDw217, is a human gene.

Interleukin 21 receptor is a type I cytokine receptor. IL21R is its human gene.

Interleukin 20 receptor, alpha subunit is a subunit for the interleukin-20 receptor. IL20RA is its human gene.

Interleukin-2 receptor subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL2RB gene. Also known as CD122; IL15RB; P70-75.

Interleukin 18 receptor accessory protein, also known as IL18RAP and CDw218b, is a human gene.

Interleukin 27 receptor, alpha is a subunit of the interleukin-27 receptor. IL27RA is its human gene.

Interleukin 3 receptor, alpha (IL3RA), also known as CD123, is a human gene.
The interleukin-27 receptor is a type I cytokine receptor for interleukin-27. It is a heterodimer composed of the interleukin 27 receptor, alpha subunit and glycoprotein 130.

The interleukin-18 receptor 1 (IL-18R1) is an interleukin receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily. IL18R1 is its human gene. IL18R1 is also known as CDw218a.

Interleukin-7 receptor subunit alpha (IL7R-α) also known as CD127 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL7R gene.





















