
Infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody, sold under the brand name Remicade among others, is a medication used to treat a number of autoimmune diseases. This includes Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and Behçet's disease. It is given by slow injection into a vein, typically at six- to eight-week intervals.

Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that occurs in people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic feature of psoriatic arthritis is swelling of entire fingers and toes with a sausage-like appearance. This often happens in association with changes to the nails such as small depressions in the nail (pitting), thickening of the nails, and detachment of the nail from the nailbed. Skin changes consistent with psoriasis frequently occur before the onset of psoriatic arthritis but psoriatic arthritis can precede the rash in 15% of affected individuals. It is classified as a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy.
Etanercept, sold under the brand name Enbrel among others, is a biologic medical product that is used to treat autoimmune diseases by interfering with tumor necrosis factor (TNF), a soluble inflammatory cytokine, by acting as a TNF inhibitor. It has US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval to treat rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis and psoriatic arthritis, plaque psoriasis and ankylosing spondylitis. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) is the "master regulator" of the inflammatory (immune) response in many organ systems. Autoimmune diseases are caused by an overactive immune response. Etanercept has the potential to treat these diseases by inhibiting TNF-alpha.
Adalimumab, sold under the brand name Humira and others, is a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug and monoclonal antibody used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and uveitis. It is administered by subcutaneous injection. It works by inactivating tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα).
Alefacept is a genetically engineered immunosuppressive drug. It was sold under the brand name Amevive in Canada, the United States, Israel, Switzerland and Australia. In 2011, the manufacturers made a decision to cease promotion, manufacturing, distribution and sales of Amevive during a supply disruption. According to Astellas Pharma US, Inc., the decision to cease Amevive sales was neither the result of any specific safety concern nor the result of any FDA-mandated or voluntary product recall. On the other hand, usage of Amevive was associated with a certain risk of development systemic diseases such as malignancies. This drug was never approved for the European drug market.
A TNF inhibitor is a pharmaceutical drug that suppresses the physiologic response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF), which is part of the inflammatory response. TNF is involved in autoimmune and immune-mediated disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa and refractory asthma, so TNF inhibitors may be used in their treatment. The important side effects of TNF inhibitors include lymphomas, infections, congestive heart failure, demyelinating disease, a lupus-like syndrome, induction of auto-antibodies, injection site reactions, and systemic side effects.
Ustekinumab, sold under the brand name Stelara among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication developed by Janssen Pharmaceuticals, for the treatment of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, targeting both IL-12 and IL-23.
Briakinumab (ABT-874) is a human monoclonal antibody being developed by Abbott Laboratories for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and multiple sclerosis. As of 2011 drug development for psoriasis has been discontinued in the U.S. and Europe.

Tofacitinib, sold under the brand Xeljanz among others, is a medication used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and ulcerative colitis. It is a janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, discovered and developed by the National Institutes of Health and Pfizer.
Brodalumab, sold under the brand name Siliq in the US and Kyntheum in the EU, is a human monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Ixekizumab, sold under the brand name Taltz, is an injectable medication for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Chemically, it is a form of a humanized monoclonal antibody. The substance acts by binding interleukin 17A and neutralizing it, reducing inflammation.

Secukinumab, sold under the brand name Cosentyx among others, is a human IgG1κ monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis. It binds to the protein interleukin (IL)-17A and is marketed by Novartis.
Namilumab is a human monoclonal antibody that targets granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF)/colony stimulating factor 2 (CSF2) and is currently being researched for application in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis. Clinical trials investigating the therapeutic utility of Namilumab have include phase I and phase II clinical trials to establish the safety, tolerability and preliminary therapeutic utility of the antibody in plaque psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis.
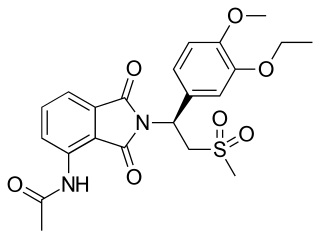
Apremilast, sold under the brand name Otezla among others, is a medication for the treatment of certain types of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. The drug acts as a selective inhibitor of the enzyme phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) and inhibits spontaneous production of TNF-alpha from human rheumatoid synovial cells. It is taken by mouth.
Tildrakizumab, sold under the brand names Ilumya and Ilumetri, is a monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of immunologically mediated inflammatory disorders. It is approved for the treatment of adult patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis in the United States and the European Union.
Guselkumab, sold under the brand name Tremfya, is a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-23 used for the treatment of plaque psoriasis.

Filgotinib, sold under the brand name Jyseleca, is a medication used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). It was developed by the Belgian-Dutch biotech company Galapagos NV.

Upadacitinib, sold under the brand name Rinvoq, is a medication used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, atopic dermatitis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, ankylosing spondylitis, and axial spondyloarthritis. Upadacitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor that works by blocking the action of enzymes called Janus kinases. These enzymes are involved in setting up processes that lead to inflammation, and blocking their effect brings inflammation in the joints under control.
Bimekizumab, sold under the brand name Bimzelx, is a humanized anti-IL17A, anti-IL-17F, and anti-IL17AF monoclonal antibody that is used to treat plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis.

Abrocitinib, sold under the brand name Cibinqo, is a medication used for the treatment of atopic dermatitis (eczema). It is a Janus kinase inhibitor and it was developed by Pfizer. It is taken by mouth.








