
A monoclonal antibody is an antibody produced from a cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
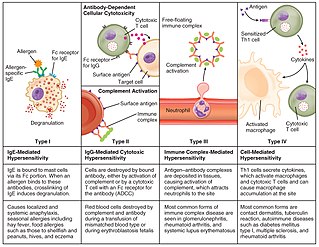
Hypersensitivity is an abnormal physiological condition in which there is an undesirable and adverse immune response to an antigen. It is an abnormality in the immune system that causes immune diseases including allergies and autoimmunity. It is caused by many types of particles and substances from the external environment or from within the body that are recognized by the immune cells as antigens. The immune reactions are usually referred to as an over-reaction of the immune system and they are often damaging and uncomfortable.
Muromonab-CD3 is an immunosuppressant medication given to reduce acute rejection in people with organ transplants. It is a monoclonal antibody targeted at the CD3 receptor, a membrane protein on the surface of T cells. It is the first monoclonal antibody to be approved for clinical use in humans.
The nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies is a naming scheme for assigning generic, or nonproprietary, names to monoclonal antibodies. An antibody is a protein that is produced in B cells and used by the immune system of humans and other vertebrate animals to identify a specific foreign object like a bacterium or a virus. Monoclonal antibodies are those that were produced in identical cells, often artificially, and so share the same target object. They have a wide range of applications including medical uses.
Lemalesomab is a mouse monoclonal antibody for the diagnosis of inflammatory lesions.
Faralimomab is a mouse monoclonal antibody and an immunomodulator.
Atorolimumab is an immunosuppressive drug directed against the Rhesus factor.
Metelimumab (CAT-192) is a human IgG4 monoclonal antibody that neutralizes TGF beta 1 which had been chosen for further development for the treatment of diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis, also known as scleroderma. It was dropped from further development in favour of fresolimumab, which was being developed by Genzyme as of 2006.
Elsilimomab is a mouse monoclonal antibody. B-E8 was developed by Diaclone, a French company which produces many mouse monoclonal antibodies.
Detumomab is a mouse monoclonal antibody targeting human B-cell lymphoma.
Morolimumab is a human monoclonal antibody against the human Rhesus factor.
Etaracizumab, also known as MEDI-522, trade name Abegrin, is a humanized monoclonal antibody which is being investigated for the treatment of metastatic melanoma, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer and various other types of cancer. It is manufactured by MedImmune.
Technetium (99mTc) votumumab is a human monoclonal antibody labelled with the radionuclide technetium-99m. It was developed for the detection of colorectal tumors, but has never been marketed.
Amatuximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancer. It was developed by Morphotek, Inc.
Ficlatuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancers.
Fulranumab is a monoclonal antibody against nerve growth factor. It was designed for the treatment of pain.
Narnatumab is a human monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancer. Clinical development was abandoned after phase I trials.
Seribantumab is a monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancer. It binds to extracellular domain of HER3 blocking NRG1 binding and thereby preventing the activation of the receptor.
Vanucizumab is an experimental humanized monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancer.
Depatuxizumab mafodotin is an antibody-drug conjugate designed for the treatment of cancer. It is composed of an EGFR IGg1 monoclonal antibody (depatuxizumab) conjugated to the tubulin inhibitor monomethyl auristatin F via a stable maleimidocaproyl link.

