
Transplant rejection occurs when transplanted tissue is rejected by the recipient's immune system, which destroys the transplanted tissue. Transplant rejection can be lessened by determining the molecular similitude between donor and recipient and by use of immunosuppressant drugs after transplant.
Anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG) is an infusion of horse or rabbit-derived antibodies against human T cells and their precursors (thymocytes), which is used in the prevention and treatment of acute rejection in organ transplantation and therapy of aplastic anemia due to bone marrow insufficiency.
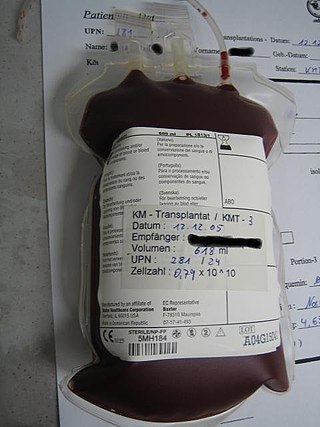
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood in order to replicate inside of a patient and to produce additional normal blood cells. It may be autologous, allogeneic or syngeneic.

Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is a syndrome, characterized by inflammation in different organs. GvHD is commonly associated with bone marrow transplants and stem cell transplants.

Alemtuzumab, sold under the brand names Campath and Lemtrada among others, is a medication used to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and multiple sclerosis. In CLL, it has been used as both a first line and second line treatment. In MS it is generally only recommended if other treatments have not worked. It is given by injection into a vein.

Pentostatin is an anticancer chemotherapeutic drug.
In medicine, photopheresis is a form of apheresis and photodynamic therapy in which blood is subject to apheresis to separate buffy coat from whole blood, chemically treated with 8-methoxypsoralen, exposed to ultraviolet light (UVA), and then returned to the patient. Activated 8-methoxypsoralen crosslinks DNA in exposed cells, ultimately resulting apoptosis of nucleated cells. The photochemically damaged T-cells returned to the patient appear to induce cytotoxic effects on T-cell formation. The mechanism of such “antitumor” action has not been elucidated.
Transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease (TA-GvHD) is a rare complication of blood transfusion, in which the immunologically competent donor T lymphocytes mount an immune response against the recipient's lymphoid tissue. These donor lymphocytes engraft, recognize recipient cells as foreign and mount an immune response against recipient tissues. Donor lymphocytes are usually identified as foreign and destroyed by the recipient's immune system. However, in situations where the recipient is severely immunocompromised, or when the donor and recipient HLA type is similar, the recipient's immune system is not able to destroy the donor lymphocytes. This can result in transfusion associated graft-versus-host disease. This is in contrast with organ/tissue transplant associated GvHD, where matching HLA reduces the incident of the complication.
Gusperimus is an immunosuppressive drug. It is a derivative of the naturally occurring HSP70 inhibitor spergualin, and inhibits the interleukin-2-stimulated maturation of T cells to the S and G2/M phases and the polarization of the T cells into IFN-gamma-secreting Th1 effector T cells, resulting in the inhibition of growth of activated naive CD4 T cells.
Inolimomab is a mouse monoclonal antibody developed as an immunosuppressive drug against graft-versus-host disease. Its target is the alpha chain of the interleukin-2 receptor.
Maraviroc, sold under the brand names Selzentry (US) and Celsentri (EU), is an antiretroviral medication used to treat HIV infection. It is taken by mouth. It is in the CCR5 receptor antagonist class.
Donor lymphocyte infusion (DLI) or buffy coat infusion is a form of adoptive immunotherapy used after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Blood irradiation therapy is an alternative medical procedure in which the blood is exposed to low-level light for therapeutic reasons. The practice was originally developed in the United States, but most recent research on it has been conducted in Germany and in Russia. Low-level laser therapy has been tested for a wide range of conditions, but rigorous double-blinded studies have not yet been performed. Furthermore, it has been claimed that ultraviolet irradiation of blood kills bacteria by DNA damage and also activation of the immune system. Blood irradiation therapy is highly controversial, and has fallen from mainstream use since its heyday in the 1940s and 1950s.

Ruxolitinib, sold under the brand name Jakafi among others, is a medication used for the treatment of intermediate or high-risk myelofibrosis, a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm that affects the bone marrow; polycythemia vera, when there has been an inadequate response to or intolerance of hydroxyurea; and steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. Ruxolitinib is a Janus kinase inhibitor. It was developed and marketed by Incyte Corp in the US under the brand name Jakafi, and by Novartis elsewhere in the world, under the brand name Jakavi.
TK is an experimental cell therapy which may be used to treat high-risk leukemia. It is currently undergoing a Phase III clinical trial to determine efficacy and clinical usefulness.
Graft-versus-tumor effect (GvT) appears after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). The graft contains donor T cells that can be beneficial for the recipient by eliminating residual malignant cells. GvT might develop after recognizing tumor-specific or recipient-specific alloantigens. It could lead to remission or immune control of hematologic malignancies. This effect applies in myeloma and lymphoid leukemias, lymphoma, multiple myeloma and possibly breast cancer. It is closely linked with graft-versus-host disease (GvHD), as the underlying principle of alloimmunity is the same. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells (Treg) can be used to suppress GvHD without loss of beneficial GvT effect. The biology of GvT response is still not fully understood but it is probable that the reaction with polymorphic minor histocompatibility antigens expressed either specifically on hematopoietic cells or more widely on a number of tissue cells or tumor-associated antigens is involved. This response is mediated largely by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) but it can be employed by natural killers as separate effectors, particularly in T-cell-depleted HLA-haploidentical HSCT.
Jo-Anne H. Young is an American physician, scientist, and Editor-in-Chief of Clinical Microbiology Reviews, published by the American Society for Microbiology.
Belumosudil, sold under the brand name Rezurock among others, is a medication used for the treatment of chronic graft versus host disease (cGvHD). It is in the class of drugs known as serine/threonine kinase inhibitors. Specifically, it is an inhibitor of Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase 2. Belumosudil binds to and inhibits the serine/threonine kinase activity of ROCK2. This inhibits ROCK2-mediated signaling pathways which play major roles in pro- and anti-inflammatory immune cell responses. A genomic study in human primary cells demonstrated that the drug also has effects on oxidative phosphorylation, WNT signaling, angiogenesis, and KRAS signaling.

Shimon Slavin is an Israeli professor of medicine. Slavin pioneered the use of immunotherapy mediated by allogeneic donor lymphocytes and innovative methods for stem cell transplantation for the cure of hematological malignancies and solid tumors, and using hematopoietic stem cells for induction of transplantation tolerance to bone marrow and donor allografts.

The University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center is a cancer research and treatment institution based in Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States. The Rogel Cancer Center is affiliated with the University of Michigan and Michigan Medicine.









