Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncotherapy) is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving on the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the fundamental research of cancer immunology and a growing subspecialty of oncology.

Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar for energy and it helps regulate glucose levels in the bloodstream. Before treatment this results in high blood sugar levels in the body. The common symptoms of this elevated blood sugar are frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger, weight loss, and other serious complications. Additional symptoms may include blurry vision, tiredness, and slow wound healing. Symptoms typically develop over a short period of time, often a matter of weeks if not months.
Slowly evolving immune-mediated diabetes, or latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA), is a form of diabetes that exhibits clinical features similar to both type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D), and is sometimes referred to as type 1.5 diabetes. It is an autoimmune form of diabetes, similar to T1D, but patients with LADA often show insulin resistance, similar to T2D, and share some risk factors for the disease with T2D. Studies have shown that LADA patients have certain types of antibodies against the insulin-producing cells, and that these cells stop producing insulin more slowly than in T1D patients. Since many people develop the disease later in life, it is often misdiagnosed as type 2 diabetes.
Muromonab-CD3 is an immunosuppressant drug given to reduce acute rejection in patients with organ transplants. It is a monoclonal antibody targeted at the CD3 receptor, a membrane protein on the surface of T cells. It was the first monoclonal antibody to be approved for clinical use in humans.

CD3 is a protein complex and T cell co-receptor that is involved in activating both the cytotoxic T cell and T helper cells. It is composed of four distinct chains. In mammals, the complex contains a CD3γ chain, a CD3δ chain, and two CD3ε chains. These chains associate with the T-cell receptor (TCR) and the CD3-zeta (ζ-chain) to generate an activation signal in T lymphocytes. The TCR, CD3-zeta, and the other CD3 molecules together constitute the TCR complex.
Ipilimumab, sold under the brand name Yervoy, is a monoclonal antibody medication that works to activate the immune system by targeting CTLA-4, a protein receptor that downregulates the immune system.
Visilizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody. It is being investigated for use as an immunosuppressive drug in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Visilizumab binds to the CD3 receptor on certain activated T cells without affecting resting T cells. It is currently under clinical studies for the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
Ibalizumab, sold under the brand name Trogarzo, is a non-immunosuppressive humanised monoclonal antibody that binds CD4, the primary receptor for HIV, and inhibits HIV from entering cells. It is a post-attachment inhibitor, blocking HIV from binding to the CCR5 and CXCR4 co-receptors after HIV binds to the CD4 receptor on the surface of a CD4 cell. Post-attachment inhibitors are a subclass of HIV drugs called entry inhibitors.
Otelixizumab, also known as TRX4, is a monoclonal antibody, which is being developed for the treatment of type 1 diabetes and other autoimmune diseases. The antibody is being developed by Tolerx, Inc. in collaboration with GlaxoSmithKline and is being manufactured by Abbott Laboratories.
Blinatumomab, sold under the brand name Blincyto, is a biopharmaceutical medication used as a second-line treatment for Philadelphia chromosome-negative relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. It belongs to a class of constructed monoclonal antibodies, bi-specific T-cell engagers (BiTEs), that exert action selectively and direct the human immune system to act against tumor cells. Blinatumomab specifically targets the CD19 antigen present on B cells. In December 2014, it was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration under the accelerated approval program; marketing authorization depended on the outcome of clinical trials that were ongoing at the time of approval.
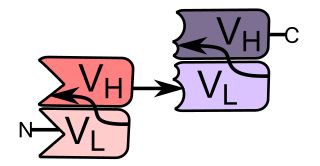
Bi-specific T-cell engagers (BiTEs) are a class of artificial bispecific monoclonal antibodies that are investigated for use as anti-cancer drugs. They direct a host's immune system, more specifically the T cells' cytotoxic activity, against cancer cells. BiTE is a registered trademark of Micromet AG.
Brentuximab vedotin, sold under the brand name Adcetris, is an antibody-drug conjugate medication used to treat relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), a type of T cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It selectively targets tumor cells expressing the CD30 antigen, a defining marker of Hodgkin lymphoma and ALCL. The drug is being jointly marketed by Millennium Pharmaceuticals outside the US and by Seagen in the US.
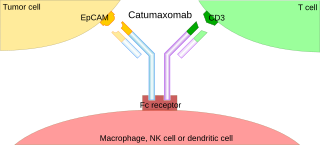
A trifunctional antibody is a monoclonal antibody with binding sites for two different antigens, typically CD3 and a tumor antigen, making it a type of bispecific monoclonal antibody. In addition, its intact Fc-part can bind to an Fc receptor on accessory cells like conventional monospecific antibodies. The net effect is that this type of drug links T cells and monocytes/macrophages, natural killer cells, dendritic cells or other Fc receptor expressing cells to the tumor cells, leading to their destruction.
An anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody is one that binds to CD3 on the surface of T cells. They are immunosuppresive drugs.
Short Course Immune Induction Therapy or SCIIT, is a therapeutic strategy employing rapid, specific, short term-modulation of the immune system using a therapeutic agent to induce T-cell non-responsiveness, also known as operational tolerance. As an alternative strategy to immunosuppression and antigen-specific tolerance inducing therapies, the primary goal of SCIIT is to re-establish or induce peripheral immune tolerance in the context of autoimmune disease and transplant rejection through the use of biological agents. In recent years, SCIIT has received increasing attention in clinical and research settings as an alternative to immunosuppressive drugs currently used in the clinic, drugs which put the patients at risk of developing infection, cancer, and cardiovascular disease.
TOL101, is a murine-monoclonal antibody specific for the human αβ T cell receptor. In 2010 it was an Investigational New Drug under development by Tolera Therapeutics, Inc.
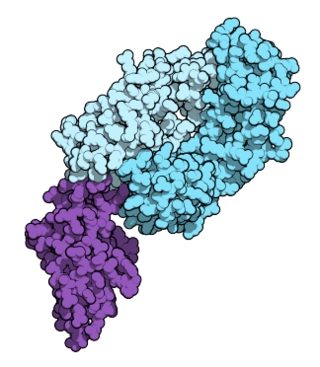
Nivolumab, sold under the brand name Opdivo, is a medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes melanoma, lung cancer, malignant pleural mesothelioma, renal cell carcinoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, head and neck cancer, urothelial carcinoma, colon cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, liver cancer, gastric cancer, and esophageal or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer. It is used by slow injection into a vein.

Dulaglutide, sold under the brand name Trulicity among others, is a medication used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in combination with diet and exercise. It is also approved in the United States for the reduction of major adverse cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes who have established cardiovascular disease or multiple cardiovascular risk factors. It is a once-weekly injection.

PD-1 inhibitors and PD-L1 inhibitors are a group of checkpoint inhibitor anticancer drugs that block the activity of PD-1 and PDL1 immune checkpoint proteins present on the surface of cells. Immune checkpoint inhibitors are emerging as a front-line treatment for several types of cancer.
Dostarlimab, sold under the brand name Jemperli, is a monoclonal antibody used as an anti-cancer medication for the treatment of endometrial cancer. Dostarlimab is a programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1)–blocking monoclonal antibody.








