
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent the activity of the immune system.

Infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody, sold under the brand name Remicade among others, is a medication used to treat a number of autoimmune diseases. This includes Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and Behçet's disease. It is given by slow injection into a vein, typically at six- to eight-week intervals.
Daclizumab is a therapeutic humanized monoclonal antibody which was used for the treatment of adults with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). Daclizumab works by binding to CD25, the alpha subunit of the IL-2 receptor of T-cells.
In immunology, antiserum is a blood serum containing antibodies that is used to spread passive immunity to many diseases via blood donation (plasmapheresis). For example, convalescent serum, passive antibody transfusion from a previous human survivor, used to be the only known effective treatment for ebola infection with a high success rate of 7 out of 8 patients surviving.
Muromonab-CD3 is an immunosuppressant drug given to reduce acute rejection in patients with organ transplants. It is a monoclonal antibody targeted at the CD3 receptor, a membrane protein on the surface of T cells. It was the first monoclonal antibody to be approved for clinical use in humans.

Biological therapy, the use of medications called biopharmaceuticals or biologics that are tailored to specifically target an immune or genetic mediator of disease, plays a major role in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Even for diseases of unknown cause, molecules that are involved in the disease process have been identified, and can be targeted for biological therapy. Many of these molecules, which are mainly cytokines, are directly involved in the immune system. Biological therapy has found a niche in the management of cancer, autoimmune diseases, and diseases of unknown cause that result in symptoms due to immune related mechanisms.

Monoclonal antibody therapy is a form of immunotherapy that uses monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to bind monospecifically to certain cells or proteins. The objective is that this treatment will stimulate the patient's immune system to attack those cells. Alternatively, in radioimmunotherapy a radioactive dose localizes a target cell line, delivering lethal chemical doses. Antibodies are used to bind to molecules involved in T-cell regulation to remove inhibitory pathways that block T-cell responses. This is known as immune checkpoint therapy.
Ustekinumab, sold under the brand name Stelara, is a monoclonal antibody medication developed by Janssen Pharmaceuticals, for the treatment of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, targeting both IL-12 and IL-23.
Cedelizumab is a monoclonal antibody acting on the immune system. Possible indications include the prevention of organ transplant rejections and the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Lintuzumab (SGN-33) is a humanized monoclonal antibody used in the treatment of cancer. The drug had been developed by Seattle Genetics as a treatment for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a condition which results in the deaths of 9,000 people a year in the United States. Lintuzumab targets the CD33 protein, which is expressed in AML and other myeloproliferative diseases, but does not appear in abundance on normal cells.
Teplizumab, sold under the brand name Tzield, is a humanized anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody that is the first approved treatment indicated to delay the onset of stage 3 type 1 diabetes (T1D) in people with stage 2 T1D.
Otelixizumab, also known as TRX4, is a monoclonal antibody, which is being developed for the treatment of type 1 diabetes and other autoimmune diseases. The antibody is being developed by Tolerx, Inc. in collaboration with GlaxoSmithKline and is being manufactured by Abbott Laboratories.
Vedolizumab, sold under the brand name Entyvio, is a monoclonal antibody medication developed by Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. for the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It binds to integrin α4β7, blocking the α4β7 integrin results in gut-selective anti-inflammatory activity.
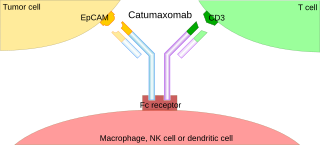
A trifunctional antibody is a monoclonal antibody with binding sites for two different antigens, typically CD3 and a tumor antigen, making it a type of bispecific monoclonal antibody. In addition, its intact Fc-part can bind to an Fc receptor on accessory cells like conventional monospecific antibodies. The net effect is that this type of drug links T cells and monocytes/macrophages, natural killer cells, dendritic cells or other Fc receptor expressing cells to the tumor cells, leading to their destruction.
An anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody is one that binds to CD3 on the surface of T cells. They are immunosuppresive drugs.
Short Course Immune Induction Therapy or SCIIT, is a therapeutic strategy employing rapid, specific, short term-modulation of the immune system using a therapeutic agent to induce T-cell non-responsiveness, also known as operational tolerance. As an alternative strategy to immunosuppression and antigen-specific tolerance inducing therapies, the primary goal of SCIIT is to re-establish or induce peripheral immune tolerance in the context of autoimmune disease and transplant rejection through the use of biological agents. In recent years, SCIIT has received increasing attention in clinical and research settings as an alternative to immunosuppressive drugs currently used in the clinic, drugs which put the patients at risk of developing infection, cancer, and cardiovascular disease.
TOL101, is a murine-monoclonal antibody specific for the human αβ T cell receptor. In 2010 it was an Investigational New Drug under development by Tolera Therapeutics, Inc.
Etrolizumab is a biopharmaceutical drug candidate being developed for the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It is a humanized monoclonal antibody against the β7 subunit of integrins α4β7 and αEβ7. Etrolizumab was developed by Genentech by engineering the FIB504 antibody to include human IgGl-heavy chain and κ-light chain frameworks; it is manufactured in CHO cells.
Shomron Ben-Horin is an Israeli physician, a co-founder & Chief Medical Officer of Evinature, and professor of medicine at the Tel-Aviv University.
Integrin α4β7 is an integrin heterodimer composed of CD49d (alpha-4) subunit and beta-7 subunit noncovalently linked. LPAM-1 is expressed on the cell surface of leukocytes. This receptor is involved in lymphocyte trafficking pathway to site of inflammation in intestinal tissues.



