Related Research Articles

In celestial mechanics, the Lagrange points are points of equilibrium for small-mass objects under the gravitational influence of two massive orbiting bodies. Mathematically, this involves the solution of the restricted three-body problem.

Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space. While the exploration of space is currently carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration is conducted both by uncrewed robotic space probes and human spaceflight. Space exploration, like its classical form astronomy, is one of the main sources for space science.

The Interplanetary Transport Network (ITN) is a collection of gravitationally determined pathways through the Solar System that require very little energy for an object to follow. The ITN makes particular use of Lagrange points as locations where trajectories through space can be redirected using little or no energy. These points have the peculiar property of allowing objects to orbit around them, despite lacking an object to orbit. While it would use little energy, transport along the network would take a long time.

In lunar astronomy, libration is the cyclic variation in the apparent position of the Moon perceived by Earth-bound observers and caused by changes between the orbital and rotational planes of the moon. It causes an observer to see slightly different hemispheres of the surface at different times. It is similar in both cause and effect to the changes in the Moon's apparent size due to changes in distance. It is caused by three mechanisms detailed below, two of which cause a relatively tiny physical libration via tidal forces exerted by the Earth. Such true librations are known as well for other moons with locked rotation.
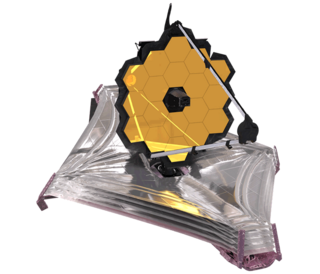
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope designed to conduct infrared astronomy. Its high-resolution and high-sensitivity instruments allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Space Telescope. This enables investigations across many fields of astronomy and cosmology, such as observation of the first stars and the formation of the first galaxies, and detailed atmospheric characterization of potentially habitable exoplanets.
In astrodynamics, orbital station-keeping is keeping a spacecraft at a fixed distance from another spacecraft or celestial body. It requires a series of orbital maneuvers made with thruster burns to keep the active craft in the same orbit as its target. For many low Earth orbit satellites, the effects of non-Keplerian forces, i.e. the deviations of the gravitational force of the Earth from that of a homogeneous sphere, gravitational forces from Sun/Moon, solar radiation pressure and air drag, must be counteracted.

The far side of the Moon is the lunar hemisphere that always faces away from Earth, opposite to the near side, because of synchronous rotation in the Moon's orbit. Compared to the near side, the far side's terrain is rugged, with a multitude of impact craters and relatively few flat and dark lunar maria ("seas"), giving it an appearance closer to other barren places in the Solar System such as Mercury and Callisto. It has one of the largest craters in the Solar System, the South Pole–Aitken basin. The hemisphere has sometimes been called the "dark side of the Moon", where "dark" means "unknown" instead of "lacking sunlight" – each location on the Moon experiences two weeks of sunlight while the opposite location experiences night.

In orbital mechanics, a Lissajous orbit, named after Jules Antoine Lissajous, is a quasi-periodic orbital trajectory that an object can follow around a Lagrangian point of a three-body system with minimal propulsion. Lyapunov orbits around a Lagrangian point are curved paths that lie entirely in the plane of the two primary bodies. In contrast, Lissajous orbits include components in this plane and perpendicular to it, and follow a Lissajous curve. Halo orbits also include components perpendicular to the plane, but they are periodic, while Lissajous orbits are usually not.

A halo orbit is a periodic, three-dimensional orbit associated with one of the L1, L2 or L3 Lagrange points in the three-body problem of orbital mechanics. Although a Lagrange point is just a point in empty space, its peculiar characteristic is that it can be orbited by a Lissajous orbit or by a halo orbit. These can be thought of as resulting from an interaction between the gravitational pull of the two planetary bodies and the Coriolis and centrifugal force on a spacecraft. Halo orbits exist in any three-body system, e.g., a Sun–Earth–orbiting satellite system or an Earth–Moon–orbiting satellite system. Continuous "families" of both northern and southern halo orbits exist at each Lagrange point. Because halo orbits tend to be unstable, station-keeping using thrusters may be required to keep a satellite on the orbit.

The Exploration Gateway Platform was a design concept proposed by Boeing in December 2011 to drastically reduce the cost of Moon, near Earth asteroids (NEAs), or Mars missions by using components already designed to construct a refueling depot and servicing station located at one of the Earth–Moon Lagrange points, L1 or L2. The system claims its cost savings based on an ability to be reused for multiple missions such as a launch platform for deep space exploration, robotic relay station for moon rovers, telescope servicing and a deep space practice platform located outside the Earth's protective radiation belts.

TRAPPIST-1b, also designated as 2MASS J23062928-0502285 b, is a mainly rocky exoplanet orbiting around the ultra-cool dwarf star TRAPPIST-1, located 40.7 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Aquarius. The planet was detected using the transit method, where a planet dims the host star's light as it passes in front of it. It was first announced on May 2, 2016, and later studies were able to refine its physical parameters.

TRAPPIST-1c, also designated as 2MASS J23062928-0502285 c, is a mainly rocky exoplanet orbiting around the ultracool dwarf star TRAPPIST-1, located 40.7 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Aquarius. It is the third most massive and third largest planet of the system, with about 131% the mass and 110% the radius of Earth. Its density indicates a primarily rocky composition, and observations by the James Webb Space Telescope announced in 2023 suggests against a thick CO2 atmosphere, however this does not exclude a thick abiotic oxygen-dominated atmosphere as is hypothesized to be common around red dwarf stars.

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is an international 21st-century space observatory that was launched on 25 December 2021. It is intended to be the premier observatory of the 2020s, combining the largest mirror yet on a near-infrared space telescope with a suite of technologically advanced instruments from around the world.

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) sunshield is a passive thermal control system deployed post-launch to shield the telescope and instrumentation from the light and heat of the Sun, Earth, and Moon. By keeping the telescope and instruments in permanent shadow, it allows them to cool to their design temperature of 40 kelvins. Its intricate deployment was successfully completed on January 4, 2022, ten days after launch, when it was more than 0.8 million kilometers (500,000 mi) away from Earth.

The spacecraft bus is a carbon fibre box that houses systems of the telescope and so is the primary support element of the James Webb Space Telescope, launched on 25 December 2021. It hosts a multitude of computing, communication, propulsion, and structural components. The other three elements of the JWST are the Optical Telescope Element (OTE), the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM) and the sunshield. Region 3 of ISIM is also inside the spacecraft bus. Region 3 includes the ISIM Command and Data Handling subsystem and the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) cryocooler.

HIP 65426 b, formally named Najsakopajk, is a super-Jupiter exoplanet orbiting the star HIP 65426. It was discovered on 6 July 2017 by the SPHERE consortium using the Spectro-Polarimetric High-Contrast Exoplanet Research (SPHERE) instrument belonging to the European Southern Observatory (ESO). It is 385 light-years from Earth. It is the first planet discovered by ESO's SPHERE instrument.

Queqiao relay satellite (Chinese: 鹊桥号中继卫星; pinyin: Quèqiáo hào zhōngjì wèixīng; lit. 'Magpie Bridge relay satellite'), is the first of the pair of communications relay and radio astronomy satellites for the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program. The China National Space Administration (CNSA) launched the Queqiao relay satellite on 20 May 2018 to a halo orbit around the Earth–Moon L2 Lagrangian point Queqiao is the first ever communication relay and radio astronomy satellite at this location.

Webb's First Deep Field is the first operational image taken by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The deep-field photograph, which covers a tiny area of sky visible from the Southern Hemisphere, is centered on SMACS 0723, a galaxy cluster in the constellation of Volans. Thousands of galaxies are visible in the image, some as old as 13 billion years. It is the highest-resolution image of the early universe ever taken. Captured by the telescope's Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), the image was revealed to the public by NASA on 11 July 2022.

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope designed primarily to conduct infrared astronomy. Its complex launch and commissioning process lasted from late 2021 until mid-2022.
References
- ↑ Pergola, P. (21 October 2012). "Libration point orbit characterization in the Earth-Moon system". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 426 (2): 1212–1222. Bibcode:2012MNRAS.426.1212P. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21585.x. S2CID 122979904 . Retrieved 20 September 2022.
- ↑ Greenhouse, Matthew (October 2011). "The James Webb Space Telescope: Mission overview and status". 2011 2nd International Conference on Space Technology. pp. 1–4. doi:10.1109/ICSpT.2011.6064655. hdl: 2060/20090026783 . ISBN 978-1-4577-1874-8. S2CID 1957332 . Retrieved 20 September 2022.
- 1 2 Dichmann, Donald J. (5 May 2014). "Stationkeeping Monte Carlo Simulation for the James Webb Space Telescope". International Symposium on Space Flight Dynamics Conference Proceeding. S2CID 51732847.