List of districts by divisions
![Map of districts of Assam, by division:
.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key>ol{margin-left:1.3em;margin-top:0}.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key>ul{margin-top:0}.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key li{page-break-inside:avoid;break-inside:avoid-column}@media(min-width:300px){.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key,.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key-wide{column-count:2}.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key-narrow{column-count:1}}@media(min-width:450px){.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key-wide{column-count:3}}
.mw-parser-output .plainlist ol,.mw-parser-output .plainlist ul{line-height:inherit;list-style:none;margin:0;padding:0}.mw-parser-output .plainlist ol li,.mw-parser-output .plainlist ul li{margin-bottom:0}
.mw-parser-output .legend{page-break-inside:avoid;break-inside:avoid-column}.mw-parser-output .legend-color{display:inline-block;min-width:1.25em;height:1.25em;line-height:1.25;margin:1px 0;text-align:center;border:1px solid black;background-color:transparent;color:black}.mw-parser-output .legend-text{}
Lower Assam
North Assam
Upper Assam
Central Assam
Barak Valley Assam districts map.svg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/2d/Assam_districts_map.svg/500px-Assam_districts_map.svg.png)
| Lower Assam division (HQ – Guwahati) | North Assam division (HQ –Tezpur) | Upper Assam division (HQ –Jorhat) | Central Assam division (HQ –Nagaon) | Barak Valley division (HQ – Silchar) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Assam, a northeastern state of India, is divided into 35 administrative geographical units called districts. Assam has 35 districts.
![Map of districts of Assam, by division:
.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key>ol{margin-left:1.3em;margin-top:0}.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key>ul{margin-top:0}.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key li{page-break-inside:avoid;break-inside:avoid-column}@media(min-width:300px){.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key,.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key-wide{column-count:2}.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key-narrow{column-count:1}}@media(min-width:450px){.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key-wide{column-count:3}}
.mw-parser-output .plainlist ol,.mw-parser-output .plainlist ul{line-height:inherit;list-style:none;margin:0;padding:0}.mw-parser-output .plainlist ol li,.mw-parser-output .plainlist ul li{margin-bottom:0}
.mw-parser-output .legend{page-break-inside:avoid;break-inside:avoid-column}.mw-parser-output .legend-color{display:inline-block;min-width:1.25em;height:1.25em;line-height:1.25;margin:1px 0;text-align:center;border:1px solid black;background-color:transparent;color:black}.mw-parser-output .legend-text{}
Lower Assam
North Assam
Upper Assam
Central Assam
Barak Valley Assam districts map.svg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/2d/Assam_districts_map.svg/500px-Assam_districts_map.svg.png)
| Lower Assam division (HQ – Guwahati) | North Assam division (HQ –Tezpur) | Upper Assam division (HQ –Jorhat) | Central Assam division (HQ –Nagaon) | Barak Valley division (HQ – Silchar) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
A district of an Indian state is an administrative geographical unit, headed by the District Commissioner (DC), which combines the offices of the District Magistrate ultimately responsible for maintaining law and order and District Collector responsible for collection of the revenue. Generally, an officer belonging to the Indian Administrative Service becomes the DC but occasionally officers belonging to the Assam Civil Service do get appointed. The DC is assisted by a number of officials belonging to different wings of the administrative services of the state.
The districts of Assam are grouped together in [Divisions of Assam, five regional divisions], headed by a Commissioner. A superintendent of Police, an officer belonging to Indian Police Service is entrusted with the responsibility of maintaining law and order and related issues. The police administration in Guwahati City is headed by the Commissioner of Police, which started functioning from 1 January 2015.


Before India's independence in 1947, Assam had 13 districts. The districts were Cachar (14 August 1832), Darrang (1833), Goalpara, Kamrup, Lakhimpur, Nagaon, Sivasagar, Jayantia parganas, Garo hills, Lushai hills, Naga hills, Sylhet and NEFA. The British India protectorate 4 princely states under Assam state were Tripura, Khasi states, Koch Bihar and Manipur (included during Independence). Sylhet district had been given to East Pakistan at the time of the Partition. After many inclusion and exclusion during the independence and later till 1972, Assam formed the present shape with its prime 7 districts. The other 6 districts curved out of Assam; Jayantia, Garo and Khasi were combined and became Meghalya State; Lushiai hills became Mizoram; Naga hills became Nagaland; NEFA became Arunachal Pradesh; the both princely states Tripura and Manipur included in Assam and later separated as state and Koch Bihar became part of West Bengal.
On 17 November 1951, United Mikir and North Cachar Hills district curved out of Golaghat, Nagaon, Cachar, Jayantia and Naga hills districts.
On 2 February 1970, Mikir Hills district curved out of North Cachar Hills.
On 2 October 1976, Dibrugarh district curved out of Lakhimpur and the Name of Mikir Hills district changed to Karbi Anglong district.
On 1 July 1983, Barpeta district curved out of Kamrup; On 14 July Sonitpur district curved out of Darrang; Jorhat district curved out of Sibsagar, Dhubri district and Kokrajhar district curved out of Goalpara; Karimganj district curved out of Cachar.
On 14 August 1985, Nalbari district curved out of Kamrup.
On 15 August 1987, Golaghat district curved out of Sibsagar.
On 29 September 1989, Hailakandi district curved out of Cachar and Bongaigaon district curved out of Goalpara and Kokrajhar. On 1 October Tinsukia district curved out of Dibrugarh. On 14 October Dhemaji district curved out of Lakhimpur and on 26 November Marigaon district curved out of Nagaon.
On 3 February 2003, Kamrup Metropolitan district curved out of Kamrup.
On 1 June 2004, Baksa district curved out of Barpeta, Nalbari, and Kamrup; on 4 June, Chirang district curved out of Bongaigaon and Kokrajhar. On 14 June, Udalguri district curved out of Darrang and Sonitpur; along with Kokrajhar district formed BTAD.
On 1 April 2010, the name of North Cachar Hills district changed to Dima Hasao.
On 15 August 2015, Tarun Gogoi, the Chief Minister of Assam, announced the formation of five new districts in the state, [1] taking the total number from 27 to 32. The five new districts are the following: [1] [2] Biswanath (carved out of Sonitpur); Charaideo (carved out of Sivasagar); Hojai (carved out of Nagaon); South Salmara-Mankachar (carved out of Dhubri); West Karbi Anglong (carved out of Karbi Anglong).
On 26 January 2016, 2 more districts were announced, but on 7 October 2016, the government has withdrawn district status of East Kamrup and South Kamrup due to inadequate infrastructure. The two sub-divisions of East Kamrup district - viz. Chandrapur and Sonapur, is now part of Kamrup Metropolitan district. The sub-divisions of South Kamrup district is now part of Kamrup Rural district.
On 27 June 2016, one more district was announced by Sarbananda Sonowal, taking the total number from 32 to 33 which is Majuli (carved out of the Northern parts of Jorhat). It is the first river island district of India. [3]
On 8 August 2020, the Assam cabinet approved a proposal to make Bajali (curved out of Barpeta) the 34th district of Assam. [4] The Assam Cabinet headed by Chief Minister Himanta Biswa Sarma approved the proposal to make Tamulpur curved out of Baksa district a full-fledged district. [5] On 23 January 2022, Tamulpur was formally declared as a 35th district of Assam. [6]
On 31 December 2022, the Assam Cabinet decided to merge four newly carved districts with existing four districts. [7] These districts were,
Assam Chief Minister Himanta Bisha Sarma said it is a temporary measure before ECI delimitation process in the state and government may reconsider it. [8]
On 25 August 2023, Assam Chief Minister Himanta Biswa Sarma announced the decision to recreate the four newly merged districts of Biswanath, Hojai, Bajali, and Tamulpur from their original districts. [9] Therefore, the total number of districts in Assam has once again become 35.
The areas and populations of the 35 districts are given below: [10] [11]
| Districts | Headquarters | Formation day | Population (2011) [12] | Area (km²) | Population Density (/km²) | Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baksa # | Mushalpur | 950,075 | 2,457 | 387 |  | |
| Bajali | Pathsala | 253,816 | 418 | 610 |  | |
| Barpeta | Barpeta | 1,693,622 | 3182 | 532 | 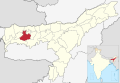 | |
| Biswanath | Biswanath Chariali | 612,491 | 1415 | 430 |  | |
| Bongaigaon | Bongaigaon | 738,804 | 1,093 | 676 |  | |
| Cachar | Silchar | 1,736,319 | 3,786 | 459 |  | |
| Charaideo [1] | Sonari [13] | 471,418 | 1,069 | 441 | 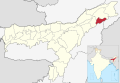 | |
| Chirang # | Kajalgaon | 482,162 | 1,170 | 412 |  | |
| Darrang | Mangaldai | 928,500 | 1,585 | 586 |  | |
| Dhemaji | Dhemaji | 14 October 1989 | 686,133 | 3,237 | 212 |  |
| Dhubri | Dhubri | 1,394,144 | 1,608 | 867 |  | |
| Dibrugarh | Dibrugarh | 2 October 1971 | 1,326,335 | 3,381 | 392 | 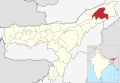 |
| Dima Hasao ## | Haflong | 214,102 | 4,890 | 44 |  | |
| Goalpara | Goalpara | 1,008,183 | 1,824 | 553 |  | |
| Golaghat | Golaghat | 15 August 1987 | 1,066,888 | 3,502 | 305 |  |
| Hailakandi | Hailakandi | 659,296 | 1,327 | 497 |  | |
| Hojai | Sankardev Nagar | 931,218 | 1,686 | 550 | 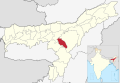 | |
| Jorhat | Jorhat | 924,952 | 2,851 | 324 |  | |
| Kamrup Metropolitan | Guwahati | 1,253,938 | 1,528 | 821 |  | |
| Kamrup | Amingaon | 1,517,542 | 3,105 | 489 |  | |
| Karbi Anglong ### | Diphu | 2 February 1970 | 660,955 | 7,366 | 90 |  |
| Sribhumi | Karimganj | 1,228,686 | 1,809 | 679 |  | |
| Kokrajhar # | Kokrajhar | 887,142 | 3,169 | 280 |  | |
| Lakhimpur | North Lakhimpur | 1,042,137 | 2,277 | 458 |  | |
| Majuli | Garamur [14] | 167,304 | 880 | 190 |  | |
| Morigaon | Morigaon | 957,423 | 1,704 | 562 |  | |
| Nagaon | Nagaon | 2,823,768 | 3,973 | 711 |  | |
| Nalbari | Nalbari | 771,639 | 2,257 | 342 |  | |
| Sivasagar | Sivasagar | 679,632 | 2,668 | 255 |  | |
| Sonitpur | Tezpur | 1,924,110 | 3,176 | 606 |  | |
| South Salmara-Mankachar [1] | Hatsingimari [15] | 555,114 | 568 | 977 |  | |
| Tamulpur | Tamulpur | 389,150 | 884 | 440 |  | |
| Tinsukia | Tinsukia | 1 October 1989 | 1,327,929 | 3,790 | 350 |  |
| Udalguri # | Udalguri | 831,688 | 1,852 | 449 |  | |
| West Karbi Anglong ### [1] | Hamren [16] | 15 August 2016 | 295,358 | 3,035 | 97 |  |
## Districts under NC Hill autonomy
### Districts under KA autonomy
{{cite web}}: |last= has generic name (help)