
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dogteeth, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. In the context of the upper jaw, they are also known as fangs. They can appear more flattened, however, causing them to resemble incisors and leading them to be called incisiform. They developed and are used primarily for firmly holding food in order to tear it apart, and occasionally as weapons. They are often the largest teeth in a mammal's mouth. Individuals of most species that develop them normally have four, two in the upper jaw and two in the lower, separated within each jaw by incisors; humans and dogs are examples. In most species, canines are the anterior-most teeth in the maxillary bone. The four canines in humans are the two upper maxillary canines and the two lower mandibular canines. They are specially prominent in dogs (Canidae), hence the name.

Permanent teeth or adult teeth are the second set of teeth formed in diphyodont mammals. In humans and old world simians, there are thirty-two permanent teeth, consisting of six maxillary and six mandibular molars, four maxillary and four mandibular premolars, two maxillary and two mandibular canines, four maxillary and four mandibular incisors.

Tooth development or odontogenesis is the process in which teeth develop and grow into the mouth. Tooth development varies among species.
Koparion is a genus of small coelurosaurian theropod dinosaur, from the late Jurassic Period, of Utah. It contains the single named species Koparion douglassi which is known only from a single isolated tooth.
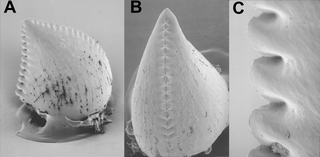
In anatomy, a heterodont is an animal which possesses more than a single tooth morphology. Human dentition is heterodont and diphyodont as an example.

Acanthothoraci is an extinct group of chimaera-like placoderms closely related to the rhenanid placoderms. Superficially, the acanthoracids resembled scaly chimaeras and (relatively) heavily armored ptyctodonts. They were distinguished from chimaeras by their large scales and plates, a pair of large spines that emanate from their chests, tooth-like beak plates, and the typical bone-enhanced placoderm eyeball. They were distinguished from other placoderms by differences in skull anatomy and by patterns on the skull plates and thoracic plates that are unique to this order.
Dens invaginatus (DI), also known as tooth within a tooth, is a rare dental malformation and a developmental anomaly where there is an infolding of enamel into dentin. The prevalence of this condition is 0.3 - 10%, affecting males more frequently than females. The condition presents in two forms, coronal involving tooth crown and radicular involving tooth root, with the former being more common.

Acrodonty is an anatomical placement of the teeth at the summit of the alveolar ridge of the jaw, without sockets, characteristic of bony fish. Functionally, acrodont tooth implantation may be related to greater bite force. However, this result is not supported when size and phylogeny is taken into account.

Dental anatomy is a field of anatomy dedicated to the study of human tooth structures. The development, appearance, and classification of teeth fall within its purview. Tooth formation begins before birth, and the teeth's eventual morphology is dictated during this time. Dental anatomy is also a taxonomical science: it is concerned with the naming of teeth and the structures of which they are made, this information serving a practical purpose in dental treatment.
In dental anatomy, the gingival fibers are the connective tissue fibers that inhabit the gingival tissue (gums) adjacent to teeth and help hold the tissue firmly against the teeth. They are primarily composed of type I collagen, although type III fibers are also involved.

Chrysochampsa is an extinct monospecific genus of caiman of the clade Brachychampsini. Fossils have been found from the Golden Valley Formation of North Dakota and date back to the Wasatchian regional North American faunal stage of the early Eocene. During this time North Dakota experienced the Early Eocene Climatic Optimum, creating lush forests, swamps and meandering rivers that were the home to at least four distinct crocodilians. Unlike the contemporary Ahdeskatanka, which was a small animal with crushing teeth, Chrysochampsa would have been a generalist and due to its size and lack of significant mammalian carnivores the apex predator of the region. The genus had been proposed to be synonymous with Allognathosuchus in 2004s, but this claim has since then been repeatedly refuted. A 2024 study has recovered it as an early branching member of the Caimaninae, forming a clade with Cretaceous forms such as Brachychampsa. Chrysochampsa is a monotypic genus, containing only the type species, Chrysochampsa mlynarskii.

A tooth is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the outermost embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm.
Gwawinapterus beardi is a species of saurodontid ray-finned fish from the Late Cretaceous period of British Columbia, Canada. While initially described as a very late-surviving member of the pterosaur family Istiodactylidae, further examination has cast doubt on the identification of the specimen as a pterosaur, and research published in 2012 identified the remains as having come from a saurodontid fish.

Henodus is an extinct placodont of the Late Triassic period during the early Carnian age. Fossils of Henodus chelyops were found in the Estherienschichten Member of the Grabfeld Formation, near Tübingen, Germany. It was around 1 metre (3.3 ft) in length. The single species within the genus is H. chelyops.

Thylacosmilidae is an extinct family of metatherian predators, related to the modern marsupials, which lived in South America between the Miocene and Pliocene epochs. Like other South American mammalian predators that lived prior to the Great American Biotic Interchange, these animals belonged to the order Sparassodonta, which occupied the ecological niche of many eutherian mammals of the order Carnivora from other continents. The family's most notable feature are the elongated, laterally flattened fangs, which is a remarkable evolutionary convergence with other saber-toothed mammals like Barbourofelis and Smilodon.

Laquintasaura is a genus of Venezuelan ornithischian dinosaur containing only the type species Laquintasaura venezuelae. It is known for being one of the most primitive ornithischians in the fossil record, as well as the first dinosaur to have been identified from Venezuela. The name is derived from the La Quinta Formation, where it was discovered and the feminine Greek suffix for lizard, with the specific name referring to the country of Venezuela. It is known from hundreds of fossil elements, all derived from a single extensive bonebed locality. Initially discovered by French palaeontologists, numerous expeditions have been conducted to excavate from the bonebed, largely led by Marcelo R Sánchez-Villagra. Once thought to represent remains of Lesothosaurus, it was formally named in a 2014 study; much of the abundant material was not yet prepared at the time and research remains ongoing.
Palacrodon is an extinct genus of Triassic reptile with a widespread distribution. It was initially described from teeth collected in Early Triassic deposits in South Africa, and later reported from the Early Triassic of Antarctica and the Late Triassic of Arizona. Although previously considered an early rhynchocephalian, it is currently considered to be a non-saurian neodiapsid.
Paradracaena is an extinct genus of lizards from northern South America. Fossils of Paradracaena colombiana have been found in the Honda Group of Colombia, Peru and Brazil. The species was described as a member of the tegus; Tupinambis huilensis by Estes in 1961.
Protenodontosaurus is an extinct genus of placodont from Italy.
Cypressaurus is an extinct genus of iguanid lizard from the Lower Oligocene of Saskatchewan. It was named in 1972 by Holman as Cypressaurus hypsodontus for jaw bones found in the Cypress Hills Formation showing unique tooth anatomy. The anatomy is very similar to the living genus Sceloporus, which Cypressaurus may be an early species of. The tooth row is 11.7 mm (0.46 in) long, with 24 very tall, pleurodont teeth.

















