
A pegmatite is an igneous rock showing a very coarse texture, with large interlocking crystals usually greater in size than 1 cm (0.4 in) and sometimes greater than 1 meter (3 ft). Most pegmatites are composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica, having a similar silicic composition to granite. However, rarer intermediate composition and mafic pegmatites are known.

Rhyolite is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral assemblage is predominantly quartz, sanidine, and plagioclase. It is the extrusive equivalent to granite.

Dacite is a volcanic rock formed by rapid solidification of lava that is high in silica and low in alkali metal oxides. It has a fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic texture and is intermediate in composition between andesite and rhyolite. It is composed predominantly of plagioclase feldspar and quartz.

Trachyte is an extrusive igneous rock composed mostly of alkali feldspar. It is usually light-colored and aphanitic (fine-grained), with minor amounts of mafic minerals, and is formed by the rapid cooling of lava enriched with silica and alkali metals. It is the volcanic equivalent of syenite.
The Llano Uplift is a geologically ancient, low geologic dome that is about 90 miles (140 km) in diameter and located mostly in Llano, Mason, San Saba, Gillespie, and Blanco counties, Texas. It consists of an island-like exposure of Precambrian igneous and metamorphic rocks surrounded by outcrops of Paleozoic and Cretaceous sedimentary strata. At their widest, the exposed Precambrian rocks extend about 65 miles (105 km) westward from the valley of the Colorado River and beneath a broad, gentle topographic basin drained by the Llano River. The subdued topographic basin is underlain by Precambrian rocks and bordered by a discontinuous rim of flat-topped hills. These hills are the dissected edge of the Edwards Plateau, which consist of overlying Cretaceous sedimentary strata. Within this basin and along its margin are down-faulted blocks and erosional remnants of Paleozoic strata which form prominent hills.

Nepheline syenite is a holocrystalline plutonic rock that consists largely of nepheline and alkali feldspar. The rocks are mostly pale colored, grey or pink, and in general appearance they are not unlike granites, but dark green varieties are also known. Phonolite is the fine-grained extrusive equivalent.

Quartz monzonite is an intrusive, felsic, igneous rock that has an approximately equal proportion of orthoclase and plagioclase feldspars. It is typically a light colored phaneritic (coarse-grained) to porphyritic granitic rock. The plagioclase is typically intermediate to sodic in composition, andesine to oligoclase. Quartz is present in significant amounts. Biotite and/or hornblende constitute the dark minerals. Because of its coloring, it is often confused with granite, but whereas granite contains more than 20% quartz, quartz monzonite is only 5–20% quartz. Rock with less than five percent quartz is classified as monzonite. A rock with more alkali feldspar is a syenite whereas one with more plagioclase is a quartz diorite. The fine grained volcanic rock equivalent of quartz monzonite is quartz latite.

Lamprophyres are uncommon, small-volume ultrapotassic igneous rocks primarily occurring as dikes, lopoliths, laccoliths, stocks, and small intrusions. They are alkaline silica-undersaturated mafic or ultramafic rocks with high magnesium oxide, >3% potassium oxide, high sodium oxide, and high nickel and chromium.

Granodiorite is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock similar to granite, but containing more plagioclase feldspar than orthoclase feldspar.

Quartz-porphyry, in layman's terms, is a type of volcanic (igneous) rock containing large porphyritic crystals of quartz. These rocks are classified as hemi-crystalline acid rocks.

Monzogranites are biotite granite rocks that are considered to be the final fractionation product of magma. Monzogranites are characteristically felsic (SiO2 > 73%, and FeO + MgO + TiO2 < 2.4), weakly peraluminous (Al2O3/ (CaO + Na2O + K2O) = 0.98–1.11), and contain ilmenite, sphene, apatite and zircon as accessory minerals. Although the compositional range of the monzogranites is small, it defines a differentiation trend that is essentially controlled by biotite and plagioclase fractionation. (Fagiono, 2002). Monzogranites can be divided into two groups (magnesio-potassic monzogranite and ferro-potassic monzogranite) and are further categorized into rock types based on their macroscopic characteristics, melt characteristics, specific features, available isotopic data, and the locality in which they are found.
Barringer Hill is a geological and mineralogical site in central Texas. It lies on the former west side of the Colorado river, beneath Lake Buchanan, about 22 miles (35 km) northeast of the town of Llano. The hill consists of a pegmatite and geologically, lies near the eastern edge of the Central Mineral Region in the Texas Hill Country. It is named for John Baringer, who discovered in it large amounts of gadolinite about 1887 (Hess).
The Mount Pleasant Caldera is a large eroded Late Devonian volcanic caldera complex, located in the northern Appalachian Mountains of southwestern New Brunswick, Canada. It is one of few noticeable pre-Cenozoic calderas, and its formation is associated to a period of crustal thinning that followed the Acadian orogeny in the northern Appalachian Mountains. It sits relatively near to the coastline.
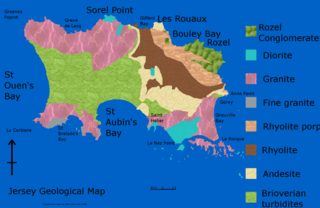
The geology of Jersey is characterised by the Late Proterozoic Brioverian volcanics, the Cadomian Orogeny, and only small signs of later deposits from the Cambrian and Quaternary periods. The kind of rocks go from conglomerate to shale, volcanic, intrusive and plutonic igneous rocks of many compositions, and metamorphic rocks as well, thus including most major types.

The Cathedral Peak Granodiorite (CPG) was named after its type locality, Cathedral Peak in Yosemite National Park, California. The granodiorite forms part of the Tuolumne Intrusive Suite, one of the four major intrusive suites within the Sierra Nevada. It has been assigned radiometric ages between 88 and 87 million years and therefore reached its cooling stage in the Coniacian.
The Piégut-Pluviers Granodiorite is situated at the northwestern edge of the Variscan Massif Central in France. Its cooling age has been determined as 325 ± 14 million years BP.
Ear Mountain is an isolated mountain located on the Seward Peninsula in the U.S. state of Alaska. The mountain, with an elevation of 2,329 feet (710 m), has a belt of Cretaceous tin "granites." Though the mountain is located in an area long known for its tin deposits, it was only in 1953 and 1954 during a survey by the US Bureau of Mines that tin deposits were confirmed to be on Ear Mountain.

The Southern Oklahoma Aulacogen(ah-lah-coh-jin) (help·info) is a failed rift, or failed rift arm (aulacogen), of the triple junction that became the Iapetus Ocean spreading ridges. It is a significant geological feature in the Western and Southern United States. It formed sometime in the early to mid Cambrian Period and spans the Wichita Mountains, Taovayan Valley, Anadarko Basin, and Hardeman Basin in Southwestern Oklahoma. The Southern Oklahoma Aulacogen is primarily composed of basaltic dikes, gabbros, and units of granitic rock.

The Lilesville Granite, also referred to as the Lilesville pluton, is a ring-shaped body of granitic rock that spans about 94 square miles (240 km2) in Anson, Richmond, and Montgomery Counties in southern North Carolina.
















