
Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center is a Chinese space vehicle launch facility (spaceport) located between the Ejin, Alxa, Inner Mongolia and Hangtian Town, Jinta County, Jiuquan, Gansu Province. It is part of the Dongfeng Aerospace City. Because 95% of JSLC located in Jinta County, Jiuquan, the launch center is named after Jiuquan. The launch center straddles both sides of the Ruo Shui river.

The space program of the People's Republic of China is about the activities in outer space conducted and directed by the People's Republic of China. The roots of the Chinese space program trace back to the 1950s, when, with the help of the newly allied Soviet Union, China began development of its first ballistic missile and rocket programs in response to the perceived American threats. Driven by the successes of Soviet Sputnik 1 and American Explorer 1 satellite launches in 1957 and 1958 respectively, China would launch its first satellite, Dong Fang Hong 1 in April 1970 aboard a Long March 1 rocket, making it the fifth nation to place a satellite in orbit.

The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) is a main contractor for the Chinese space program. It is state-owned and has subsidiaries which design, develop and manufacture a range of spacecraft, launch vehicles, and ground equipment. It also has a division for strategic and tactical missile systems.

The Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center (TSLC) also known as Base 25 (Chinese: 二十五基地), is a People's Republic of China space and defense launch facility (spaceport). It is situated in Kelan County, Xinzhou, Shanxi Province and is the second of four launch sites having been founded in March 1966 and coming into full operation in 1968.

The People's Liberation Army Rocket Force, formerly the Second Artillery Corps, is the strategic and tactical missile force of the People's Republic of China. The PLARF is the 4th branch of the People's Liberation Army (PLA) and controls China's arsenal of land-based ballistic, hypersonic, cruise missiles—both nuclear and conventional. The armed service branch was established on 1 July 1966 and made its first public appearance on 1 October 1984. The headquarters for operations is located at Qinghe, Beijing. The PLARF is under the direct command of the Chinese Communist Party's Central Military Commission (CMC).

The Wenchang Space Launch Site is a rocket launch site located in Wenchang on the island of Hainan, in China.

Beijing Aerospace Flight Control Center, formerly known as Beijing Aerospace Command and Control Center, is a command center for the Chinese space program which includes the Shenzhou missions, and is located in a suburb northwest of Beijing under the administration of Haidian District. The space center main entrance is located at the intersection of Beiqing Road and You Yi Road as shown by the photograph.

The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) is the sixth-ranked executive department of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. It is responsible for regulation and development of the postal service, Internet, wireless, broadcasting, communications, production of electronic and information goods, software industry and the promotion of the national knowledge economy.
The People's Republic of China carried out a land-based high-altitude anti-ballistic missile test on 11 January 2010. This reportedly made China the second country in the world after the United States of America to successfully destroy an incoming missile beyond the Earth's atmosphere.
The Xi'an Satellite Tracking, Telemetry, and Control Center, also known as Base 26, is the primary satellite telemetry, tracking, and control facility of the People's Republic of China. Located in the Beilin District of Xi'an, Shaanxi Province, XSCC is subordinate to the Satellite Launch, Tracking, and Control Department of the People's Liberation Army Strategic Support Force (PLASSF).

The People's Liberation Army Strategic Support Force was a service branch of the People's Liberation Army that existed from December 2015 to April 2024.

Ren Xinmin was a Chinese aerospace engineer and a specialist in astronautics and liquid rocket engine technology. He was the technical director of the Long March 1 rocket, which launched the Dong Fang Hong I, China's first satellite, and the chief designer of Chinese storable propellant rocket engine. He was also the chief designer for the Long March 3 launch vehicle, Fengyun, and SJ (Shijian) series satellites.
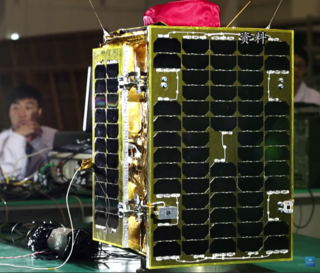
Jilin-1 is China's first self-developed commercial remote sensing satellite system. The satellites are operated by Chang Guang Satellite Technology Corporation and named after Jilin Province where the company is headquartered. The first set of satellites were launched by Long March 2D in Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center on 7 October 2015, at 04:13 UTC. All launched Jilin-1 satellites are in Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO).
Tiantong is China's first mobile communications satellite system. The first satellite Tiantong-1-01 was launched on August 6, 2016 (UTC+8).

The Hongtu-1, known commonly by its English-language name PIESAT-1 and infrequently as Nuwa-1, is a Chinese commercial X-band interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) satellite constellation performing Earth observation missions in Sun-synchronous orbit. Hongtu-1 satellites are intended to map global non-polar regions at a scale of 1:50,000 meters to produce high-precision digital surface models (DSM), likely fulfilling both commercial, scientific, and military reconnaissance tasks.

The Luoyang Electronic Equipment Test Center (洛阳电子装备试验中心), also known as the 33rd Test and Training Base of the People's Liberation Army (中国人民解放军第三十三试验训练基地) is a research and development center of the People's Liberation Army located in Luoyang, Henan) Province and is affiliated to the PLA's Aerospace Force. It is a Division Grade unit that mainly performs scientific research and defense technology development, including during the last few decades, projects related to the Chinese space program.

The China Maritime Satellite Tracking and Control Department ), MUCD 63680, is a corps deputy grade naval base located at Jiangyin City in Jiangsu Province, established in 1978 as the headquarter and home port for the Yuan Wang-class tracking ships, which are used to track rocket and missile launches, in particular the testing of the Dongfeng series ballistic missiles and Long March rockets. Since 1 January 2016, it has been subordinate to the Main Department of Satellite Launches and Orbit Tracking and Control (卫星发射测控系统部) of the Strategic Support Force, and then from April 2024, of the Aerospace Force.

The China Astronautic Scientific Research and Training Center (中国航天员科研训练中心), usually referred to as the Astronaut Center of China, located at the Beijing Space City, is the principal institution in charge of the training of astronauts and of researching all matters related to crewed space travel. It is dually affiliated to the Central Military Commission Equipment Development Department and the People's Liberation Army Aerospace Force. It is the third specialized research and training center for astronauts in the world after the Soviet/Russian Yuri Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center and the United States's Houston Space Center. Known as "the cradle of China's space heroes", the center's motto is "From here into the Universe" (“从這里走向太空”).

The Beijing Institute of Tracking and Telecommunications Technology aka BITTT is a research institution of the Aerospace Force of the People's Liberation Army. The head office is located in the Beijing Space City in the north of Haidian district. The head of the institute, Dong Guangliang (董光亮), is also the Technical Director of the Control and Communication Systems of the Manned Space Program of the PRC since September 2015. The BITTT is an observer member of the Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems.













