
In electronics, a remote control is a component of an electronic device used to operate the device from a distance, usually wirelessly. For example, in consumer electronics, a remote control can be used to operate devices such as a television set, DVD player, or other home appliance, from a short distance. A remote control is primarily a convenience feature for the user, and can allow operation of devices that are out of convenient reach for direct operation of controls. In some cases, remote controls allow a person to operate a device that they otherwise would not be able to reach, as when a garage door opener is triggered from outside or when a Digital Light Processing projector that is mounted on a high ceiling is controlled by a person from the floor level.

A flash is a device used in photography producing a flash of artificial light at a color temperature of about 5500 K to help illuminate a scene. A major purpose of a flash is to illuminate a dark scene. Other uses are capturing quickly moving objects or changing the quality of light. Flash refers either to the flash of light itself or to the electronic flash unit discharging the light. Most current flash units are electronic, having evolved from single-use flashbulbs and flammable powders. Modern cameras often activate flash units automatically.

A flashtube, also called a flashlamp, is an electric arc lamp designed to produce extremely intense, incoherent, full-spectrum white light for very short durations. Flashtubes are made of a length of glass tubing with electrodes at either end and are filled with a gas that, when triggered, ionizes and conducts a high voltage pulse to produce the light. Flashtubes are used mostly for photographic purposes but are also employed in scientific, medical, industrial, and entertainment applications.
In photography, through-the-lens (TTL) metering refers to a feature of cameras whereby the intensity of light reflected from the scene is measured through the lens; as opposed to using a separate metering window or external hand-held light meter. In some cameras various TTL metering modes can be selected. This information can then be used to set the optimal film or image sensor exposure, it can also be used to control the amount of light emitted by a flash unit connected to the camera.

The Canon F-1 is a 35 mm single-lens reflex camera produced by Canon of Japan from March 1971 until the end of 1981, at which point it had been superseded by the New F-1 launched earlier that year. The Canon FD lens mount was introduced along with the F-1, but the previous Canon FL-mount lenses and older R- series lenses were also compatible with the camera with some limitations. The Canon F-1 was marketed as a competitor to the Nikon F and Nikon F2 single lens reflex cameras by Nikon.
Canon's EOS flash system refers to the photographic flash mechanism used on Canon's film or digital EOS single-lens reflex cameras. The line was first introduced in 1987. It has gone through a number of revisions over the years, as new flash exposure metering systems have been introduced. The main light-metering technologies are known as A-TTL, E-TTL, and E-TTL II.

The Leica R8 & R9 are manual focus 35 mm single-lens reflex cameras produced by the German firm Leica as the final models of their R series. Development of the R8 began in 1990:
the camera was introduced at the 1996 photokina trade show, and was succeeded by the similar Leica R9 in 2002.

A remote camera is a camera placed by a photographer in areas where the photographer generally cannot be at the camera to snap the shutter. This includes areas with limited access, tight spaces where a person is not allowed, or just another angle so that the photographer can simultaneously take pictures of the same moment from different locations.
A monolight is a self-contained photographic flash lighting unit usually found in a studio. Each monolight has its own independent power source. It does not depend on a centralized power supply as a "pack and head" system does. Monolights are also independently controlled: each has its own power settings and light output. Flash power is predominantly measured by the industry in watt seconds, which is unit-equivalent to the joule.

The Nikon D90 is a 12.3 megapixel digital single-lens reflex camera (DSLR) model announced by Nikon on August 27, 2008. It is a prosumer model that replaces the Nikon D80, fitting between the company's entry-level and professional DSLR models. It has a Nikon DX format crop sensor.

iISO flash shoe is the unofficial name for the proprietary accessory flash attachment and control interface used on Minolta cameras since the i-series introduced in 1988, and subsequently Konica Minolta and later Sony α DSLRs and NEX-7 up to 2012. Sony called it the Auto-lock Accessory Shoe (AAS). In order to speed up and enhance attachment, detachment and latching, it departs from the conventional circa-1913 mechanical design that is now standardized as ISO 518:2006 and used by other camera systems, including Canon, Nikon, Pentax, Olympus, and Leica.

The Nikon D3100 is a 14.2-megapixel DX format DSLR Nikon F-mount camera announced by Nikon on August 19, 2010. It replaced the D3000 as Nikon's entry level DSLR. It introduced Nikon's new EXPEED 2 image processor and was the first Nikon DSLR featuring full high-definition video recording with full-time autofocus and H.264 compression, instead of Motion JPEG compression. It was also the first Nikon DSLR to provide high-definition video recording at more than one frame rate.

The Nikon D7000 is a 16.2-megapixel digital single-lens reflex camera (DSLR) model announced by Nikon on September 15, 2010. At the time of announcement, it replaced the outdated D300/D300s & D90. The D7000 offers numerous professional-style features over the D90, such as magnesium alloy body construction, weather and moisture sealing, a 2,016-segment color exposure meter, built-in timed interval exposure features, 39 rather than 11 focus points, dual SD memory card slots, virtual horizon and compatibility with older non-CPU autofocus and manual-focus AI and AI-S Nikon F-mount lenses as well as tilt-shift PC-E lenses. Other built-in features are a wireless flash commander, two user-customizable modes, full HD video with autofocus and mono audio, automatic correction of lateral chromatic aberration and support for GPS and WLAN.

The Nikon D5100 is a 16.2-megapixel DX-format DSLR F-mount camera announced by Nikon on April 5, 2011. It features the same 16.2-megapixel CMOS sensor as the D7000 with 14-bit depth, while delivering Full HD 1080p video mode at either 24, 25 or 30fps. The D5100 is the first Nikon DSLR to offer 1080p video at a choice of frame rates; previous Nikon DSLRs that recorded 1080p only did so at 24 fps. It replaces the D5000 and was replaced by the D5200.
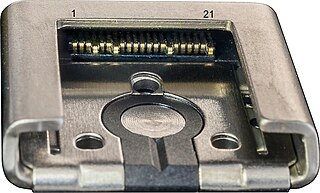
The Multi Interface Shoe is a proprietary camera hotshoe introduced by Sony in 2012, replacing an assortment of other proprietary hotshoes used by Sony in various types of cameras in the past.

The Olympus OM-D E-M10 was the third model in the OM-D series of compact, mirrorless, interchangeable-lens cameras. It is of the Micro Four Thirds type and was introduced in January 2014.
Cactus is a brand owned by Harvest One Limited, a Hong Kong company specialized in the design and engineering of photographic wireless lighting equipment including wireless flash triggers, wireless flashes, portable softboxes and studio umbrellas. Its headquarters is in Tuen Mun, Hong Kong.




















