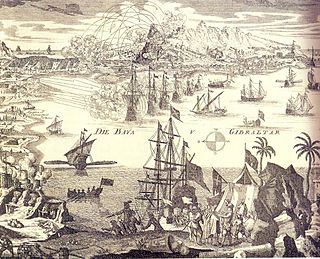
The siege of Gibraltar of 1727 saw Spanish forces besiege the British garrison of Gibraltar as part of the Anglo-Spanish War. Depending on the sources, Spanish troops numbered between 12,000 and 25,000. British defenders were 1,500 at the beginning of the siege, increasing up to about 5,000. After a five-month siege with several unsuccessful and costly assaults, Spanish troops gave up and withdrew. Following the failure the war drew to a close, opening the way for the 1728 Treaty of El Pardo and the Treaty of Seville signed in 1729.

The North Bastion, formerly the Baluarte San Pablo was part of the fortifications of Gibraltar, in the north of the peninsula, protecting the town against attack from the mainland of Spain. The bastion was based on the older Giralda tower, built in 1309. The bastion, with a mole that extended into the Bay of Gibraltar to the west and a curtain wall stretching to the Rock of Gibraltar on its east, was a key element in the defenses of the peninsula. After the British took Gibraltar in 1704 they further strengthened these fortifications, flooding the land in front and turning the curtain wall into the Grand Battery.

Princess Royal's Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located on Willis's Plateau at the northern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, just southeast of Princess Anne's Battery. Formerly known as Willis' Battery, and later, Queen Anne's Battery or Queen's Battery, it was renamed in the late 18th century after Charlotte, Princess Royal, the eldest daughter of George III. The battery was active from the early 18th century until at least the mid-20th century. However, it has been decommissioned and guns are no longer present. Princess Royal's Battery is listed with the Gibraltar Heritage Trust.

Middle Hill is a hill in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located at the northern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve. It figured prominently in the early history of the 1704 siege of Gibraltar by the Spanish and French. The artillery battery at Middle Hill had been constructed by 1727 and was active for more than two centuries. In the mid twentieth century, Middle Hill transitioned to use as an aerial farm for the Ministry of Defence. The radio farm was refurbished in 1958. About 1970, the Princess Caroline's Battery Group of Barbary macaques were moved to Middle Hill, where they were provisioned at a group of derelict buildings that were part of the battery complex. In 2005, much of Middle Hill was transferred from the Ministry of Defence to the Government of Gibraltar, and is now managed by the Gibraltar Ornithological and Natural History Society.

Middle Hill Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located on Middle Hill, at the northeastern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, just south of Green's Lodge Battery and Rock Gun Battery. The emplacement dates to 1727, when a single gun was mounted. By the turn of the twentieth century, six 10-inch rifled muzzle-loading guns were present at Middle Hill Battery. Other buildings documented at that time as part of the battery complex included the Nursery Hut and the Middle Hill Group, the latter a cluster of buildings which perched on the cliff edge. An anti-aircraft Bofors gun had been installed at the battery by the Second World War. After the war, the area transitioned to use as a Ministry of Defence aerial farm. In 2005, the battery and surrounding area were transferred to the Government of Gibraltar. The site is now managed by the Gibraltar Ornithological and Natural History Society.

Farringdon's Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. Named after Sir Anthony Farrington, 1st Baronet, it is located above the north face of the Rock of Gibraltar within the Upper Rock Nature Reserve.

Devil's Tongue Battery was an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The battery could overlook the harbour but the remains are now surrounded by reclaimed land.

The Europa Batteries are a group of artillery batteries in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. Facing the North African coast, they are the most southerly batteries in Gibraltar and were built to cover ships approaching from the Mediterranean Sea. They run along the fortified clifftops of Europa Point from Camp Bay on the west side of the Rock of Gibraltar to the Europa Advance Batteries on the east side.

Forbes' Batteries are a pair of artillery batteries in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The batteries are casemated.

Gardiner's Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is named after the governor Sir Robert Gardiner.

Hanover Battery was an artillery battery on the north west part of the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The battery is casemated. Beneath the battery was a tunnel known as Hanover Gallery.
Jones' Battery is one of the best preserved of the "retired" artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It was named after Sir John Thomas Jones who once controlled the fortifications here.

Signal Hill Battery or Signal Battery was an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The battery was mounted high on the rock. Little remains today as the Gibraltar Cable Car top station was built on the site of the old battery.

Harding's Battery is a restored artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located at Europa Point and includes the Europa Sunken Magazine that is now used as a visitor centre.
Civil Hospital Battery was an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar.
Lady Augusta's Battery was an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar.
Willis' Battery is a former artillery battery on the north side of the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It overlooks the isthmus between Spain and Gibraltar.
Woodford's Battery was an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located at Europa Flats between the Defensible Barracks and the Officer's Barracks and Eliott's Battery.
Princess Charlotte's Battery was an artillery battery built in Gibraltar during the 18th century. It was constructed in the Willis's Plateau area on the upper northern slopes of the Rock of Gibraltar. Formerly called Catalan Battery, it was renamed after Sophia Charlotte of Hanover, the wife of King Frederick I of Prussia, who was the brother of King George I of Great Britain. The battery saw service in the Thirteenth Siege of Gibraltar in 1727 and inflicted substantial damage on the attacking Spanish forces. By 1773 it had two 12-pdr guns. Its armament was upgraded to four 24-pdrs in 1834, and from 1885 to 1889 it mounted two 64-pdr rifled muzzle loaders.

The Queen's Lines are a set of fortified lines, part of the fortifications of Gibraltar, situated on the lower slopes of the north-west face of the Rock of Gibraltar. They occupy a natural ledge which overlooks the landward entrance to Gibraltar and were an extension to the north-east of the King's Lines. They run from a natural fault called the Orillon to a cliff above the modern Laguna Estate, which stands on the site of the Inundation, an artificial lake created to obstruct landward access to Gibraltar. The Prince's Lines run immediately behind and above them on a higher ledge. All three of the Lines were constructed to enfilade attackers approaching Gibraltar's Landport Front from the landward direction.















