Parson's Lodge Battery is a coastal battery and fort in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar.

Princess Anne's Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located on Willis's Plateau at the northern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, above Princess Caroline's Battery. It was named after Anne, Princess Royal and Princess of Orange, the eldest daughter of George II. However, its name is often confused with those of other batteries in the area. In 1732, guns were first mounted on the battery, which also saw action during the Great Siege of Gibraltar. Princess Anne's Battery was updated in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, with the latter modernisation entailing the installation of four QF 5.25 inch guns with both anti-aircraft and coastal defence capabilities. The battery was manned into the early 1980s, after which it was decommissioned. The guns were refurbished in the early twenty-first century, and represent the world's only intact battery of 5.25 inch anti-aircraft guns. Princess Anne's Battery is listed with the Gibraltar Heritage Trust.

O'Hara's Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located at the highest point of the Rock of Gibraltar, near the southern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, in close proximity to Lord Airey's Battery. It was constructed in 1890 at the former site of a watchtower that had earned the name O'Hara's Folly. The battery and tower were both named after the Governor of Gibraltar Charles O'Hara. The first gun mounted on the battery was a 6-inch breech loading gun, which was replaced with a 9.2 inch Mark X BL gun in 1901. The battery was in use during World War II and was last fired during training exercises in 1976. O'Hara's Battery has been refurbished and is open to the public. The battery and its associated works are listed with the Gibraltar Heritage Trust.

Princess Amelia's Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located on Willis's Plateau at the northern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, adjacent to Gun No. 4 of Princess Anne's Battery. It was named after Princess Amelia of Great Britain, the second daughter of George II. It was formerly referred to as the 2nd Willis's Battery. The plateau and its batteries had previously been named after an artillery officer by the name of Willis who was outstanding during the capture of Gibraltar in 1704. Princess Amelia's Battery saw action during the Great Siege of Gibraltar, during which it sustained substantial damage. Little remains of the original site, aside from two derelict buildings. The battery is listed with the Gibraltar Heritage Trust.

Lord Airey's Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located near the southern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, just north of O'Hara's Battery. It was named after the Governor of Gibraltar, General Sir Richard Airey. Construction of the battery was completed in 1891. The first gun mounted on the battery was a 6-inch breech loading gun, which was replaced with a 9.2-inch Mark X BL gun by 1900. The gun at the battery was last fired in the 1970s. In 1997, it was discovered that Lord Airey's Shelter, adjacent to Lord Airey's Battery, was the site chosen for a covert World War II operation that entailed construction of a cave complex in the Rock of Gibraltar, to serve as an observation post. The battery is listed with the Gibraltar Heritage Trust.

Princess Royal's Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located on Willis's Plateau at the northern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, just southeast of Princess Anne's Battery. Formerly known as Willis's Battery, and later, Queen Anne's Battery or Queen's Battery, it was renamed in the late 18th century after Charlotte, Princess Royal, the eldest daughter of George III. The battery was active from the early 18th century until at least the mid-20th century. However, it has been decommissioned and guns are no longer present. Princess Royal's Battery is listed with the Gibraltar Heritage Trust.

Levant Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located on Windmill Hill, at the southern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, below observation post Fire Control South. It was named after the Levanter cloud, below which it perched, giving it an unobstructed view. Construction started in 1901 and, by 1903, a 9.2-inch Mark X breech-loading gun had been mounted. The battery was decommissioned in the 1970s and the gun was later removed, to rest in a scrap yard. A community group has been formed to garner support for the gun's recovery and restoration.

Rock Gun Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located on the North Face of the Rock of Gibraltar at the northern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, above Green's Lodge Battery. The emplacement on Middle Hill is at the northern summit of the Rock. It was constructed during the Great Siege of Gibraltar, due to its advantageous position and the success of the gun at Green's Lodge Battery. It was used effectively during the Great Siege and was rebuilt during the Second World War. During the mid-twentieth century, the Ministry of Defence began to use the site as an aerial farm, which was then refurbished in 1958. The Rock Gun Battery and the Middle Hill Battery were closed to the public for decades. In 2005, the radio farm was closed and the Ministry of Defence withdrew from most of the area, transferring it to the Government of Gibraltar. However, the summit, the site of the Rock Gun Battery, continues to be under MOD authority.
Lord Airey's Shelter is a subterranean military shelter in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located near the southern end of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve, adjacent to Lord Airey's Battery. It was named after the Governor of Gibraltar, General Sir Richard Airey. The tunnel system for the shelter was chosen as the site for the highly classified, Second World War military operation known as Operation Tracer.

Hanover Battery was an artillery battery on the north west part of the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The battery is casemated. Beneath the battery was a tunnel known as Hanover Gallery.

Hayne's Cave Battery is the remains of two gun positions that made up an artillery battery on the west side of the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar at Hayne's Cave. Gun emplacements can still be visited at this cave.

The Orillon Batteries were artillery batteries in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The batteries were three-storey gun positions within a natural fault in the Rock of Gibraltar.

Raglan's Battery was an artillery battery overlooking the harbour in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. During World War II the Raglan Battery Shelter was here.

Signal Hill Battery or Signal Battery was an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The battery was mounted high on the rock. Little remains today as the Gibraltar Cable Car top station was built on the site of the old battery.

Spy Glass Battery or Spyglass Battery was originally a high angle artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The battery is mounted high on the rock to give extra range and protection. The battery was still in use during the Second World War as a listening post and site for a Bofors Gun.
Genista Battery is an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar.

Lathbury Barracks was a military barracks in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar now used by civilians. It is located in the southern part of the Rock, south of Spur Battery on Windmill Hill. The last United Kingdom regiment was the 3rd Battalion Royal Green Jackets who handed it over to the local Royal Gibraltar Regiment and it is now owned by the Government of Gibraltar.

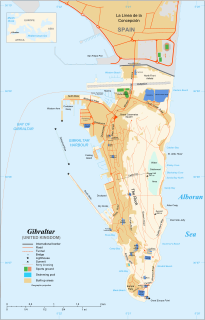
The fortifications of Gibraltar have made the Rock of Gibraltar and its environs "probably the most fought over and most densely fortified place in Europe, and probably, therefore, in the world", as Field Marshal Sir John Chapple has put it. The Gibraltar peninsula, located at the far southern end of Iberia, has great strategic importance as a result of its position by the Strait of Gibraltar where the Mediterranean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean. It has repeatedly been contested between European and North African powers and has endured fourteen sieges since it was first settled in the 11th century. The peninsula's occupants – Moors, Spanish, and British – have built successive layers of fortifications and defences including walls, bastions, casemates, gun batteries, magazines, tunnels and galleries. At their peak in 1865, the fortifications housed around 681 guns mounted in 110 batteries and positions, guarding all land and sea approaches to Gibraltar. The fortifications continued to be in military use until as late as the 1970s and by the time tunnelling ceased in the late 1960s, over 34 miles (55 km) of galleries had been dug in an area of only 2.6 square miles (6.7 km2).

The Great North Road is a large road tunnel in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It was constructed by the British military during World War II inside the Rock of Gibraltar and remains property of the Ministry of Defence to this day. The road allowed lorries to travel from the north to the south of Gibraltar entirely within the Rock. The tunnel still contains the remains of World War II buildings such as Nissen huts, kitchens, offices as well as a generating station and period anti-submarine nets.