Garrison Point Fort is a former artillery fort situated at the end of the Garrison Point peninsula at Sheerness on the Isle of Sheppey in Kent. Built in the 1860s in response to concerns about a possible French invasion, it was the last in a series of artillery batteries that had existed on the site since the mid-16th century. The fort's position enabled it to guard the strategic point where the River Medway meets the Thames. It is a rare example of a two-tiered casemated fort – one of only two of that era in the country – with a design that is otherwise similar to that of several of the other forts along the lower Thames. It remained operational until 1956 and is now used by the Sheerness Docks as a port installation.

Shornemead Fort is a now-disused artillery fort that was built in the 1860s to guard the entrance to the Thames from seaborne attack. Constructed during a period of tension with France, it stands on the south bank of the river at a point where the Thames curves sharply north and west, giving the fort long views up and downriver in both directions. It was the third fort constructed on the site since the 18th century, but its location on marshy ground led to major problems with subsidence. The fort was equipped for a time with a variety of large-calibre artillery guns which were intended to support two other nearby Thamesside forts. However, the extent of the subsidence meant that it became unsafe for the guns to be fired and the fort was disarmed by the early 20th century.

The Royal Commission on the Defence of the United Kingdom was a committee formed in 1859 to enquire into the ability of the United Kingdom to defend itself against an attempted invasion by a foreign power, and to advise the British Government on the remedial action required. The appointment of the Commission had been prompted by public concern about the growing military and naval power of the French Empire and was instigated by the Prime Minister, Henry Temple, 3rd Viscount Palmerston, who came to be closely associated with the project. In the following year, the Commission's report recommended a huge programme of fortification to defend the country's arsenals and naval bases. Many of the recommendations were acted upon; however, the great expense, the length of time taken to complete the various works and their perceived usefulness were all subjects of critical political, press and public debate.

The Victoria Lines, originally known as the North West Front, are a line of fortifications that spans 12 kilometres along the width of Malta, dividing the north of the island from the more heavily populated south.

The North Bastion, formerly the Baluarte San Pablo was part of the fortifications of Gibraltar, in the north of the peninsula, protecting the town against attack from the mainland of Spain. The bastion was based on the older Giralda tower, built in 1309. The bastion, with a mole that extended into the Bay of Gibraltar to the west and a curtain wall stretching to the Rock of Gibraltar on its east, was a key element in the defenses of the peninsula. After the British took Gibraltar in 1704 they further strengthened these fortifications, flooding the land in front and turning the curtain wall into the Grand Battery.

Jumper's Bastion may refer to one of two adjacent bastions in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. They were both created in 1785 on the sites of previous constructions and named for a British Captain who was one on the first on shore during the Capture of Gibraltar in 1704.

The Europa Batteries are a group of artillery batteries in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. Facing the North African coast, they are the most southerly batteries in Gibraltar and were built to cover ships approaching from the Mediterranean Sea. They run along the fortified clifftops of Europa Point from Camp Bay on the west side of the Rock of Gibraltar to the Europa Advance Batteries on the east side.
Woodford's Battery was an artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located at Europa Flats between the Defensible Barracks and the Officer's Barracks and Eliott's Battery.

The Gibraltar peninsula, located at the far southern end of Iberia, has great strategic importance as a result of its position by the Strait of Gibraltar where the Mediterranean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean. It has repeatedly been contested between European and North African powers and has endured fourteen sieges since it was first settled in the 11th century. The peninsula's occupants – Moors, Spanish, and British – have built successive layers of fortifications and defences including walls, bastions, casemates, gun batteries, magazines, tunnels and galleries. At their peak in 1865, the fortifications housed around 681 guns mounted in 110 batteries and positions, guarding all land and sea approaches to Gibraltar. The fortifications continued to be in military use until as late as the 1970s and by the time tunnelling ceased in the late 1960s, over 34 miles (55 km) of galleries had been dug in an area of only 2.6 square miles (6.7 km2).

The Inundation was a flooded and fortified area of ground on the sandy isthmus between Spain and Gibraltar, created by the British in the 18th century to restrict access to the territory as part of the fortifications of Gibraltar. It was originally a marshy area known as the Morass at the far south-western end of the isthmus, occupying the area adjacent to the north-western flank of the Rock of Gibraltar. The Morass was dug out and expanded to create an artificial lake which was further obstructed by iron and wooden obstacles in the water. Two small fortifications on either side controlled access to Gibraltar. The only road to and from the town ran along a narrow causeway between the Inundation and the sea which was enfiladed by batteries mounted on the lower slopes of the Rock. The Inundation existed for about 200 years before it was infilled and built over after the Second World War.

The Lines of Contravallation of Gibraltar, known in English as the "Spanish Lines", were a set of fortifications built by the Spanish across the northern part of the isthmus linking Spain with Gibraltar. They later gave their name to the Spanish town of La Línea de la Concepción. The Lines were constructed after 1730 to establish a defensive barrier across the peninsula, with the aim of preventing any British incursions, and to serve as a base for fresh Spanish attempts to retake Gibraltar. They played an important role in the Great Siege of Gibraltar between 1779 and 1783 when they supported the unsuccessful French and Spanish assault on the British-held fortress. The siege was ended after the lines of contravallation were attacked by British and Dutch forces under the command of the Governor of Gibraltar, General Augustus Eliot. The attack caused the Spanish forces to retreat and abandon the fortifications and the combined British led forces virtually destroyed all the Spanish gun batteries and the enemy cannon and munitions either captured or destroyed. This attack is still commemorated to this day and is known as 'Sortie Day'.

The King's Lines are a walled rock-cut trench on the lower slopes of the north-west face of the Rock of Gibraltar. Forming part of the Northern Defences of the fortifications of Gibraltar, they were originally created some time during the periods when Gibraltar was under the control of the Moors or Spanish. They are depicted in a 1627 map by Don Luis Bravo de Acuña, which shows their parapet following a tenaille trace. The lines seem to have been altered subsequently, as maps from the start of the 18th century show a more erratic course leading from the Landport, Gibraltar's main land entrance, to the Round Tower, a fortification at their western end. A 1704 map by Johannes Kip calls the Lines the "Communication Line of the Round Tower".

The Prince's Lines are part of the fortifications of Gibraltar, situated on the lower slopes of the north-west face of the Rock of Gibraltar. They are located at a height of about 70 feet (21 m) on a natural ledge above the Queen's Lines, overlooking the landward entrance to Gibraltar, and run from a natural fault called the Orillon to a cliff at the southern end of the isthmus linking Gibraltar with Spain. The lines face out across the modern Laguna Estate, which stands on the site of the Inundation, an artificial lake created to obstruct landward access to Gibraltar. They were constructed to enfilade attackers approaching Gibraltar's Landport Front from the landward direction.

Windmill Hill or Windmill Hill Flats is one of a pair of plateaux, known collectively as the Southern Plateaux, at the southern end of the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It is located just to the south of the Rock of Gibraltar, which descends steeply to the plateau. Windmill Hill slopes down gently to the south with a height varying from 120 metres (390 ft) at the north end to 90 metres (300 ft) at the south end. It covers an area of about 19 hectares, though about 6 hectares at the north end is built over. The plateau is ringed to the south and east with a line of cliffs which descend to the second of the Southern Plateaux, Europa Flats, which is itself ringed by sea cliffs. Both plateaux are the product of marine erosion during the Quaternary period and subsequent tectonic uplift. Windmill Hill was originally on the shoreline and its cliffs were cut by the action of waves, before the ground was uplifted and the shoreline moved further out to the edge of what is now Europa Flats.
The Retrenched Barracks was a fortified barracks located at Windmill Hill in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It stands to the north of the southern tip of Gibraltar, Europa Point, which was long felt to be potentially vulnerable to a surprise attack from the sea and was heavily fortified with gun batteries, perimeter walls and scarped cliffs.
The University of Gibraltar is a degree-awarding higher education institution established by the Government of Gibraltar through the University of Gibraltar Act 2015. The founding of the university was described by Gibraltar's Chief Minister Fabian Picardo as "a coming-of-age" for the British Overseas Territory.
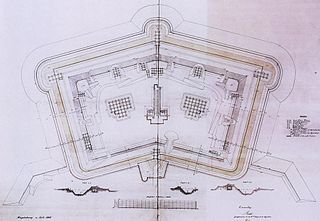
A polygonal fort is a type of fortification originating in France in the late 18th century and fully developed in Germany in the first half of the 19th century. Unlike earlier forts, polygonal forts had no bastions, which had proved to be vulnerable. As part of ring fortresses, polygonal forts were generally arranged in a ring around the place they were intended to protect, so that each fort could support its neighbours. The concept of the polygonal fort proved to be adaptable to improvements in the artillery which might be used against them, and they continued to be built and rebuilt well into the 20th century.

Imperial fortress was the designation given in the British Empire to four colonies that were located in strategic positions from each of which Royal Navy squadrons could control the surrounding regions and, between them, much of the planet.