
New Tavern Fort is an historic artillery fort in Gravesend, Kent. Dating mostly from the 18th and 19th centuries, it is an unusually well-preserved example of an 18th-century fortification and remained in use for defensive purposes until the Second World War. It was built during the American War of Independence to guard the Thames against French and Spanish raiders operating in support of the newly formed United States of America. It was redesigned and rebuilt in the mid-19th century to defend against a new generation of iron-clad French warships.

Fort Ricasoli is a bastioned fort in Kalkara, Malta, which was built by the Order of Saint John between 1670 and 1698. The fort occupies a promontory known as Gallows' Point and the north shore of Rinella Bay, commanding the entrance to the Grand Harbour along with Fort Saint Elmo. It is not only the largest fort in Malta but also the largest in Europe, and it has been on the tentative list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites since 1998, as part of the Knights' Fortifications around the Harbours of Malta.
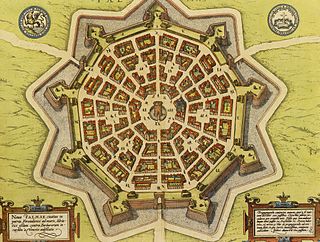
A bastion fort or trace italienne is a fortification in a style that evolved during the early modern period of gunpowder when the cannon came to dominate the battlefield. It was first seen in the mid-fifteenth century in Italy. Some types, especially when combined with ravelins and other outworks, resembled the related star fort of the same era.

Parson's Lodge Battery is a coastal battery and fort in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar.

The Line Wall Curtain is a defensive curtain wall that forms part of the fortifications of the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar.

Flat Bastion is a bastion which projects southward from the Charles V Wall in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. Once known as the St. Jago's Bastion or the Baluarte de Santiago in Spanish, the fortification was built by the Spanish in the mid 16th century and formed part of the southern defences of the city of Gibraltar, together with Charles V Wall, Southport Gates, Southport Ditch, and South Bastion. In 1859, six guns, four 12-pounders and two 12-pound carronades, were installed on the bastion, and four years later, five 32-pounders were mounted on the fortification.

The Southport Gates are three city gates in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. They are located in the Charles V Wall, one of the 16th century fortifications of Gibraltar. The gates are clustered together, with the South Bastion to the west, and the Trafalgar Cemetery to the east. The first and second Southport Gates were constructed at present day Trafalgar Road in 1552 and 1883, respectively. The third gate, Referendum Gate, is the widest of the three and was constructed in 1967 at Main Street, immediately west of the first two gates. The Southport Gates are listed with the Gibraltar Heritage Trust.

The North Bastion, formerly the Baluarte San Pablo was part of the fortifications of Gibraltar, in the north of the peninsula, protecting the town against attack from the mainland of Spain. The bastion was based on the older Giralda tower, built in 1309. The bastion, with a mole that extended into the Bay of Gibraltar to the west and a curtain wall stretching to the Rock of Gibraltar on its east, was a key element in the defenses of the peninsula. After the British took Gibraltar in 1704 they further strengthened these fortifications, flooding the land in front and turning the curtain wall into the Grand Battery.

The Montagu Bastion is one of many bastions which were designed to protect Gibraltar. Montagu was joined to Orange Bastion by a curtain wall known as Montagu Curtain and this bastion was protected by the Montagu Counterguard.

King's Bastion is a coastal bastion on the western front of the fortifications of the British overseas territory of Gibraltar, protruding from the Line Wall Curtain. It is located between Line Wall Road and Queensway and overlooks the Bay of Gibraltar. It played a crucial role in defending The Rock during the Great Siege of Gibraltar. In more recent history the bastion was converted into a generating station which powered Gibraltar's electricity needs. Today it continues to serve the community as Gibraltar's leisure centre.

Wellington Front is a fortification in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It was built in 1840 on a site established by the Spanish in 1618.

Zoca Flank Battery is an artillery battery on the west side of the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar.

Alexandra Battery is a coastal artillery battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It was constructed at the neck of the South Mole to enfilade the coastal fortifications of Gibraltar. The battery stood on the site of several previous fortifications; it was built over the New Mole Battery, which was itself constructed on the site of an old Spanish fort in front of the Tuerto Tower.

The Gibraltar peninsula, located at the far southern end of Iberia, has great strategic importance as a result of its position by the Strait of Gibraltar where the Mediterranean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean. It has repeatedly been contested between European and North African powers and has endured fourteen sieges since it was first settled in the 11th century. The peninsula's occupants – Moors, Spanish, and British – have built successive layers of fortifications and defences including walls, bastions, casemates, gun batteries, magazines, tunnels and galleries. At their peak in 1865, the fortifications housed around 681 guns mounted in 110 batteries and positions, guarding all land and sea approaches to Gibraltar. The fortifications continued to be in military use until as late as the 1970s and by the time tunnelling ceased in the late 1960s, over 34 miles (55 km) of galleries had been dug in an area of only 2.6 square miles (6.7 km2).

The Lines of Contravallation of Gibraltar, known in English as the "Spanish Lines", were a set of fortifications built by the Spanish across the northern part of the isthmus linking Spain with Gibraltar. They later gave their name to the Spanish town of La Línea de la Concepción. The Lines were constructed after 1730 to establish a defensive barrier across the peninsula, with the aim of preventing any British incursions, and to serve as a base for fresh Spanish attempts to retake Gibraltar. They played an important role in the Great Siege of Gibraltar between 1779 and 1783 when they supported the unsuccessful French and Spanish assault on the British-held fortress. The siege was ended after the lines of contravallation were attacked by British and Dutch forces under the command of the Governor of Gibraltar, General Augustus Eliot. The attack caused the Spanish forces to retreat and abandon the fortifications and the combined British led forces virtually destroyed all the Spanish gun batteries and the enemy cannon and munitions either captured or destroyed. This attack is still commemorated to this day and is known as 'Sortie Day'.

Prince Albert's Front is a curtain wall that formerly comprised part of the seafront fortifications of Gibraltar. It runs between the King's Bastion and Orange Bastion. The Front was constructed in 1842 after a report by Major General Sir John Thomas Jones recommended improving Gibraltar's seafront defences to guard against the threat of an amphibious assault. It was named after Prince Albert, Queen Victoria's prince consort. The Front straightened out the line of Gibraltar's coastal curtain wall; parts of the original curtain wall, some of which dates from the Moorish period over 500 years ago, can still be seen.

The Prince's Lines are part of the fortifications of Gibraltar, situated on the lower slopes of the north-west face of the Rock of Gibraltar. They are located at a height of about 70 feet (21 m) on a natural ledge above the Queen's Lines, overlooking the landward entrance to Gibraltar, and run from a natural fault called the Orillon to a cliff at the southern end of the isthmus linking Gibraltar with Spain. The lines face out across the modern Laguna Estate, which stands on the site of the Inundation, an artificial lake created to obstruct landward access to Gibraltar. They were constructed to enfilade attackers approaching Gibraltar's Landport Front from the landward direction.

The counterguard is an outwork in a bastioned fortification system that usually comprises only a low rampart and which is sited in front of the actual fortress moat that runs around the bastions or ravelins. The rampart way of a counterguard is, however, so constructed and at least wide enough that it enables the positioning of guns. An additional ditch in front of it guards the work from a frontal enemy assault. The function of counterguards was to protect the higher ravelin or bastion behind it from direct fire and to delay an attack on it as long as possible. So that the counterguards and the works that they were to protect, could not come under simultaneous fire along the line of the rampart they were not allowed to run parallel to one another.

The fortifications of Valletta are a series of defensive walls and other fortifications which surround Valletta, the capital city of Malta. The first fortification to be built was Fort Saint Elmo in 1552, but the fortifications of the city proper began to be built in 1566 when it was founded by Grand Master Jean de Valette. Modifications were made throughout the following centuries, with the last major addition being Fort Lascaris which was completed in 1856. Most of the fortifications remain largely intact today.

The fortifications of Birgu are a series of defensive walls and other fortifications which surround the city of Birgu, Malta. The first fortification to be built was Fort Saint Angelo in the Middle Ages, and the majority of the fortifications were built between the 16th and 18th centuries by the Order of Saint John. Most of the fortifications remain largely intact today.






















