
Enterobacteriaceae is a large family of Gram-negative bacteria. It includes over 30 genera and more than 100 species. Its classification above the level of family is still a subject of debate, but one classification places it in the order Enterobacterales of the class Gammaproteobacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota. In 2016, the description and members of this family were emended based on comparative genomic analyses by Adeolu et al.

Rickettsia is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci, bacilli, or threads. The genus was named after Howard Taylor Ricketts in honor of his pioneering work on tick-borne spotted fever.
The Chloroflexia are a class of bacteria in the phylum Chloroflexota. Chloroflexia are typically filamentous, and can move about through bacterial gliding. It is named after the order Chloroflexales.

The Chlamydiota are a bacterial phylum and class whose members are remarkably diverse, including pathogens of humans and animals, symbionts of ubiquitous protozoa, and marine sediment forms not yet well understood. All of the Chlamydiota that humans have known about for many decades are obligate intracellular bacteria; in 2020 many additional Chlamydiota were discovered in ocean-floor environments, and it is not yet known whether they all have hosts. Historically it was believed that all Chlamydiota had a peptidoglycan-free cell wall, but studies in the 2010s demonstrated a detectable presence of peptidoglycan, as well as other important proteins.

"Candidatus Pelagibacter", with the single species "Ca. P. communis", was isolated in 2002 and given a specific name, although it has not yet been described as required by the bacteriological code. It is an abundant member of the SAR11 clade in the phylum Alphaproteobacteria. SAR11 members are highly dominant organisms found in both salt and fresh water worldwide and were originally known only from their rRNA genes, first identified in the Sargasso Sea in 1990 by Stephen Giovannoni's laboratory at Oregon State University and later found in oceans worldwide. "Ca. P. communis" and its relatives may be the most abundant organisms in the ocean, and quite possibly the most abundant bacteria in the entire world. It can make up about 25% of all microbial plankton cells, and in the summer they may account for approximately half the cells present in temperate ocean surface water. The total abundance of "Ca. P. communis" and relatives is estimated to be about 2 × 1028 microbes.
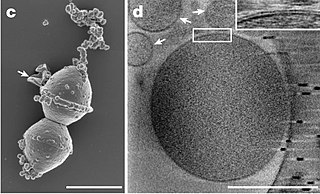
In prokaryote nomenclature, Candidatus is used to name prokaryotic taxa that are well characterized but yet-uncultured. Contemporary sequencing approaches, such as 16S ribosomal RNA sequencing or metagenomics, provide much information about the analyzed organisms and thus allow to identify and characterize individual species. However, the majority of prokaryotic species remain uncultivable and hence inaccessible for further characterization in in vitro study. The recent discoveries of a multitude of candidate taxa has led to candidate phyla radiation expanding the tree of life through the new insights in bacterial diversity.
The bacterial order Chlamydiales includes only obligately intracellular bacteria that have a chlamydia-like developmental cycle of replication and at least 80% 16S rRNA or 23S rRNA gene sequence identity with other members of Chlamydiales. Chlamydiales live in animals, insects, and protozoa.
Fibrobacterota is a small bacterial phylum which includes many of the major rumen bacteria, allowing for the degradation of plant-based cellulose in ruminant animals. Members of this phylum were categorized in other phyla. The genus Fibrobacter was removed from the genus Bacteroides in 1988.

Chlamydophila is a controversial bacterial genus belonging to the family Chlamydiaceae.
Parachlamydiaceae is a family of bacteria in the order Chlamydiales. Species in this family have a Chlamydia–like cycle of replication and their ribosomal RNA genes are 80–90% identical to ribosomal genes in the Chlamydiaceae. The Parachlamydiaceae naturally infect amoebae and can be grown in cultured Vero cells. The Parachlamydiaceae are not recognized by monoclonal antibodies that detect Chlamydiaceae lipopolysaccharide.

Alphaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota. The Magnetococcales and Mariprofundales are considered basal or sister to the Alphaproteobacteria. The Alphaproteobacteria are highly diverse and possess few commonalities, but nevertheless share a common ancestor. Like all Proteobacteria, its members are gram-negative and some of its intracellular parasitic members lack peptidoglycan and are consequently gram variable.

Chlamydia is a genus of pathogenic Gram-negative bacteria that are obligate intracellular parasites. Chlamydia infections are the most common bacterial sexually transmitted diseases in humans and are the leading cause of infectious blindness worldwide.
The Synergistota is a phylum of anaerobic bacteria that show Gram-negative staining and have rod/vibrioid cell shape. Although Synergistota have a diderm cell envelope, the genes for various proteins involved in lipopolysaccharides biosynthesis have not yet been detected in Synergistota, indicating that they may have an atypical outer cell envelope. The Synergistota inhabit a majority of anaerobic environments including animal gastrointestinal tracts, soil, oil wells, and wastewater treatment plants and they are also present in sites of human diseases such as cysts, abscesses, and areas of periodontal disease. Due to their presence at illness related sites, the Synergistota are suggested to be opportunistic pathogens but they can also be found in healthy individuals in the microbiome of the umbilicus and in normal vaginal flora. Species within this phylum have also been implicated in periodontal disease, gastrointestinal infections and soft tissue infections. Other species from this phylum have been identified as significant contributors in the degradation of sludge for production of biogas in anaerobic digesters and are potential candidates for use in renewable energy production through their production of hydrogen gas. All of the known Synergistota species and genera are presently part of a single class (Synergistia), order (Synergistiales), and family (Synergistaceae).
The Chloroflexota are a phylum of bacteria containing isolates with a diversity of phenotypes, including members that are aerobic thermophiles, which use oxygen and grow well in high temperatures; anoxygenic phototrophs, which use light for photosynthesis ; and anaerobic halorespirers, which uses halogenated organics as electron acceptors.
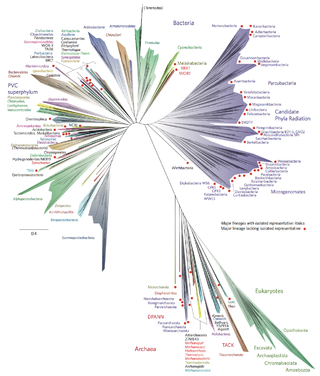
Bacterial phyla constitute the major lineages of the domain Bacteria. While the exact definition of a bacterial phylum is debated, a popular definition is that a bacterial phylum is a monophyletic lineage of bacteria whose 16S rRNA genes share a pairwise sequence identity of ~75% or less with those of the members of other bacterial phyla.
Armatimonadota is a phylum of gram-negative bacteria.
Parachlamydia acanthamoebae are bacterium that fall into the category of host-associated microorganisms. This bacterium lives within free-living amoebae that are an intricate part of their reproduction. Originally named Candidatus Parachlamydia acanthamoebae, its current scientific name was introduced shortly after. This species has shown to have over eighty percent 16S rRNA gene sequencing identity with the class Chlamydiia. Parachlamydia acanthamoebae has the same family as the genus Neochlamydia with which it shares many similarities.

Blochmannia is a genus of symbiotic bacteria found in carpenter ant. There are over 1000 species of these ants and, as of 2014, of the over 30 species of carpenter ant that have been investigated, all contain some form of Blochmannia. The bacteria filled cells currently known as members of the genus Blochmannia were first discovered by zoologist F. Blochmann in the ovaries and midguts of insects in the 1880s. In 2000 Candidatus Blochmannia was proposed as its own genus.
Shimwellia blattae is a species of bacterium, one of two in the genus Shimwellia. It is an aerobic enteric bacterium first isolated from the hindgut of cockroaches. Although it is related to human pathogens, including Escherichia coli, S. blattae is not pathogenic to humans. It is notable for its ability to synthesize vitamin B12 de novo.
Nitrospinota is a bacterial phylum. Despite only few described species, members of this phylum are major nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in surface waters in oceans. By oxidation of nitrite to nitrate they are important in the process of nitrification in marine environments.








