Road signs in Finland Last updated January 20, 2026 This article needs to be updated . The reason given is: Please check completeness. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (June 2020 )
Skier warning road sign in Savonlinna Bilingual direction sign , in Finnish and Northern Sami Road signs in Finland were formerly regulated in the Road Traffic Regulation (5.3.1982/182) (Finnish : Tieliikenneasetus [ 1] but now are currently regulated in the Road Traffic Act (8.5.2020/360) (Finnish : Tieliikennelaki [ 2]
Most signs are based on pictograms, except signs like the prohibition-sign for stop at customs and the sign indicating a taxi rank . If the sign includes text, the text is written in Finnish or Swedish , except the stop sign and taxi signs which are written in English (some taxi signs are written TAKSI in Finnish). Many roads and places in Finland have Finnish and Swedish names, so both are marked on the traffic signs. This is common in the Swedish-speaking areas on the southern and western coasts, whereas in the inland Swedish names are far less common. In northern Lapland there are also traffic signs in the Northern Sámi , Skolt Sámi and Inari Sámi languages.
At many unregulated intersections the practice is to yield to traffic on-coming from the right, unless there is a "yield" or "give way" sign posted for the right on-coming traffic. This can be a problem on some streets since these signs are not always visible to traffic that does not have to yield. Therefore, unless a driver is experienced with the area and its signs, they are expected to give way to the right at an intersection, even if the road they are on appears to be the priority road.
Finnish road signs depict gender-neutral people with stylized silhouettes since 2020; between 1982 and 2020, the designs were realistic, as was common in most Nordic countries at the time. Since the last legal reform, most of the pictograms and arrows are identical to their German counterparts, whereas the new diagrams for people are similar to the Danish models.
In addition, Åland , an autonomous region of Finland, has some in Swedish-style signs and all are written in the Swedish language.
Finland signed the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals on December 16, 1969 and ratified it on April 1, 1985. [ 3]
Major differences between Finnish and general European signs Whereas European signs usually have white background on warning and prohibition signs, Finnish signs have a yellow/orange colour. This is for the purpose of enhancing the visibility of the sign during the winter, as white signs would be hard to see in the snow. Prohibition signs displaying a symbol other than a numeric value have a diagonal red line across them. Prohibition signs in Iceland and Sweden are similar in this respect. In most European countries, however, such signs do not usually include a red line.
Warning signs Warning signs are triangular, but in contrast to those of most other states using triangular warning signs, Finnish signs have yellow backgrounds, rather than white.
Dangerous curve to right
(formerly used
)
Dangerous curve to left
(formerly used
)
Dangerous curves, first bend to right
(formerly used
)
Dangerous curves, first bend to left
(formerly used
)
Steep hill upwards
(formerly used
)
Steep hill downwards
(formerly used
)
Road narrows on both sides
Two-way traffic
(formerly used
)
Opening or swing bridge
(formerly used
)
Quayside or ferry berth
(formerly used
)
Queuing traffic
(formerly used
)
Uneven road ahead
Speed bumps
(formerly used
)
Road works
(formerly used
)
Loose chippings
(formerly used
)
Slippery road
(formerly used
)
Dangerous shoulders
(formerly used
)
Pedestrian crossing
(formerly used
)
Pedestrians
Children
(formerly used
)
Cyclists and moped riders on carriageway
(formerly used
)
Skiers crossing
(formerly used
)
Intersection, equal (rightside has the priority)
Junction with a minor road
(formerly used
)
Junction with a minor road
(formerly used
)
Junction with a minor road
(formerly used
)
Junction with a minor road
(formerly used
)
Traffic signals
Roundabout warning
(formerly used
)
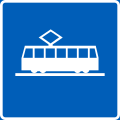
Tramway
Level crossing without gates
Level crossing with gates
Distance to level crossing
Distance to level crossing
Distance to level crossing
Single track level crossing
Multitrack level crossing
Falling rocks
(formerly used
)
Low-flying aircraft
Crosswind
(formerly used
)
Other dangers
Priority signs Priority road
End of priority road
Priority over oncoming vehicles
(formerly used
)
Priority for oncoming vehicles
(formerly used
)
Give way
Stop
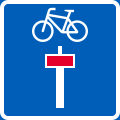
Cycle crossing
Prohibitory signs Prohibitory signs are round with yellow backgrounds and red borders, except the no parking and no standing signs that have a blue background instead of yellow.
Closed to all vehicles in both directions
No power-driven vehicles
(formerly used
)
No lorries
(formerly used
)
No combinations of a vehicle and a trailer
(formerly used
)
No tractors, construction vehicles etc.
(formerly used
)
No motorcycles
(formerly used
)
No off-road vehicles
(formerly used
)
No vehicles carrying
dangerous goods No buses
No mopeds
(formerly used
)
No cycles
(formerly used
)
No cycles or mopeds
No pedestrians
(formerly used
)
No pedestrians or cycles
(formerly used
)
No equestrians
(formerly used
)
No entry
No left turn
(formerly used
)
No right turn
(formerly used
)
No U-turn
(formerly used
)
No vehicles having an overall width exceeding [...] meters
(formerly used
)
No vehicles having an overall height exceeding [...] meters
(formerly used
)
No vehicles or combination of vehicles exceeding [...] meters
(formerly used
)
No vehicles exceeding [...] tonnes laden weight
No vehicles or combination of vehicles exceeding [...] tonnes laden weight or bearing capacity class
(formerly used
)
No vehicles having a weight exceeding [...] tonnes on one axle
(formerly used
)
No vehicles having a weight exceeding [...] tonnes on a tandem axle
(formerly used
)
No overtaking
(formerly used
)
End of overtaking restriction
(formerly used
)
No overtaking by lorries
(formerly used
)
End of overtaking by lorries restriction
(formerly used
)
Speed limit
End of speed limit
(formerly used
)
Speed limit zone
End of speed limit zone
(formerly used
)
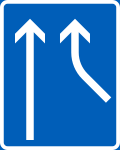
Prohibition or restriction applying to one or more traffic lanes
(formerly used
)
No standing or parking
(formerly used
)
No parking
(formerly used
)
No parking zone
(formerly used
)
End of no parking zone
(formerly used
)
Taxi waiting zone
(formerly used
)
Taxi stopping zone
(formerly used
)
Loading zone
Loading zone
Alternative parking (prohibited on the odd days of month from 08:00 on that day until 08:00 on the next)
(formerly used
)
Alternative parking (prohibited on the even days of month from 08:00 on that day until 08:00 on the next)
(formerly used
)
Passing without stopping prohibited (customs control)
Passing without stopping prohibited (customs control)
Passing without stopping prohibited (customs control)
Passing without stopping prohibited (police control)
(formerly used
)
Minimum distance between power driven vehicles
(formerly used
)
Vehicles equipped with studded tyres prohibited
Mandatory signs Mandatory signs are always round blue signs with white border.
Special regulation signs Pedestrian crossing
(formerly used
)
Park and ride
Park and ride
Park and ride
Park and ride
Park and ride
Parking
Placing vehicles on a parking place
Placing vehicles on a parking place
Placing vehicles on a parking place
Passing place (on narrow roads)
(formerly used
)
Bus stop
(formerly used
for local traffic and
for long-distance traffic)
Tramway stop
(formerly used
)
Taxi station
Bus lane (sign above the line)
Bus and taxi lane (sign above the line)
End of bus lane (sign above the line)
(formerly used
)
End of bus and taxi lane (sign above the line)
(formerly used
)
Tramway lane (sign above the line)
Tramway and taxi lane (sign above the line)
End of tramway lane (sign above the line)
(formerly used
)
End of tramway and taxi lane (sign above the lane)
(formerly used
)
Cycle lane (sign above the line)
Cycle lane (sign above the line)
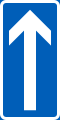
One-way traffic
One-way traffic
(formerly used
)
Motorway
End of motorway (formerly used
)
Road for motor vehicles (formerly used
)
End of road for motor vehicles (formerly used
)
Tunnel
End of tunnel
(formerly used
)
Emergency stopping place
(formerly used
)
End of built-up area
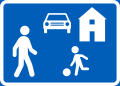
Residential area
(formerly used
)
End of residential area
(formerly used
)
Pedestrian zone
(formerly used
)
End of pedestrian zone
(formerly used
)
Cycle street
End of cycle street
Advance direction sign (type A)
Advance direction sign (type B)
Advisory sign for detour
(formerly used
)
Advisory sign for detour
Detour
Route to be followed (in order to turn left)
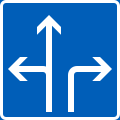
Information on traffic lanes
(formerly used
)
Information on traffic lanes
(formerly used
)
Information on traffic lanes
(formerly used
)
Information on traffic lanes
Information on traffic lanes
Information on traffic lanes
End of lane
(formerly used
)
End of lane
(formerly used
)
Advance direction sign (above the lane; type A)
Advance direction sign (above the lane; type B)
Exit sign (above the lane)
Direction sign
Exit sign
Direction sign on private road
Location sign
Advance location sign
Direction sign for light traffic (pedestrian and cycle traffic)
Direction sign for detour
Direction sign for detour
Direction sign for local purposes
Direction sign showing a motorway or road for motor vehicles
Direction sign showing park-and-ride facilities
No through road
No through road
No through road
(formerly used
)
Advisory speed
Sign showing distances
Place name
(formerly used
)
Place name (waterway)
Road number (E-road;
European route )
Road number (primary road; main road, Class I; 1–39)
Road number (secondary road; main road, Class II; 40–99)
Road number (regional road; 100–999)
Road number (ordinary road; connecting road; 1000–9999)
Road number (ring road)
Direction to the numbered road
Symbol of motorway
(formerly used
)
Symbol of road for motor vehicles
(formerly used
)
Airport
Ferry
Passenger terminal
Cargo terminal
Freight terminal
Industrial area
(formerly used
)
Retail park
Parking
(formerly used
)
Parking garage
(formerly used
)
Railway station
Bus station
City Centre symbol
Itinerary for indicated vehicle category
(formerly used
)
Itinerary for pedestrians
(formerly used
)
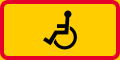
Itinerary for handicapped
Itinerary for transport of dangerous goods
(formerly used
)
Overpass or underpass with steps (formerly used
)
Overpass or underpass without steps (formerly used
)
Emergency exit
Direction to emergency exit
Service signs Information sign for services
Information sign for services
Advance information sign for services
Location sign for tourist service
Advance location sign for tourist service
Radio station (frequency in MHz)
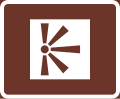
Information point
(formerly used
)
Information centre
(formerly used
)
First-aid
(formerly used
)
Breakdown service
(formerly used
)
Gasoline station
(formerly used
)
Gasoline station (with compressed natural gas)
Electric vehicle charging station
Petrol station (with hydrogen)
Hotel or motel
(formerly used
)
Restaurant
(formerly used
)
Cafeteria or refreshments
(formerly used
)
Public lavatory
(formerly used
)
Youth hostel
(formerly used
)
Camping site
(formerly used
)
Caravan site
(formerly used
)
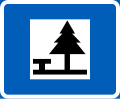
Picnic site
(formerly used
)
Recreational area
(formerly used
)
Emergency telephone
(formerly used
)
Extinguisher
(formerly used
)
Museum or historic building
(formerly used
)
Nature site
(formerly used
)
Viewpoint
(formerly used
)
Zoo
(formerly used
)
Other tourist attraction
(formerly used
)
Swimming place
(formerly used
)
Fishing place
(formerly used
)
Ski lift
(formerly used
)
Cross-country skiing centre
Golf course
(formerly used
)
Pleasure or theme park
(formerly used
)
Cottage accommodation
(formerly used
)
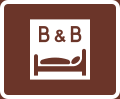
Bed and breakfast
(formerly used
)
Direct sale
(formerly used
)
Handicrafts
(formerly used
)
Farm park
(formerly used
)
Horseback riding
(formerly used
)
Tourist route
(formerly used
)
Tourist route
(formerly used
)
Additional panels Sign applies to crossing road
(formerly used
)
Sign applies in the direction of the arrow
(formerly used
)
Sign applies [...] km in the direction of the arrow
(formerly used
)
Sign applies [...] km in the direction of the arrow
Distance to which the sign applies
(formerly used
)
Distance from the sign to the point to which the sign applies
(formerly used
)
Distance to the compulsory stop
(formerly used
)
Free width
(formerly used
)
Free height
(formerly used
)
Height of electric line
(formerly used
)
Sign applies to both directions
(formerly used
)
Sign applies to both directions
(formerly used
)
Sign applies in the direction of the arrow
(formerly used
)
Regulation begins from the sign
(formerly used
)
Regulation ends to the sign
(formerly used
)
Private vehicle
(formerly used
)
Bus
(formerly used
)
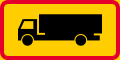
Truck
(formerly used
)
Delivery van
(formerly used
)
Caravan
(formerly used
)
Camper van
Vehicle for handicapped
(formerly used
)
Motorcycle
(formerly used
)
Moped
(formerly used
)
Pedal cycle
(formerly used
)
Snowmobiles
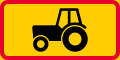
Tractors
Low-emission vehicles
Method of parking (formerly used
)
Method of parking (formerly used
)
No entry for vehicles carrying dangerous goods of group A
No entry for vehicles carrying dangerous goods of group B
Tunnel class B
Tunnel class C
Tunnel class D
Tunnel class E
Sign applies between 08.00 and 17.00 hours, Mo-Fr
(formerly used
)
Sign applies between 08.00 and 13.00 hours, on Saturdays
(formerly used
)
Sign applies between 08.00 and 14.00 hours, on Sundays and holidays
(formerly used
)
Time limit
(formerly used
)
Obligatory use of parking disc
(formerly used
)
Parking against fee
(formerly used
)
Charging space for electric vehicles
Direction of priority road
(formerly used
)
Direction of priority road
(formerly used
)
Two-way cycle track
(formerly used
)
Two-way path
Additional panel with text "Occasionally foggy"
Additional panel with text "Driving in service purposes allowed"
(formerly used
)
Additional panel with text "Zone"
Additional panel with text "General limit"
Emergency telephone and extinguisher
(formerly used
)
Sharp Curve
Below, signs are withdrawn or replaced with new diagrams of the same meaning.
Warning signs Winding road (1937–1974)
Steep hill downwards (1982–1994)
Steep hill upwards (1982–1994)
High pavement edge (1982–1994)
Weak shoulder (1982–1994)
Pedestrian crossing (1969–1980s)
Children (1957–1974)
Crossroads (1937–1994)
Tramway (1957–1982)
Single track level crossing (1932–1974)
Multitrack level crossing (1932–1974)
Level crossing front (1932–1970s)
Other dangers (1921–1924)
Other dangers (1924–1937)
Other dangers (1937–1994)
Prohibitory signs Closed to all vehicles in both directions (1937–1994)
No power-driven vehicles (1937–1957)
No power-driven vehicles (1957–1982)
No cars (1937–1957)
No lorries (1957–1982)
No motorcycles (1957–1982)
No cycles (1957–1982)
No pedestrians (1969–1982)
No entry (1930–1937)
No entry (1937–1995)
No left turn (1957–1982)
No right turn (1957–1982)
No overtaking (1937–1957)
Speed limit (1937–1969)
End of speed limit (1957–1969)
No stopping or parking (1937–1969)
No parking (1930–1937)
No parking (1937–1969)
Taxi waiting zone (1982–1994)
Taxi stopping zone (1982–1994)
No horns (1937–1957)
Alternate date parking zone (1982–1994)
End of alternate date parking zone (1982–1994)
Mandatory signs Direction to be followed (turn right only) (1937–1957)
Direction to be followed (turn right only) (1957–1974)
Direction to be followed (turn left only) (1937–1957)
Direction to be followed (turn left only) (1957–1974)
Compulsory roundabout (1937–1957)
Compulsory roundabout (1957–1982)
Pass this side (right side) (1957–1974)
Pass this side (left side) (1957–1974)
Pass either side (1957–1974)
Footpath (1937–1957)
Footpath (1957–1974)
Footpath (1974–1982)
Cycleway (1937–1957)
Cycleway (1957–1974)
Special regulation signs Pedestrian crossing (1957–1974)
Pedestrian crossing (1974–1985)
Parking (1937–1974)
Passing place (on narrow roads) (1937–1974)
Bus stop (local) (1957–1974)
Bus stop (local) (1974–1994)
Bus stop (long-distance) (1957–1974)
Bus stop (long-distance) (1974–1994)
Tramway stop (1957–1974)
Tramway stop (1974–1982)
Taxi station (1957–1974)
Taxi station (1974–1994)
Bus lane (1972–1994)
End of bus lane (1972–1994)
One-way street (1957–1982)
Motorway (1962–1982)
End of motorway (1962–1982)
Place name (1937-1994)
Lane preselection (1957–1982)
Lane preselection (1957–1982)
Lane preselection (1957–1982)
Road number (secondary road; main road, Class II; 40–99) (1937-1994)
Road number (regional road; 100–999) (1960s–1994)
Direction sign (1937–1960s)
Direction sign showing highways (1937–1960s)
Direction sign showing main roads (1937–1960s)
Direction sign on villages or municipal roads (1937–1960s)
Direction sign on private roads (1937–1960s)
Direction sign on through roads for local purposes (1937–1960s)
Advance direction sign (1957–1960s)
Information on traffic lanes (1969–1982)
Creep lane (1974–1982)
Direction sign for detour (1970s–1994)
Advisory sign for detour (1970s–1994)
Detour (1970s–1982)
Detour (1982–1994)
Direction to the numbered road (1937-1994)
Cycle route (1974–1982)
Pedestrian route (1974–1982)
Service signs Tourist route (1995–2007)
Information point (1969–2007)
Telephone (1957–1982)
Telephone (1982–2007)
Emergency telephone (1978–2007)
First-aid (1957–1978)
Tourist attraction (1969–2007)
Cottage accommodation (1982–2007)
Swimming place (1969–2007)
Fishing place (1982–2007)
Ski lift (1982–2007)
Direct sale (1994–2007)
Direction signs in Åland Road signs in Åland are mostly based on the Swedish road signs , even though being a part of Finland.
Other signs A3 Home zone
A4 End of home zone
A5 Pedestrian zone
A6 Pedestrian zone ends
A11 Pedestrian crossing
Tourist Area
Postal Road
Detour information
Midway sign bike
External links finlex.fi Tie , a digitisation of the Finnish road sign typeface
Signs
By country
Lights Typefaces International conventions National standards Comparisons
Sovereign states States with limited Dependencies and
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.