Directional sign with distance shown
Directional sign with distance shown and with lane divides
T-junction directional sign with distance shown
Intersection with distance shown
Intersection with distance shown (Example 2)
Intersection from campus road with distance shown
Intersection
Intersection (Example 2)
Intersection from campus road
Directional sign to roads given
Directional sign with distances to places given
Directional sign to places given
Ramp (Left)
Ramp (Right)
T-junction
Exits to left and right
Roundabout
National Highway interchange
Interchange
Exit (Left)
Exit (Right)
National Highway
Provincial Highway
County Highway
Rural Highway
Street sign
Vertically-written street sign
Street sign with directions and address numbers on either side
Distance to roads given
Place name
Place name with elevation
City limits
Road maintenance team
Road maintenance team (Example 2)
Hospital ahead
Low-flying aircraft
Fuel station and car wash
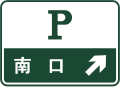
Parking
Parking ahead
Emergency curb
Disabled parking
Sightseeing area and parking (Right)
Sightseeing area and parking (Left)
Rest area (left)
Rest area (right)
Alternative route to street desired
Alternative route to street desired
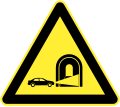
Alternative route for height-restricted vehicles
Cul-de-sac/dead end
3-lane road merges to 2 lanes
4-lane road merges to 3 lanes
2-lane road expands to 3 lanes
Traffic cameras ahead
Tunnel ends in 2500m
Tunnel ends in 2500m (left)
Chevron (Left)
Chevron (Left)
Chevron with two arrows (Left)
Chevron with three arrows (Left)
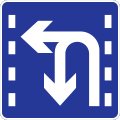
T-junction both ways
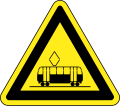
Hazard marker or pass either side
Hazard marker (Right)
Hazard marker (Left)
Exit (Left)
Exit (Left)
Exit to highway (Left)
Exit to highway (Right)
National Highway sign without name below
Provincial Highway sign without name below
National Highway sign with name below
Provincial Highway sign with name below (S9 should not be Changjia (G1521))
Highway name
Distance to cities given
Distance to cities and highway given
Area name with number of exits within
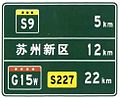
Distance to cities and highway given (example 2)
Distance to cities and highway given (example 3)
Next exit with road name only
Next exit with exit number only
Next exit with both exit number and road name
Next exit in without either exit number and road name
Exit number
Exit number (Left exit)
Highway Exit in 2km
Highway Exit in 1km
Highway Exit in 500m
Highway Exit
Highway Exit in 2km (Example 2)
Highway Exit in 1km (Example 2)
Highway Exit in 500m (Example 2)
Highway Exit (Example 2)
Highway Exit in 2km (Left)
Highway Exit in 1km (Left)
Highway Exit in 500m (Left)
Highway Exit (Left)
Highway Exit in 2km (Left) (Example 2)
Highway Exit in 1km (Left) (Example 2)
Highway Exit in 500m (Left) (Example 2)
Highway Exit (Left) (Example 2)
Exit with exit number
Exit with exit number (Left)
Overhead highway sign plus exit
Overhead highway sign plus exit (Left)
National Highway
National Highway branch
Highway name
National Highway ends in 2km
National Highway ends in 1km
National Highway ends in 500m
Highway ends in 2km
Highway ends in 1km
Highway ends in 500m
National Highway ends
National Highway branch ends
Highway ends
Highway ends in 200m; Reduce speed
Tune to 1620kHz for traffic information
Milestone with highway designation
Milestone with highway name
Milestone
Park to receive toll ticket
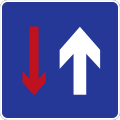
Danger of tailgating (i.e. high traffic zone); Keep your distance
Maintain a distance of 200m from vehicles ahead
0 meters marker
50 meters marker
100 meters marker
Advisory speed in fog
Advisory speed in fog: 50 km/h
Emergency telephone
Emergency telephone in 400m (Left)
Emergency telephone in 400m (Right)
Emergency telephone on both sides in 500m
Rescue telephone
Rescue telephone (Example 2)
1km to toll gate
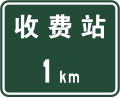
500m to toll gate
Toll gate
2km to toll gate that supports
ETC 1km to toll gate that supports ETC
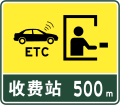
500m to toll gate that supports ETC
Toll gate that supports ETC
ETC lane to shoulder
ETC lane straight ahead
Weigh station with tolls
Gas station
Emergency curb
Full service area and restaurant in 2km
Full service area and restaurant in 1km
Full service area and restaurant exit
Full service and lodging area in 2km
Full service area and lodging in 1km
Full service area and lodging exit
Service area exit
Service area exit (Example 2)
Exit to parking and cafe in 1km
Exit to parking and cafe
Rest area exit
Parking in 1km
Parking exit
Parking exit (Small)
Outdoor parking area
Indoor parking area
Climbing lane for large trucks
Climbing lane (Right lane) for large trucks
Climbing lane
Climbing lane ends
Weigh station in 2km
Weigh station in 1km
Weigh station in 500m
Weigh station exit
Compass direction
Straight exit to compass direction given
Cloverleaf exit to compass direction given
Straight exit to compass direction given (Green)
Cloverleaf exit to compass direction given (Green)
Compass direction (Green)