Road signs in Sri Lanka are legally prescribed in the Motor Traffic Act (Chapter 203). [1] They are also laid out in a supplementary guide, the Manual on Traffic Control Devices, published by the Ministry of Transport and Highways and the Road Development Authority. [2]
Contents
- Warning signs
- Regulatory signs
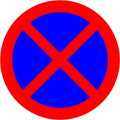
- Prohibitory signs
- Restrictive signs
- Mandatory signs
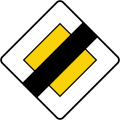
- Priority signs
- Additional panels
- Directional informative signs
- National highways
- Provincial roads
- Expressways
- Other signs useful for drivers
- Road markings
- Traffic light signals
- Light signals for pedestrians
- See also
- References
Sri Lankan road signs display text in Sinhala, Tamil and English.